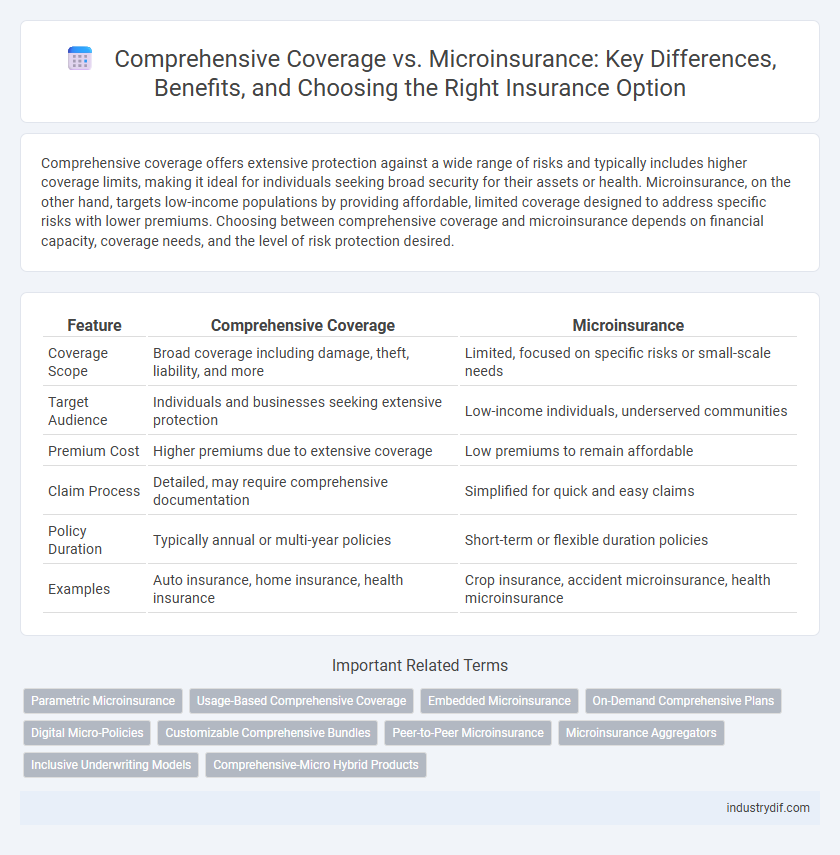
Comprehensive coverage offers extensive protection against a wide range of risks and typically includes higher coverage limits, making it ideal for individuals seeking broad security for their assets or health. Microinsurance, on the other hand, targets low-income populations by providing affordable, limited coverage designed to address specific risks with lower premiums. Choosing between comprehensive coverage and microinsurance depends on financial capacity, coverage needs, and the level of risk protection desired.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Comprehensive Coverage | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Scope | Broad coverage including damage, theft, liability, and more | Limited, focused on specific risks or small-scale needs |
| Target Audience | Individuals and businesses seeking extensive protection | Low-income individuals, underserved communities |
| Premium Cost | Higher premiums due to extensive coverage | Low premiums to remain affordable |
| Claim Process | Detailed, may require comprehensive documentation | Simplified for quick and easy claims |
| Policy Duration | Typically annual or multi-year policies | Short-term or flexible duration policies |
| Examples | Auto insurance, home insurance, health insurance | Crop insurance, accident microinsurance, health microinsurance |
Introduction to Comprehensive Coverage and Microinsurance
Comprehensive coverage provides extensive protection against a wide range of risks including theft, natural disasters, and accidental damage, making it ideal for individuals seeking robust insurance policies. Microinsurance offers affordable, limited coverage tailored for low-income individuals or small businesses, focusing on specific risks such as health, agriculture, or property. Both types of insurance serve key market segments by addressing different financial capabilities and risk exposures in the insurance industry.
