Term insurance provides coverage for a specified period with higher sum assured, ideal for income protection and long-term financial planning. Microinsurance offers affordable, low-premium policies targeting low-income individuals, ensuring basic risk protection against specific emergencies. Choosing between them depends on coverage needs, budget, and the level of financial security required.
Table of Comparison
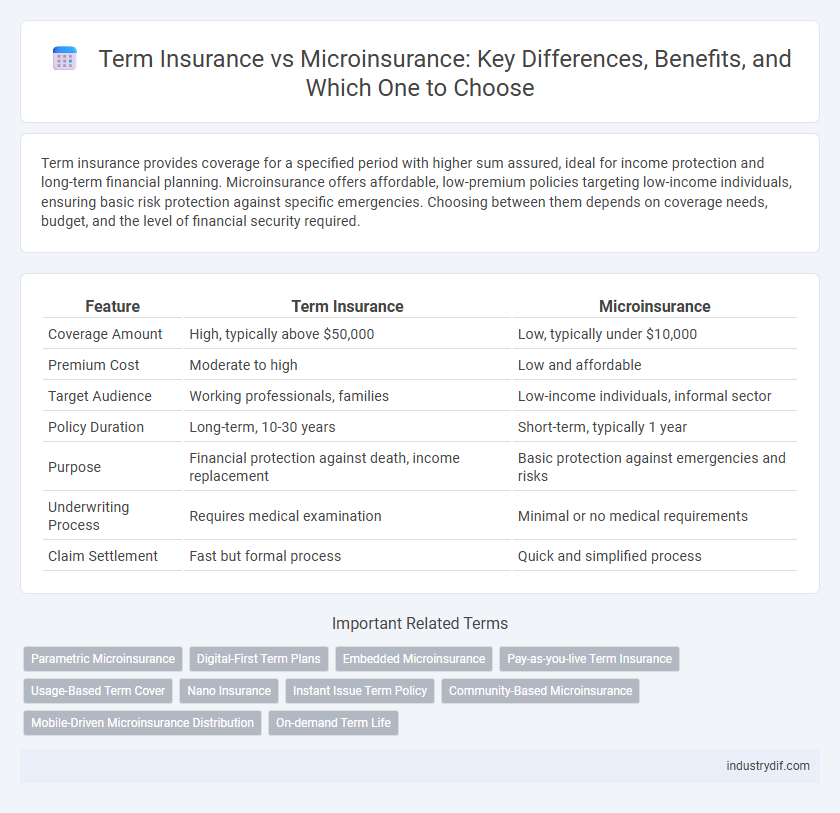
| Feature | Term Insurance | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Amount | High, typically above $50,000 | Low, typically under $10,000 |
| Premium Cost | Moderate to high | Low and affordable |
| Target Audience | Working professionals, families | Low-income individuals, informal sector |
| Policy Duration | Long-term, 10-30 years | Short-term, typically 1 year |
| Purpose | Financial protection against death, income replacement | Basic protection against emergencies and risks |
| Underwriting Process | Requires medical examination | Minimal or no medical requirements |
| Claim Settlement | Fast but formal process | Quick and simplified process |
Understanding Term Insurance: Key Features
Term insurance offers coverage for a specific period, providing high sum assured at affordable premiums, making it ideal for financial protection during critical years. Key features include fixed benefits, no maturity value, and straightforward policy terms without cash value accumulation. It ensures financial security for beneficiaries in case of the policyholder's untimely death, emphasizing risk coverage over savings.
What is Microinsurance? An Overview
Microinsurance is a specialized insurance product designed to provide affordable coverage primarily to low-income individuals and families who lack access to traditional insurance. It typically offers modest premiums and limited benefits tailored to risks such as health, life, property, or agriculture. By focusing on underserved populations, microinsurance promotes financial inclusion and risk management in emerging markets.
Coverage Scope: Term Insurance vs Microinsurance
Term insurance offers extensive coverage with higher sum assured amounts, typically protecting the policyholder for a fixed period ranging from 5 to 30 years, ensuring financial security against death or critical illness. Microinsurance provides limited coverage designed for low-income individuals, with lower premiums and smaller benefit amounts tailored to protect against specific risks such as health emergencies or natural disasters. The broad coverage scope of term insurance contrasts with the targeted, essential risk protection focus of microinsurance, making each suitable for different financial needs and income levels.
