Tailings management involves the safe storage and containment of fine waste materials left after mineral extraction, minimizing environmental impact and water contamination risks. Paste backfill, in contrast, uses a mixture of tailings and binding agents to fill underground mine voids, improving ground stability and allowing for safer, more efficient mine operations. Both methods are essential for sustainable mining practices, with paste backfill offering enhanced resource recovery and reduced surface tailings footprint.
Table of Comparison
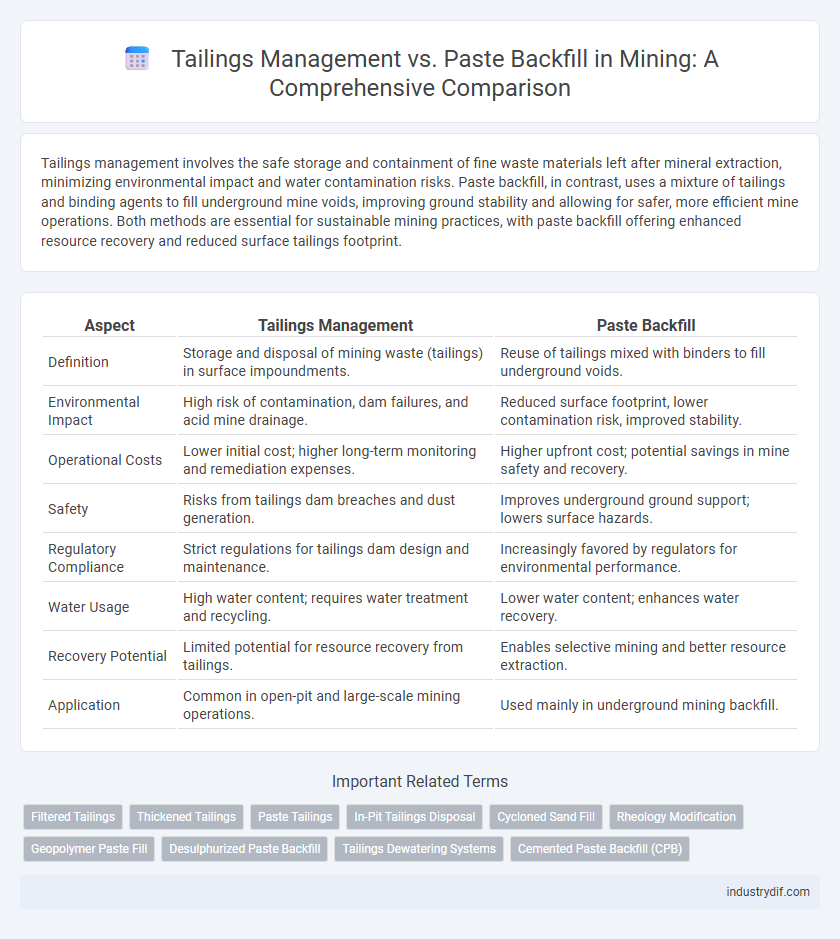
| Aspect | Tailings Management | Paste Backfill |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Storage and disposal of mining waste (tailings) in surface impoundments. | Reuse of tailings mixed with binders to fill underground voids. |
| Environmental Impact | High risk of contamination, dam failures, and acid mine drainage. | Reduced surface footprint, lower contamination risk, improved stability. |
| Operational Costs | Lower initial cost; higher long-term monitoring and remediation expenses. | Higher upfront cost; potential savings in mine safety and recovery. |
| Safety | Risks from tailings dam breaches and dust generation. | Improves underground ground support; lowers surface hazards. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Strict regulations for tailings dam design and maintenance. | Increasingly favored by regulators for environmental performance. |
| Water Usage | High water content; requires water treatment and recycling. | Lower water content; enhances water recovery. |
| Recovery Potential | Limited potential for resource recovery from tailings. | Enables selective mining and better resource extraction. |
| Application | Common in open-pit and large-scale mining operations. | Used mainly in underground mining backfill. |
Introduction to Tailings Management and Paste Backfill
Tailings management involves the safe storage and disposal of mining byproducts to minimize environmental impact and ensure operational safety. Paste backfill is a technique that recycles tailings by mixing them with binders to create a viscous material that supports underground mine structures and reduces surface tailings storage. Effective implementation of paste backfill enhances resource recovery and promotes sustainable mine closure practices.
