Risk pools spread financial risk across a large group to lower individual premiums, making insurance more affordable and stable. Microinsurance targets low-income populations, offering tailored coverage options with smaller premiums and simplified claims processes to address their unique risks. Both approaches enhance access to protection but differ in scale, structure, and customer focus within the insurance market.
Table of Comparison
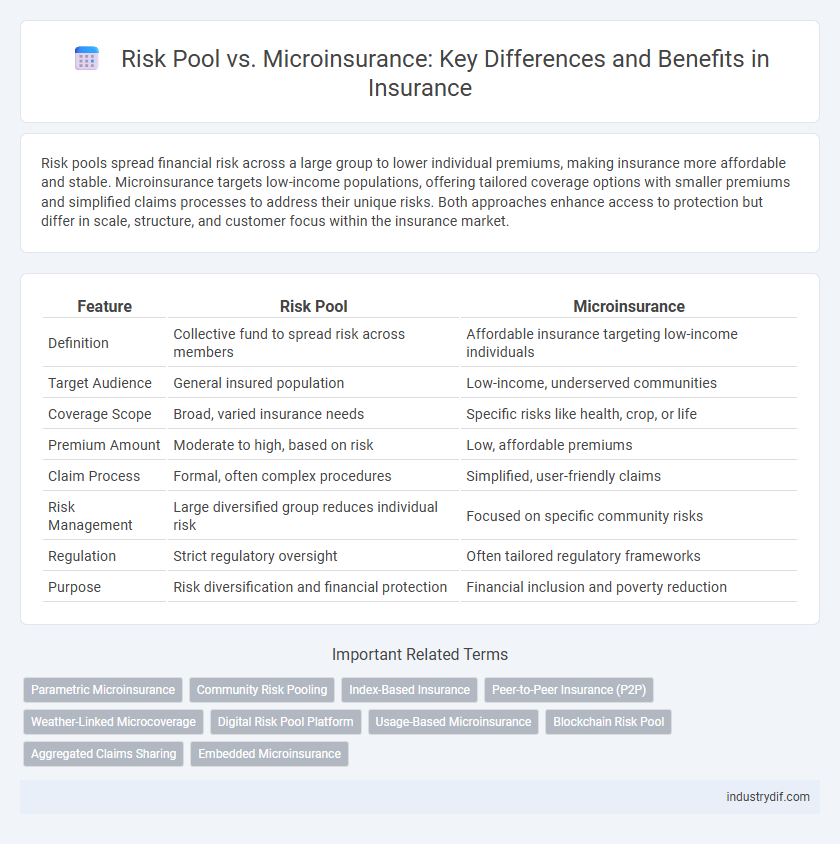
| Feature | Risk Pool | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collective fund to spread risk across members | Affordable insurance targeting low-income individuals |
| Target Audience | General insured population | Low-income, underserved communities |
| Coverage Scope | Broad, varied insurance needs | Specific risks like health, crop, or life |
| Premium Amount | Moderate to high, based on risk | Low, affordable premiums |
| Claim Process | Formal, often complex procedures | Simplified, user-friendly claims |
| Risk Management | Large diversified group reduces individual risk | Focused on specific community risks |
| Regulation | Strict regulatory oversight | Often tailored regulatory frameworks |
| Purpose | Risk diversification and financial protection | Financial inclusion and poverty reduction |
Understanding Risk Pools in Insurance
Risk pools in insurance aggregate policyholders to spread and manage financial risk, enhancing premium stability and claims predictability. These pools collect premiums and pay out claims collectively, reducing the impact of individual losses on the overall pool. Unlike microinsurance, which targets low-income individuals with limited coverage, risk pools accommodate a broader range of risks and policy sizes, supporting more balanced risk distribution.
Defining Microinsurance: Key Features
Microinsurance is a specialized insurance product designed to provide affordable coverage to low-income individuals, focusing on risks such as health, life, and property within vulnerable populations. Unlike traditional risk pools that aggregate large numbers of policyholders to spread risk broadly, microinsurance emphasizes accessibility, simplicity, and tailored benefits to meet the specific needs of underserved communities. Key features include low premiums, simplified claims processes, and partnerships with local organizations to enhance outreach and trust.
Core Differences Between Risk Pools and Microinsurance
Risk pools aggregate diverse individual policies to spread risk among a large group, reducing the financial impact of claims for insurers. Microinsurance targets low-income populations with tailored, affordable coverage options addressing specific risks like health, agriculture, or property losses. The core difference lies in scale and approach: risk pools function on broad risk distribution, while microinsurance emphasizes accessibility and affordability for underserved communities.
Benefits of Risk Pooling in Insurance Schemes
Risk pooling in insurance schemes enhances risk diversification by aggregating individual risks into a collective fund, thereby reducing the overall uncertainty and financial burden on each participant. It enables more affordable premiums and improves access to coverage for vulnerable populations by spreading losses across a larger group. This approach increases financial stability and resilience, making insurance schemes more sustainable compared to microinsurance models that often cover smaller, high-risk groups with limited risk-sharing capacity.
Microinsurance: Addressing Low-Income Market Needs
Microinsurance caters specifically to low-income populations by offering affordable, tailored coverage that addresses unique risks such as health emergencies, crop failure, and natural disasters. Unlike traditional risk pools, which aggregate large groups to spread risk, microinsurance employs community-based models and flexible premium payments to ensure accessibility and sustainability. This approach enhances financial inclusion by providing essential protection to underserved markets often excluded from conventional insurance products.
