General liability insurance covers physical risks such as bodily injury and property damage occurring on business premises or caused by business operations, while cyber liability insurance specifically addresses risks related to data breaches, cyberattacks, and other technology-related exposures. Businesses facing increased digital threats benefit from cyber liability coverage that includes expenses for notification, credit monitoring, and legal fees arising from cyber incidents. Combining both policies ensures comprehensive protection against traditional physical claims and evolving cyber risks.
Table of Comparison
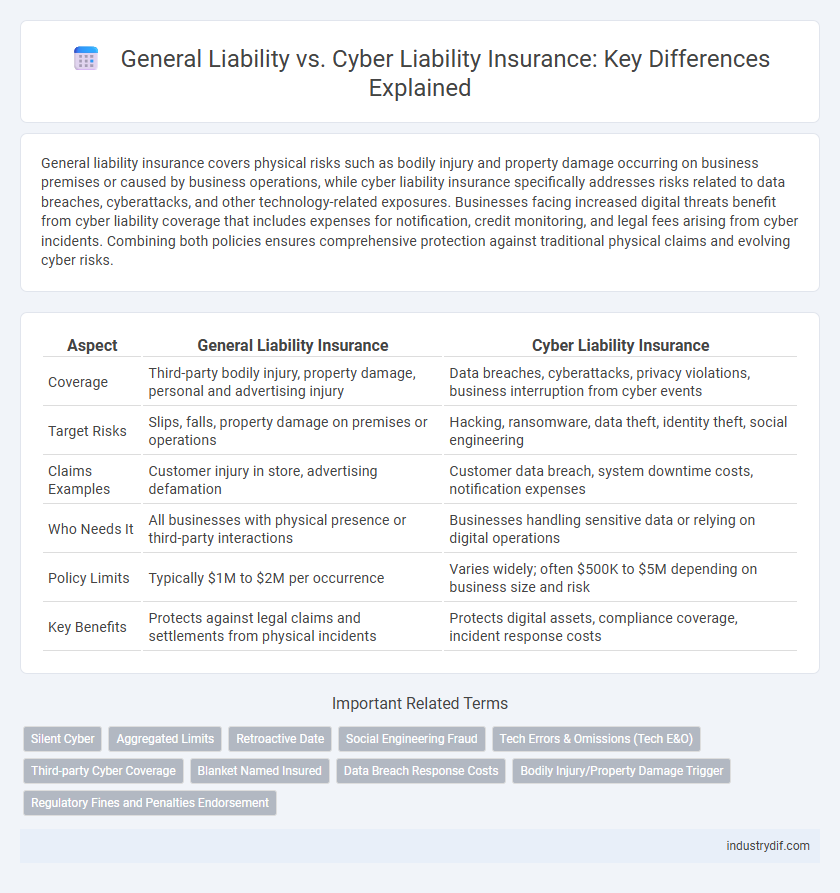
| Aspect | General Liability Insurance | Cyber Liability Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Third-party bodily injury, property damage, personal and advertising injury | Data breaches, cyberattacks, privacy violations, business interruption from cyber events |
| Target Risks | Slips, falls, property damage on premises or operations | Hacking, ransomware, data theft, identity theft, social engineering |
| Claims Examples | Customer injury in store, advertising defamation | Customer data breach, system downtime costs, notification expenses |
| Who Needs It | All businesses with physical presence or third-party interactions | Businesses handling sensitive data or relying on digital operations |
| Policy Limits | Typically $1M to $2M per occurrence | Varies widely; often $500K to $5M depending on business size and risk |
| Key Benefits | Protects against legal claims and settlements from physical incidents | Protects digital assets, compliance coverage, incident response costs |
Understanding General Liability Insurance
General Liability Insurance provides essential coverage for businesses against claims of bodily injury, property damage, and personal injury occurring on their premises or due to their operations. It safeguards companies from financial losses related to lawsuits and settlements arising from accidents, medical expenses, and legal defense costs. Understanding the scope of General Liability is crucial for distinguishing it from Cyber Liability, which specifically addresses risks related to data breaches and cyber threats.
What is Cyber Liability Insurance?
Cyber Liability Insurance provides protection against financial losses resulting from data breaches, cyberattacks, and other technology-related risks. It covers expenses such as legal fees, notification costs, and damages related to compromised sensitive information or business interruptions caused by cyber incidents. Unlike General Liability Insurance, which addresses physical injury and property damage claims, Cyber Liability specifically targets the unique threats posed by digital operations and cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
Key Differences Between General and Cyber Liability
General Liability insurance primarily covers physical property damage, bodily injury, and personal injury claims arising from everyday business operations. Cyber Liability insurance specifically addresses risks related to data breaches, cyberattacks, and digital asset exposures, including customer data loss and network security failures. Key differences lie in their coverage scopes: General Liability protects against traditional third-party claims, while Cyber Liability focuses on technology-driven threats and privacy violations.
Coverage Scope: Physical vs. Digital Risks
General liability insurance primarily covers physical risks such as bodily injury, property damage, and advertising injury occurring on business premises or from business operations. Cyber liability insurance addresses digital risks including data breaches, cyberattacks, and loss of sensitive information affecting a company's information systems. Businesses must assess both coverage scopes to ensure protection against traditional physical liabilities and emerging cyber threats.
Common Claims Under General Liability
Common claims under General Liability insurance include bodily injury, property damage, and personal and advertising injury resulting from business operations. These claims often arise from slip-and-fall accidents, product defects, or libel and slander lawsuits. General Liability insurance protects businesses against financial losses from third-party claims of physical harm or property damage.