Overview of Conventional Tailings Storage Methods
Conventional tailings storage methods primarily involve surface impoundments like tailings dams and slurry ponds designed to contain mining residues safely. These structures rely on engineered embankments and controlled water decant systems to manage solid-liquid separation and reduce environmental impact. While widely used, such methods pose challenges including potential dam failure risks, groundwater contamination, and substantial land footprint compared to alternatives like paste backfill.
Paste Backfill: Definition and Process
Paste backfill is a mining technique that involves mixing finely ground tailings with binders such as cement to create a thick, pumpable slurry used to fill voids in underground mines. This process improves ground stability, reduces surface tailings storage needs, and enhances environmental safety by minimizing tailings discharge. The controlled placement of paste backfill supports mine structure, enables ore extraction from adjacent stopes, and facilitates efficient waste management compared to conventional tailings disposal.
Key Differences Between Tailings Management and Paste Backfill
Tailings management involves the storage and containment of mining waste materials, primarily focusing on environmental safety and preventing contamination, while paste backfill is a method of recycling tailings by mixing them with binders and water to create a solid support for underground mine voids. Tailings management systems often include tailings dams or impoundments, which require extensive monitoring to mitigate risks such as dam failures, whereas paste backfill enhances mine stability and reduces surface waste footprint. The key differences lie in their purpose: tailings management emphasizes waste containment, whereas paste backfill integrates waste reuse to improve mine safety and reduce environmental impact.
Environmental Impacts and Sustainability Considerations
Tailings management often poses significant environmental risks including water contamination, landscape alteration, and heavy metal toxicity due to the storage of large volumes of waste material. Paste backfill enhances sustainability by recycling tailings into a cemented slurry used to fill underground voids, reducing surface storage needs and mitigating acid mine drainage. This method improves ground stability, lowers footprint, and minimizes the risk of tailings dam failures, promoting safer and more sustainable mining operations.
Cost Analysis: Tailings Storage vs Paste Backfill
Tailings storage facilities (TSFs) typically incur higher long-term costs due to extensive land use, regulatory compliance, and environmental monitoring requirements. Paste backfill systems, while demanding significant initial capital investment for infrastructure and processing equipment, often reduce operational costs by enabling underground void filling and lowering tailings volume on surface storage. Comparative cost analysis shows paste backfill technology can enhance mine safety and environmental sustainability, potentially offsetting upfront expenses through improved resource recovery and reduced environmental liabilities.
Safety and Risk Mitigation in Tailings and Backfill Operations
Effective tailings management reduces environmental hazards by preventing dam failures and minimizing toxic seepage, enhancing operational safety. Paste backfill strengthens underground mine stability by filling voids and supporting rock structures, significantly lowering collapse risks and worker exposure to dangerous conditions. Integrating robust monitoring systems with these methods ensures early detection of potential failures, thereby improving overall risk mitigation in mining operations.
Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
Tailings management and paste backfill are critical in meeting regulatory compliance and industry standards, with tailings management requiring strict adherence to environmental regulations on waste containment and water quality. Paste backfill, often used underground, meets safety standards by reducing surface tailings storage and improving mine stability, aligning with sustainable mining practices mandated by regulators. Both methods necessitate comprehensive monitoring and reporting to ensure regulatory frameworks such as the Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) are consistently followed.