Key Differences Between Comprehensive Coverage and Microinsurance
Comprehensive coverage offers extensive protection against a wide range of risks including theft, damage, and liability, typically catering to high-value assets or individuals seeking broad insurance policies. Microinsurance targets low-income populations with affordable premiums and limited coverage, focusing on basic protection against specific risks such as health emergencies or crop failure. The fundamental differences lie in coverage scope, premium cost, and target market, with comprehensive coverage providing in-depth risk management and microinsurance emphasizing accessibility and affordability.
Target Markets: Who Needs Which Insurance?
Comprehensive coverage is designed for individuals and businesses seeking extensive protection against a wide range of risks, including property damage, theft, liability, and natural disasters, making it ideal for homeowners, vehicle owners, and large enterprises. Microinsurance targets low-income individuals, informal sector workers, and small-scale entrepreneurs who require affordable, basic insurance solutions tailored to cover specific risks like health, agriculture, or accident insurance. Choosing between comprehensive coverage and microinsurance depends on the policyholder's financial capacity, risk exposure, and the scope of protection needed.
Cost Comparison: Premiums and Affordability
Comprehensive coverage typically involves higher premiums due to its extensive protection against a wide range of risks, including theft, fire, and damage, making it less affordable for low-income individuals. Microinsurance offers significantly lower premiums by providing limited but essential coverage tailored to meet the needs and budgets of underserved populations, enhancing financial accessibility. The cost-effectiveness of microinsurance makes it an attractive alternative for those seeking basic protection without the financial burden of traditional comprehensive policies.
Coverage Scope: What’s Protected?
Comprehensive coverage typically protects a wide range of risks including property damage, theft, liability, and natural disasters, offering extensive financial security for individuals and businesses. Microinsurance focuses on essential protection with limited scope, targeting specific risks like health emergencies, crop failure, or small asset loss, designed for low-income populations. The breadth of protection in comprehensive coverage far exceeds microinsurance, which aims at affordability and accessibility rather than completeness.
Claims Process: Ease and Accessibility
Comprehensive coverage typically offers a streamlined claims process with dedicated customer support and faster claim settlements, ensuring ease and accessibility for policyholders. Microinsurance often features simplified claim procedures designed for low-income clients, leveraging mobile platforms to facilitate quick and convenient access. Both options aim to reduce barriers, but comprehensive coverage tends to provide more extensive service infrastructure for claim handling.
Flexibility and Customization Options
Comprehensive coverage offers extensive protection with flexible policy options tailored to individual needs, allowing for customization in coverage limits, deductibles, and add-ons such as roadside assistance or rental car reimbursement. Microinsurance, designed for low-income clients, provides basic yet essential protection with limited flexibility but ensures affordability and accessibility, often customizable with modular benefits targeting specific risks. Choosing between the two depends on the balance needed between extensive customization and cost-effective, targeted coverage.
Risk Management Strategies in Both Models
Comprehensive coverage provides extensive risk protection by covering a wide range of potential damages and losses, making it suitable for individuals and businesses seeking extensive financial security. Microinsurance targets low-income populations with affordable, limited coverage tailored to specific risks such as health, crop failure, or property damage, emphasizing accessibility and cost-efficiency. Both models implement risk management strategies through risk pooling, loss prevention incentives, and actuarial analysis, but comprehensive coverage uses broader underwriting criteria while microinsurance often leverages community-based assessment and simplified claims processes.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Comprehensive coverage typically involves strict regulatory requirements due to its broad risk protection and higher premium structures, necessitating rigorous compliance with solvency, capital adequacy, and consumer protection standards established by authorities like state insurance departments or international regulators. Microinsurance, designed for low-income populations, often benefits from tailored regulatory frameworks that promote inclusivity while maintaining essential consumer safeguards, including simplified licensing, reduced capital requirements, and streamlined claims processes. Insurers must navigate these distinct regulatory landscapes carefully to ensure adherence to legal guidelines, avoid penalties, and maintain trust with regulators and policyholders alike.
