Automated storage systems enhance warehouse efficiency by using mechanized equipment to organize and retrieve inventory with precision and speed. Robotic fulfillment integrates autonomous robots to handle picking, packing, and shipping tasks, reducing human error and increasing throughput. Choosing between automated storage and robotic fulfillment depends on warehouse size, order complexity, and scalability requirements.
Table of Comparison
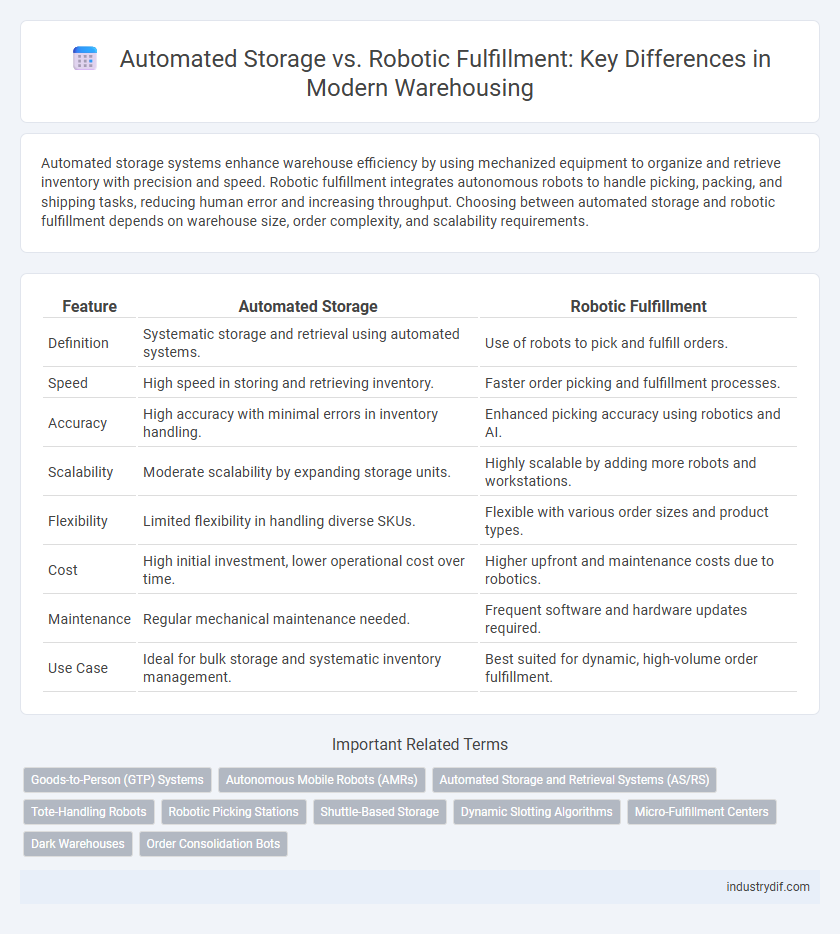
| Feature | Automated Storage | Robotic Fulfillment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic storage and retrieval using automated systems. | Use of robots to pick and fulfill orders. |
| Speed | High speed in storing and retrieving inventory. | Faster order picking and fulfillment processes. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy with minimal errors in inventory handling. | Enhanced picking accuracy using robotics and AI. |
| Scalability | Moderate scalability by expanding storage units. | Highly scalable by adding more robots and workstations. |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility in handling diverse SKUs. | Flexible with various order sizes and product types. |
| Cost | High initial investment, lower operational cost over time. | Higher upfront and maintenance costs due to robotics. |
| Maintenance | Regular mechanical maintenance needed. | Frequent software and hardware updates required. |
| Use Case | Ideal for bulk storage and systematic inventory management. | Best suited for dynamic, high-volume order fulfillment. |
Introduction to Automated Storage and Robotic Fulfillment
Automated storage systems utilize technologies like AS/RS (Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems) to optimize warehouse space, improve inventory accuracy, and speed up material handling with minimal human intervention. Robotic fulfillment integrates autonomous robots to navigate warehouse floors, selecting and transporting goods, which enhances order processing efficiency and reduces labor costs. Both technologies drive warehouse automation but differ in approach, with automated storage focusing on static storage optimization and robotic fulfillment emphasizing dynamic order handling and picking.
