Reinsurance offers traditional risk transfer by allowing insurers to share liabilities with specialized companies, providing financial stability and expertise. Alternative capital introduces market-based solutions such as insurance-linked securities, broadening risk capacity and diversifying sources of funding. Both mechanisms enhance risk management but differ in structure, cost, and flexibility.
Table of Comparison
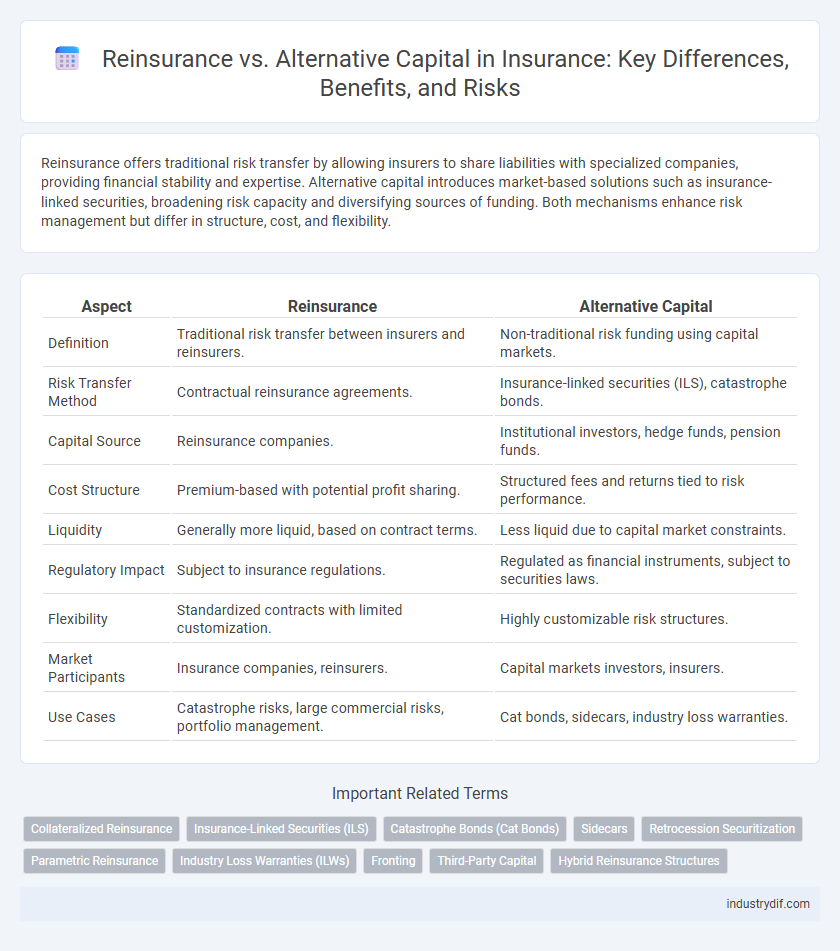
| Aspect | Reinsurance | Alternative Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional risk transfer between insurers and reinsurers. | Non-traditional risk funding using capital markets. |
| Risk Transfer Method | Contractual reinsurance agreements. | Insurance-linked securities (ILS), catastrophe bonds. |
| Capital Source | Reinsurance companies. | Institutional investors, hedge funds, pension funds. |
| Cost Structure | Premium-based with potential profit sharing. | Structured fees and returns tied to risk performance. |
| Liquidity | Generally more liquid, based on contract terms. | Less liquid due to capital market constraints. |
| Regulatory Impact | Subject to insurance regulations. | Regulated as financial instruments, subject to securities laws. |
| Flexibility | Standardized contracts with limited customization. | Highly customizable risk structures. |
| Market Participants | Insurance companies, reinsurers. | Capital markets investors, insurers. |
| Use Cases | Catastrophe risks, large commercial risks, portfolio management. | Cat bonds, sidecars, industry loss warranties. |
Introduction to Reinsurance and Alternative Capital
Reinsurance enables insurance companies to transfer portions of their risk portfolios to other insurers, thereby enhancing capital efficiency and stabilizing earnings. Alternative capital involves investment funds and capital markets instruments that provide risk-bearing capacity outside traditional reinsurance mechanisms, often through insurance-linked securities like catastrophe bonds. Both strategies play crucial roles in risk management, with reinsurance offering underwriting expertise and alternative capital delivering diversified, scalable financing solutions.