Eligibility Criteria: Risk Pool vs. Microinsurance
Risk pools typically require members to meet broad eligibility criteria related to shared risk factors such as age, occupation, or location, enabling collective risk management and premium distribution. Microinsurance targets low-income individuals with more flexible and inclusive eligibility standards, often prioritizing financial vulnerability and lack of access to traditional insurance. The tailored eligibility criteria of microinsurance increase coverage for underserved populations, while risk pools emphasize homogeneity for risk prediction and stability.
Premium Structures and Affordability
Risk pools aggregate premiums from a large group to spread risk, enabling more stable and predictable pricing structures for traditional insurance products. Microinsurance offers tailored premium structures with lower, more frequent payments designed to enhance affordability for low-income individuals or underserved markets. The flexible premium models of microinsurance improve access by reducing financial barriers compared to conventional risk pooling mechanisms.
Claims Process: Efficiency and Accessibility
Risk pools streamline the claims process by aggregating resources to cover large numbers of policyholders, enhancing efficiency through standardized procedures and centralized claims handling. Microinsurance offers greater accessibility with simpler documentation and mobile-based claims submission, catering to low-income populations often excluded from traditional insurance. Both models prioritize fast claim settlements, but microinsurance emphasizes ease of access and minimal bureaucracy to accommodate underserved communities.
Scalability Challenges in Risk Pooling and Microinsurance
Risk pooling faces scalability challenges due to limited participant diversity and capital constraints, which restrict risk distribution and financial sustainability. Microinsurance struggles with high administrative costs and low premium volumes, making it difficult to expand coverage while maintaining affordability and efficient claims processing. Innovative digital platforms and partnerships with local organizations are crucial to overcoming these barriers and achieving scalable insurance solutions.
Future Trends: Integrating Risk Pools and Microinsurance
Future trends in insurance highlight the growing integration of risk pools and microinsurance to enhance financial inclusion and risk mitigation for underserved populations. Combining large-scale risk pools with microinsurance products leverages community-based funding and data analytics to tailor affordable coverage and improve claim response efficiency. Technological advancements such as blockchain and AI-driven underwriting are pivotal in streamlining this integration, enabling scalable, transparent, and accessible insurance solutions.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Microinsurance
Parametric microinsurance leverages predefined triggers such as weather data or seismic activity to provide rapid, automatic payouts, distinguishing it from traditional risk pools that aggregate and redistribute funds based on collective claim experience. This innovative model enhances financial inclusion by offering affordable, transparent coverage and immediate liquidity to low-income populations vulnerable to specific, measurable risks.
Community Risk Pooling
Community risk pooling enables groups of individuals to share and manage insurance risks collectively, reducing individual financial burden caused by unpredictable events. Unlike traditional microinsurance that often targets individuals, community-based risk pools leverage local knowledge and trust to enhance coverage accessibility and affordability for underserved populations.
Index-Based Insurance
Index-based insurance leverages predefined indices such as rainfall or crop yields to trigger payouts, minimizing the need for individual loss assessments and making it highly scalable for risk pools. Unlike traditional microinsurance, this model reduces transaction costs and adverse selection by automating claims based on objective data, enhancing financial protection for low-income populations vulnerable to climate risks.
Peer-to-Peer Insurance (P2P)
Risk pools aggregate premiums from a large group to spread risk evenly, while microinsurance targets low-income individuals with tailored coverage and affordable premiums; Peer-to-Peer Insurance (P2P) leverages social networks to create smaller, trust-based risk pools that reduce administrative costs and increase transparency. By connecting peers directly, P2P insurance fosters community participation and incentivizes good risk management, making it an innovative hybrid model within the microinsurance market.
Weather-Linked Microcoverage
Risk pools aggregate financial resources from multiple policyholders to spread and mitigate losses in weather-linked microinsurance, providing affordable protection for low-income communities vulnerable to climate risks. Weather-linked microcoverage offers parametric payouts based on measurable weather triggers such as rainfall or temperature thresholds, enabling rapid claims settlement and enhancing resilience against climate-related agricultural and livelihood shocks.
Digital Risk Pool Platform
Digital risk pool platforms leverage advanced algorithms and blockchain technology to aggregate premiums and distribute claims efficiently, enhancing transparency and trust compared to traditional risk pools. Microinsurance benefits from these platforms by offering affordable coverage to underserved populations through mobile access, enabling real-time risk assessment and faster claim settlements.
Usage-Based Microinsurance
Usage-based microinsurance leverages telematics and real-time data to tailor premiums and coverage within risk pools, enhancing affordability and risk assessment for low-income individuals. By integrating behavior-driven metrics, this innovative approach optimizes risk distribution and promotes more accurate underwriting in microinsurance markets.
Blockchain Risk Pool
Blockchain Risk Pools leverage decentralized ledger technology to enhance transparency, reduce fraud, and streamline claims processing compared to traditional Risk Pools and Microinsurance models. This innovation enables more efficient risk sharing among participants while lowering operational costs and improving accessibility for underserved populations.
Aggregated Claims Sharing
Risk pools aggregate claims from multiple policyholders, spreading financial risk across a large group to stabilize premiums and ensure solvency. Microinsurance utilizes similar aggregated claims sharing on a smaller scale, targeting low-income populations with affordable coverage by pooling risks within specific communities or segments.
Embedded Microinsurance
Embedded microinsurance integrates seamlessly with existing financial products, leveraging risk pools to spread potential losses across a larger base, thereby reducing individual premiums and enhancing coverage affordability. This approach optimizes risk-sharing mechanisms by combining targeted microinsurance benefits with traditional pooling frameworks, improving accessibility and financial protection for underserved populations.
Risk Pool vs Microinsurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com