Future Trends in Comprehensive Coverage and Microinsurance
Future trends in comprehensive coverage include the integration of advanced analytics and AI to enhance risk assessment and personalize policies, addressing emerging risks like cyber threats and climate change. Microinsurance is expected to expand rapidly in developing markets through mobile technology, increasing accessibility for low-income populations and enabling real-time claim processing. Both coverage types are evolving with digital innovations to improve customer experience and operational efficiency in the insurance industry.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Microinsurance
Parametric microinsurance offers a streamlined, data-driven alternative to traditional comprehensive coverage by triggering payouts based on predefined events such as weather conditions or natural disasters, enhancing speed and transparency for policyholders. This model lowers administrative costs and expands accessibility for low-income populations, providing targeted financial protection with measurable parameters rather than relying on conventional claim assessments.
Usage-Based Comprehensive Coverage
Usage-based comprehensive coverage leverages telematics technology to monitor driver behavior, offering personalized insurance premiums based on actual risk and driving patterns. Microinsurance targets low-income individuals with affordable, limited-coverage policies, while usage-based models enhance comprehensive coverage by adjusting rates dynamically to promote safer driving and increased cost-efficiency.
Embedded Microinsurance
Embedded microinsurance integrates tailored, low-cost coverage within existing financial products, providing accessible protection for underserved populations. Comprehensive coverage offers broader risk protection but often at higher premiums and complexity, making embedded microinsurance a strategic solution for inclusive insurance markets.
On-Demand Comprehensive Plans
On-demand comprehensive insurance plans offer flexible protection tailored to specific timeframes or events, bridging the gap between extensive traditional comprehensive coverage and the limited scope of microinsurance. These plans provide policyholders with customizable benefits and instant activation, enhancing convenience and cost-efficiency in managing diverse insurance needs.
Digital Micro-Policies
Digital micro-policies revolutionize insurance by offering affordable, flexible coverage tailored to specific risks, contrasting with comprehensive coverage's broad protection scope and higher premiums. Leveraging mobile platforms, digital microinsurance enhances accessibility for underserved markets, enabling on-demand, cost-efficient insurance solutions with streamlined claims processing.
Customizable Comprehensive Bundles
Customizable comprehensive insurance bundles offer tailored protection that integrates multiple coverages like liability, collision, and personal injury, addressing diverse risk profiles effectively. Microinsurance, while affordable and accessible, typically provides limited scope, making comprehensive bundles preferable for individuals seeking all-encompassing, adaptable financial security solutions.
Peer-to-Peer Microinsurance
Peer-to-peer microinsurance leverages social networks to pool risk and lower premiums, offering an affordable alternative to traditional comprehensive coverage for low-income groups. This model enables direct member control, enhanced transparency, and tailored insurance solutions, addressing gaps left by conventional insurance in underserved communities.
Microinsurance Aggregators
Microinsurance aggregators leverage digital platforms to streamline access to affordable, low-premium insurance products tailored for low-income populations, enhancing financial inclusion. These aggregators partner with insurers to offer comprehensive coverage options that address specific risks, improving claim processing efficiency and customer outreach.
Inclusive Underwriting Models
Comprehensive coverage typically applies inclusive underwriting models that assess broad risk factors, enabling tailored protection for diverse assets and liabilities. Microinsurance leverages simplified, inclusive underwriting approaches to offer affordable, accessible insurance solutions for low-income populations with limited data availability.
Comprehensive-Micro Hybrid Products
Comprehensive-micro hybrid insurance products combine extensive protection with affordable, low-premium coverage tailored for underserved populations, bridging the gap between traditional comprehensive policies and microinsurance. These hybrid solutions leverage technology and data analytics to optimize risk assessment, ensuring broader access and enhanced financial security for low-income individuals while maintaining robust coverage features.
Comprehensive Coverage vs Microinsurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com