Key Differences Between Automated Storage and Robotic Fulfillment
Automated storage systems primarily focus on efficient space utilization and inventory management through technologies like AS/RS (automated storage and retrieval systems), optimizing warehouse density and retrieval speed. Robotic fulfillment emphasizes autonomous mobile robots that pick, pack, and transport goods, enhancing flexibility and reducing manual labor in order fulfillment. Key differences include the fixed infrastructure dependency of automated storage versus the adaptability and scalability of robotic fulfillment solutions.
Core Technologies Driving Warehousing Automation
Automated storage systems rely heavily on conveyor belts, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and warehouse management software (WMS) to optimize inventory placement and retrieval, enhancing speed and accuracy in material handling. Robotic fulfillment centers integrate advanced robotics such as autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), robotic arms, and machine learning algorithms to dynamically pick, sort, and pack orders with minimal human intervention. Key technologies like AI-driven analytics, IoT sensors, and real-time data processing fuel both systems, enabling seamless inventory tracking and maximizing operational efficiency in modern warehousing.
Efficiency Gains: Automated Storage vs Robotic Fulfillment
Automated storage systems maximize space utilization and reduce retrieval times through precise, programmed movements of goods in high-density environments. Robotic fulfillment enhances efficiency by employing autonomous robots that dynamically navigate warehouse floors to pick and transport items with minimal human intervention. Both technologies significantly increase overall operational throughput, but robotic fulfillment offers greater flexibility in handling diverse product types and fluctuating order volumes.
Cost Implications and ROI Analysis
Automated storage systems typically involve higher upfront capital investment due to complex infrastructure and maintenance requirements, but they offer consistent long-term cost savings through increased storage density and reduced labor expenses. Robotic fulfillment solutions often require lower initial costs and provide scalable, flexible automation that can adapt to fluctuating demand, leading to faster ROI in dynamic environments. Evaluating cost implications and ROI involves analyzing factors such as equipment costs, integration complexity, labor reduction, throughput improvements, and maintenance expenses to determine the best fit for specific warehousing operations.
Scalability in Modern Warehousing Solutions
Automated storage systems offer scalable solutions by efficiently managing large volumes of inventory through fixed infrastructure designed for high-density storage. Robotic fulfillment enhances scalability by allowing flexible and rapid adaptation to fluctuating order volumes using autonomous mobile robots that optimize picking and sorting processes. Combining these technologies supports seamless expansion of warehousing capacity while maintaining operational efficiency in dynamic supply chain environments.
Labor Dynamics: Human Roles in Automated Environments
Automated storage systems streamline inventory management by reducing manual labor and minimizing human error, shifting worker roles towards system oversight and exception handling. Robotic fulfillment centers emphasize collaboration between robots and humans, where workers engage in tasks requiring cognitive skills, such as quality control and problem-solving. This evolution in labor dynamics enhances operational efficiency while demanding upskilling and adaptability from the workforce in warehousing environments.
Data Integration and System Interoperability
Automated storage systems rely heavily on seamless data integration to synchronize inventory levels, order processing, and real-time location tracking within warehouse management systems (WMS). Robotic fulfillment enhances system interoperability by enabling autonomous robots to communicate effortlessly with warehouse control software and automated storage units, ensuring optimized task allocation and dynamic route planning. Advanced APIs and IoT protocols facilitate this integration, reducing errors and improving operational efficiency across both automated storage and robotic fulfillment environments.
Industry Case Studies and Success Stories
Industry case studies reveal that automated storage systems enhance inventory accuracy and reduce labor costs by utilizing high-density shelving and automated retrieval technologies. Robotic fulfillment solutions demonstrate significant gains in order processing speed and operational flexibility through autonomous mobile robots and AI-driven picking algorithms. Success stories from leading e-commerce and manufacturing companies highlight measurable improvements in throughput, scalability, and workforce safety.