Typical Cyber Liability Incident Scenarios
Typical cyber liability incident scenarios include data breaches exposing sensitive customer information, ransomware attacks encrypting critical business data, and phishing scams leading to credential theft or unauthorized access. These incidents often result in significant financial losses due to notification costs, legal fees, and regulatory fines. General liability insurance generally excludes cover for these digital risks, making cyber liability insurance essential for protection against evolving cyber threats.
Risk Assessment: Which Policy Does Your Business Need?
General Liability insurance covers physical risks such as property damage and bodily injury, making it essential for businesses exposed to onsite accidents or customer interactions. Cyber Liability insurance focuses on digital risks, including data breaches, cyberattacks, and network security failures, crucial for companies handling sensitive information or operating online. Conducting a thorough risk assessment of your business operations helps determine if the primary threats arise from physical exposures or cyber vulnerabilities, guiding the appropriate policy selection.
Cost Comparison: General vs. Cyber Liability
General Liability insurance typically involves lower premiums, ranging from $400 to $1,500 annually, depending on the business size and industry risk profile. Cyber Liability insurance costs more due to the specialized coverage for data breaches and cyber threats, often averaging between $1,000 and $7,500 per year, influenced by factors such as company size and data sensitivity. Businesses with extensive digital operations or sensitive customer information usually face higher cyber liability premiums compared to general liability coverage.
Policy Exclusions to Watch For
General Liability insurance typically excludes damages caused by data breaches, cyberattacks, and privacy violations, which fall under Cyber Liability insurance. Cyber Liability policies may have exclusions for acts of terrorism, prior known incidents, or certain types of social engineering fraud. Careful review of policy exclusions in both General Liability and Cyber Liability coverages is essential to avoid coverage gaps in risk management strategies.
Integrating Both Policies for Comprehensive Protection
Integrating general liability and cyber liability policies ensures businesses are protected against a broad spectrum of risks, from bodily injury and property damage to data breaches and cyberattacks. Combining these coverages addresses both physical and digital threats, reducing vulnerabilities and financial exposure. Comprehensive protection through dual policies supports risk management strategies tailored to today's interconnected operational environments.
Related Important Terms
Silent Cyber
General Liability insurance typically excludes coverage for cyber incidents, creating gaps that Cyber Liability insurance specifically addresses by covering data breaches, cyberattacks, and privacy violations. Silent Cyber refers to the inadvertent exposure to cyber risks within traditional General Liability policies, highlighting the importance of explicit Cyber Liability coverage to mitigate these often overlooked exposures.
Aggregated Limits
General Liability insurance typically features aggregated limits that cap the total payout for all claims during the policy period, protecting businesses against physical injury and property damage claims. Cyber Liability insurance, however, often has separate aggregated limits tailored to data breaches and cyber incidents, addressing the unique risks and financial exposures in digital security.
Retroactive Date
General Liability insurance covers bodily injury and property damage occurring during the policy period, but its Retroactive Date determines how far back claims are covered if extended reporting is included. Cyber Liability insurance's Retroactive Date is critical because it defines the start point for coverage of undiscovered cyber incidents, protecting against liabilities from data breaches or network damage that occurred prior to the policy inception.
Social Engineering Fraud
General Liability insurance covers bodily injury and property damage claims but typically excludes losses from Social Engineering Fraud, which deceive employees into transferring funds or sensitive information. Cyber Liability insurance specifically addresses financial losses and data breaches caused by Social Engineering Fraud, providing essential protection against increasingly sophisticated cyber attacks on businesses.
Tech Errors & Omissions (Tech E&O)
General Liability insurance covers physical damages and bodily injury claims, while Cyber Liability focuses on data breaches, cyber attacks, and privacy issues; Tech Errors & Omissions (Tech E&O) specifically addresses technology-related professional services errors, software malfunctions, and failure to deliver technology products or services as promised. Combining Cyber Liability with Tech E&O coverage ensures comprehensive protection against both security risks and technology service failures prevalent in the IT and software industries.
Third-party Cyber Coverage
General Liability insurance covers bodily injury and property damage claims from third parties, but does not protect against cyber risks related to data breaches or cyberattacks. Cyber Liability insurance includes third-party cyber coverage that addresses liabilities arising from unauthorized data access, privacy violations, and network security failures affecting customers or partners.
Blanket Named Insured
Blanket Named Insured provisions in General Liability policies extend coverage to multiple entities under a single policy, ensuring broad protection for varied business operations, whereas Cyber Liability policies with Blanket Named Insured clauses specifically safeguard multiple subsidiaries or affiliates against data breaches and cyber threats. Understanding the scope of these provisions is essential for comprehensive risk management in both physical and digital realms.
Data Breach Response Costs
General Liability insurance typically excludes coverage for data breach response costs, leaving businesses vulnerable to expenses related to notification, credit monitoring, and legal fees after a cyber incident. In contrast, Cyber Liability insurance specifically covers these data breach response costs, helping organizations manage the financial impact of cyberattacks and regulatory compliance.
Bodily Injury/Property Damage Trigger
General Liability insurance specifically covers bodily injury and property damage caused by accidents, offering protection against physical harm or damage claims. Cyber Liability insurance, however, focuses on digital risks like data breaches and cyberattacks, typically excluding bodily injury or property damage triggers from its coverage.
Regulatory Fines and Penalties Endorsement
General Liability insurance typically excludes coverage for regulatory fines and penalties, whereas Cyber Liability insurance often includes endorsements specifically designed to cover these financial risks arising from data breaches and cybersecurity incidents. Regulatory fines and penalties endorsements in Cyber Liability policies provide critical protection against costs imposed by laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, and other data privacy regulations.
General Liability vs Cyber Liability Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com