Technological Innovations in Tailings Management
Technological innovations in tailings management focus on enhancing environmental safety and operational efficiency through methods like thickened tailings, filtered tailings, and paste backfill systems. Paste backfill employs dewatered tailings mixed with binders, reducing surface storage volumes and mitigating risks of dam failures while improving ground stability in underground mining operations. Advanced monitoring technologies, such as real-time sensor networks and automated control systems, optimize tailings deposition and paste backfill consistency, supporting sustainable mine closure practices.
Future Trends in Tailings Disposal and Backfill Solutions
Emerging trends in tailings disposal emphasize sustainable practices such as paste backfill, which enhances underground mine stability while reducing surface tailings storage. Advances in paste backfill technology include improved binders and real-time monitoring systems to optimize flow properties and strength development. Future tailings management increasingly integrates circular economy principles, aiming to minimize environmental impact and recover valuable minerals from mine waste.
Related Important Terms
Filtered Tailings
Filtered tailings offer enhanced water recovery and reduced storage footprint compared to conventional tailings management, minimizing environmental risks such as dam failures. Incorporating filtered tailings into paste backfill systems improves underground mine stability and reduces surface disposal, promoting sustainable mining practices.
Thickened Tailings
Thickened tailings improve tailings management by reducing water content, allowing safer storage with minimized environmental impact and enhanced stability compared to conventional tailings disposal. Paste backfill utilizes thickened tailings mixed with binders to fill mined-out voids, increasing underground mine stability while promoting sustainable waste recycling and reducing surface tailings footprint.
Paste Tailings
Paste tailings, a thickened slurry with reduced water content, enhance mine stability and reduce environmental risks by minimizing surface tailings storage. Compared to traditional tailings management, paste backfill improves underground support, optimizes resource recovery, and lowers the potential for tailings dam failures.
In-Pit Tailings Disposal
In-pit tailings disposal (IPTD) maximizes mining efficiency by depositing tailings directly into mined-out pits, reducing surface footprint and water usage compared to conventional tailings management. Paste backfill, while also utilizing tailings, enhances underground ground support and stability but involves higher processing costs and complex infrastructure relative to IPTD strategies.
Cycloned Sand Fill
Cycloned sand fill in paste backfill systems enhances underground mine stability by repurposing fine tailings while reducing surface tailings storage requirements and environmental risks. Effective tailings management through cycloned sand fill optimizes material handling, improves ground support, and minimizes water usage compared to conventional tailings disposal methods.
Rheology Modification
Tailings management requires effective rheology modification to enhance stability and reduce environmental risks, typically achieved through water content adjustment and the addition of chemical stabilizers. Paste backfill optimizes rheological properties by incorporating binders and thickeners, improving flowability and strength for underground support while minimizing water usage and surface storage volume.
Geopolymer Paste Fill
Geopolymer paste fill offers enhanced tailings management by utilizing waste materials in a stable, eco-friendly binder that reduces environmental hazards and improves underground ground support. This sustainable solution outperforms traditional tailings disposal by minimizing surface storage volumes and promoting safer mine backfill practices.
Desulphurized Paste Backfill
Desulphurized paste backfill enhances tailings management by reducing environmental impact through the stabilization of sulphide minerals, minimizing acid mine drainage risks and improving underground mine support. This method optimizes resource recovery and waste control compared to conventional tailings disposal, promoting sustainable mining operations.
Tailings Dewatering Systems
Tailings dewatering systems enhance solid-liquid separation to reduce moisture content in tailings, improving storage stability and minimizing environmental risks. Compared to paste backfill, tailings dewatering provides more efficient volume reduction and facilitates safer disposal in tailings dams or dry stacking operations.
Cemented Paste Backfill (CPB)
Cemented Paste Backfill (CPB) enhances tailings management by stabilizing mine voids, reducing surface disposal volumes, and mitigating environmental risks associated with tailings dams. CPB combines tailings, water, and binders like Portland cement to create a durable, cost-effective backfill that supports mine structure integrity and minimizes long-term ecological impact.
Tailings management vs Paste backfill Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com