Future Trends in Warehousing Automation
Automated storage systems are increasingly integrating AI and IoT technologies to optimize inventory management and reduce human error. Robotic fulfillment solutions are evolving with advanced machine learning algorithms, enabling faster, more accurate order picking and real-time adaptability in warehouse environments. Future trends in warehousing automation emphasize seamless collaboration between automated storage and robotic fulfillment to enhance efficiency, scalability, and operational transparency.
Related Important Terms
Goods-to-Person (GTP) Systems
Goods-to-Person (GTP) systems in warehousing optimize order fulfillment by automating the delivery of inventory directly to workers, significantly reducing travel time and increasing picking accuracy. Unlike traditional robotic fulfillment where robots navigate aisles to pick items, GTP systems utilize automated storage and retrieval machines (AS/RS) to transport goods to stationary pickers, enhancing efficiency in high-volume environments.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) enhance automated storage by dynamically navigating warehouses to optimize inventory management, reducing human error and increasing operational efficiency. Unlike traditional robotic fulfillment systems fixed to specific tasks, AMRs adapt to varying workflows and scale seamlessly, improving throughput and flexibility in modern warehousing environments.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) use advanced technology to efficiently manage inventory by automating the storage and retrieval process, significantly reducing labor costs and minimizing errors. These systems enhance warehouse space utilization and improve order accuracy through precise control of goods movement within high-density storage environments.
Tote-Handling Robots
Tote-handling robots in automated storage systems enhance pick accuracy and reduce labor costs by efficiently navigating warehouse aisles to retrieve and deliver totes. These robots outperform traditional robotic fulfillment by optimizing space utilization and enabling faster order processing through precise, real-time inventory management.
Robotic Picking Stations
Robotic picking stations leverage advanced AI and machine learning algorithms to increase accuracy and throughput in warehousing operations, reducing labor costs and minimizing human error. These systems integrate seamlessly with warehouse management software, optimizing inventory flow and enabling real-time order fulfillment at scale.
Shuttle-Based Storage
Shuttle-based storage systems optimize warehousing efficiency by using automated shuttles to retrieve and store goods within dense rack configurations, reducing picking time and maximizing space utilization. Compared to robotic fulfillment, shuttle systems excel in high-density storage environments by enabling faster vertical and horizontal movement of inventory, enhancing throughput and scalability in automated warehousing operations.
Dynamic Slotting Algorithms
Dynamic slotting algorithms optimize inventory placement by continuously analyzing order patterns and product velocity, significantly enhancing space utilization in both automated storage systems and robotic fulfillment centers. These algorithms enable real-time adjustments that reduce retrieval times and improve throughput, driving efficiency in high-volume warehousing operations.
Micro-Fulfillment Centers
Automated storage systems in micro-fulfillment centers optimize space utilization and inventory accuracy through conveyor belts and shuttle systems, while robotic fulfillment leverages autonomous mobile robots for dynamic picking and rapid order processing. The integration of robotic fulfillment enhances operational speed and scalability, crucial for meeting high-demand e-commerce requirements within compact urban warehousing environments.
Dark Warehouses
Automated storage systems in dark warehouses maximize space utilization and inventory accuracy through mechanized retrieval, while robotic fulfillment integrates autonomous robots to enhance order picking speed and flexibility without human intervention. Both technologies reduce labor costs and improve operational efficiency but differ in scalability and adaptability to complex order profiles.
Order Consolidation Bots
Order consolidation bots in automated storage systems streamline inventory management by accurately gathering and combining multiple order items, reducing picking errors and enhancing throughput speed. Robotic fulfillment leverages these bots to optimize space utilization and order accuracy, drastically lowering labor costs while improving overall warehouse efficiency.
Automated Storage vs Robotic Fulfillment Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com