Traditional Reinsurance: Definition and Key Features
Traditional reinsurance involves a contractual agreement where the primary insurer transfers a portion of risk to the reinsurer in exchange for a premium, providing financial stability and capacity. Key features include risk sharing, loss mitigation, and underwriting expertise, allowing insurers to manage large or unforeseen claims effectively. This established mechanism supports solvency requirements and enables insurers to offer higher coverage limits while maintaining balanced portfolios.
Types of Alternative Capital in Insurance
Types of alternative capital in insurance include catastrophe bonds, collateralized reinsurance, sidecars, and insurance-linked securities (ILS). Catastrophe bonds transfer risk to investors, providing insurers with access to capital following extreme events. Sidecars and collateralized reinsurance offer capital backed by investors, enhancing capacity without traditional reinsurance, while ILS diversify risk by securitizing insurance liabilities in financial markets.
Key Differences Between Reinsurance and Alternative Capital
Reinsurance involves traditional risk transfer between insurers and reinsurers, providing financial protection against large losses through contractually agreed terms, while alternative capital leverages non-traditional investors and capital markets, using instruments like catastrophe bonds and insurance-linked securities. Reinsurance emphasizes underwriting expertise and ongoing risk management, whereas alternative capital focuses on fixed returns and diversification for investors outside the insurance industry. The cost structures also differ, with reinsurance premiums reflecting actuarial risk assessments, while alternative capital often offers capital at competitive rates driven by market demand and investor appetite.
Risk Transfer Mechanisms in Reinsurance vs Alternative Capital
Risk transfer mechanisms in reinsurance primarily involve traditional insurance contracts where the reinsurer assumes a portion of the insurer's risk exposure, optimizing capital efficiency and stabilizing loss volatility. Alternative capital employs insurance-linked securities (ILS) such as catastrophe bonds and sidecars, transferring risk to the capital markets and providing diversified sources of capital beyond conventional reinsurance. Both methods enhance risk distribution but differ in transparency, liquidity, and investor participation, with alternative capital offering more market-driven pricing and risk exposure options.
Benefits and Challenges of Reinsurance
Reinsurance provides insurers with risk transfer, financial stability, and claims management expertise, allowing them to underwrite larger or more complex risks while maintaining solvency. Challenges in reinsurance include pricing volatility, counterparty credit risk, and regulatory constraints that can limit coverage scope. Compared to alternative capital, reinsurance offers tailored risk solutions but may involve longer negotiation times and less flexible contract structures.
Advantages and Limitations of Alternative Capital
Alternative capital in reinsurance offers advantages such as increased capacity, diversification of risk sources, and access to non-traditional investors, enhancing market stability. Its limitations include potentially higher costs, complexity in structuring deals, and sensitivity to market conditions that can affect liquidity and pricing. This form of capital complements traditional reinsurance but demands careful assessment of terms and investor alignment.
Market Trends: Growth of Alternative Capital in Insurance
The growth of alternative capital in insurance has significantly reshaped the reinsurance market, with assets in insurance-linked securities (ILS) exceeding $100 billion in recent years. Investors are increasingly attracted to the uncorrelated returns offered by catastrophe bonds and other alternative risk transfer mechanisms. This trend drives innovation and competition, prompting traditional reinsurers to adapt their models and pricing strategies accordingly.
Impact of Alternative Capital on Reinsurance Pricing
Alternative capital has introduced significant competition in the reinsurance market, often resulting in more aggressive pricing models. The influx of non-traditional investors utilizing collateralized reinsurance structures lowers risk premiums, forcing traditional reinsurers to adjust pricing strategies. This shift has enhanced market liquidity but compressed margins, reshaping the valuation benchmarks for reinsurance contracts.
Future Outlook: Reinsurance and Alternative Capital Integration
The future outlook of the insurance industry emphasizes a deeper integration between traditional reinsurance and alternative capital sources, driven by the increasing demand for diversified risk transfer solutions. Advances in data analytics and technology are enabling more efficient assessment and pricing of risks, facilitating smoother collaboration between reinsurers and capital market investors. This synergy is expected to enhance market capacity, improve risk management, and create innovative insurance-linked securities, reshaping the landscape of global reinsurance.
Related Important Terms
Collateralized Reinsurance
Collateralized reinsurance provides insurers with secure, upfront capital by holding assets as collateral, balancing risk transfer without credit risk exposure typical in traditional reinsurance. Alternative capital, including insurance-linked securities and catastrophe bonds, offers market-driven risk financing but often lacks the direct counterparty security that collateralized reinsurance ensures.
Insurance-Linked Securities (ILS)
Insurance-linked securities (ILS) offer an alternative capital solution by transferring insurance risks to the capital markets, providing liquidity beyond traditional reinsurance capacity. Unlike reinsurance, ILS instruments such as catastrophe bonds allow insurers to diversify funding sources and manage risk exposure with transparent, market-driven pricing.
Catastrophe Bonds (Cat Bonds)
Catastrophe bonds (Cat Bonds) serve as a vital alternative capital instrument in reinsurance, transferring catastrophic risk from insurers to capital market investors and thereby enhancing risk diversification. Unlike traditional reinsurance, Cat Bonds offer predefined trigger events and payout structures, providing insurers with transparent, non-correlated capital to manage peak catastrophe exposure efficiently.
Sidecars
Sidecars provide insurance companies with efficient access to alternative capital by allowing investors to take on specific portions of reinsurance risks while maintaining direct relationship with primary insurers. This structure offers flexibility and transparency compared to traditional reinsurance, optimizing capital deployment and enhancing risk diversification in the insurance market.
Retrocession Securitization
Retrocession securitization transfers insurance risk from reinsurers to capital markets by converting retrocession contracts into tradable securities, enhancing liquidity and risk diversification. This alternative capital approach reduces reliance on traditional reinsurance by allowing investors to assume portions of catastrophic and underwriting risks through structured financial instruments.
Parametric Reinsurance
Parametric reinsurance provides predetermined payouts based on specific trigger events like natural disasters, offering faster claim settlements compared to traditional indemnity reinsurance. Alternative capital, including catastrophe bonds and insurance-linked securities, complements parametric reinsurance by accessing broader capital markets to enhance risk transfer efficiency and capacity for insurers.
Industry Loss Warranties (ILWs)
Industry Loss Warranties (ILWs) serve as a critical financial instrument in reinsurance, providing coverage triggered by industry-wide loss events, whereas Alternative Capital leverages investor funds through catastrophe bonds and sidecars to offer risk transfer solutions. ILWs typically offer indemnity-based payouts based on predefined loss indices, achieving efficient hazard risk distribution, while Alternative Capital solutions diversify risk financing by attracting non-traditional market participants seeking exposure to catastrophic events.
Fronting
Fronting in reinsurance involves a licensed insurer issuing a policy and then transferring most of the risk to a reinsurer, enabling access to alternative capital without directly underwriting the risk. Alternative capital provides non-traditional funding sources like insurance-linked securities, enhancing capacity and diversification compared to traditional reinsurance structures focused on risk transfer through fronting arrangements.
Third-Party Capital
Third-party capital in reinsurance includes funds from non-traditional investors like hedge funds, pension funds, and private equity that provide alternative capital to insurers for risk transfer without traditional underwriting. This capital enhances market capacity, offers cost-efficient risk sharing, and diversifies sources beyond conventional reinsurance, transforming risk management strategies.
Hybrid Reinsurance Structures
Hybrid reinsurance structures combine traditional reinsurance with alternative capital solutions, leveraging both risk transfer and capital market mechanisms to optimize capital efficiency and risk management. These innovative arrangements enable insurers to access diversified sources of capital while tailoring coverage and cost to specific risk profiles, enhancing overall financial flexibility.
Reinsurance vs Alternative Capital Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com