Eligibility and Accessibility Comparison
Term insurance typically requires applicants to meet age limits between 18 and 65 years with standard health criteria, making it accessible primarily to individuals with stable income and medical histories. Microinsurance targets low-income populations and informal sector workers, offering more flexible eligibility with minimal documentation and simplified health assessments to enhance accessibility. This distinction highlights term insurance's focus on comprehensive coverage for higher-risk profiles, while microinsurance prioritizes affordability and ease of access for underserved communities.
Premium Structure and Affordability
Term insurance offers a fixed premium structure with coverage periods typically ranging from 10 to 30 years, making it suitable for long-term financial protection with predictable costs. Microinsurance is designed with low premium payments tailored to low-income individuals, providing affordable short-term coverage for specific risks like health or crop damage. The affordability of microinsurance premiums ensures broader accessibility, while term insurance premiums, though higher, provide comprehensive protection over extended durations.
Policy Duration and Flexibility
Term insurance offers longer policy durations, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years, providing comprehensive coverage suited for financial planning and asset protection. Microinsurance policies feature shorter durations, often less than a year, designed for low-income individuals needing affordable, flexible, and easily renewable protection. The flexibility of microinsurance allows quick adaptation to policyholders' changing needs, whereas term insurance requires commitment over extended periods.
Claim Process: Differences and Similarities
Term insurance claim processes typically involve submitting a death certificate, policy documents, and sometimes medical records, with claims settled within 15 to 30 days. Microinsurance claims are designed for simplicity and speed, often requiring minimal documentation like an identity proof and a claim form, enabling quicker payouts in rural or underserved areas. Both types emphasize transparency and timely settlement, but microinsurance prioritizes accessibility for low-income policyholders with streamlined procedures.
Target Market and Customer Segments
Term insurance primarily targets middle to upper-income individuals seeking affordable, straightforward life coverage with fixed premiums and high sum assured, suitable for families aiming for financial security. Microinsurance focuses on low-income populations, including informal sector workers and rural communities, offering accessible, low-cost insurance products designed to meet specific risks and limited financial capacity. Both cater to distinct customer segments by tailoring coverage, premium structure, and distribution channels to match the economic realities and needs of their respective markets.
Regulatory Perspectives: Term Insurance vs Microinsurance
Regulatory frameworks for term insurance typically involve stringent capital requirements and extensive compliance standards due to the higher coverage amounts and longer policy durations. Microinsurance regulations prioritize accessibility and affordability, often allowing for simplified underwriting and reduced documentation to serve low-income populations effectively. Authorities emphasize consumer protection and transparency across both, but microinsurance policies benefit from tailored regulatory support to encourage wider financial inclusion.
Choosing the Right Plan: Factors to Consider
When choosing between term insurance and microinsurance, consider factors such as coverage amount, premium affordability, and coverage duration. Term insurance typically offers higher coverage for a fixed period, ideal for long-term financial protection, while microinsurance provides affordable, limited coverage suited for low-income individuals or specific risks. Assess personal financial goals, risk exposure, and budget constraints to select the plan that best balances protection and cost-effectiveness.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Microinsurance
Term insurance offers fixed coverage for a specified period with a predetermined sum assured, ideal for individuals seeking straightforward risk protection. Parametric microinsurance provides affordable, trigger-based payouts for low-income groups, using predefined parameters such as weather events to expedite claims and reduce administrative costs.
Digital-First Term Plans
Digital-first term plans offer streamlined, affordable coverage with quick online approvals and minimal paperwork, making them ideal for tech-savvy consumers seeking comprehensive protection. In contrast, microinsurance targets low-income segments with limited coverage and lower premiums but often lacks the extensive benefits and digital convenience of term insurance products.
Embedded Microinsurance
Embedded microinsurance integrates affordable, low-sum coverage directly into everyday products or services, providing accessible protection to low-income populations often excluded from traditional term insurance. This model enhances financial inclusion by offering customized risk management solutions that complement rather than replace conventional term insurance policies.
Pay-as-you-live Term Insurance
Pay-as-you-live Term Insurance offers flexible premiums based on real-time lifestyle data, contrasting with traditional Microinsurance's fixed low-cost coverage primarily targeting low-income groups. This innovative approach enhances affordability and personalized risk assessment, making term insurance more adaptable to individual health and activity patterns.
Usage-Based Term Cover
Usage-based term cover leverages telematics and real-time data to tailor premium rates based on driving behavior, offering cost-efficient protection compared to traditional term insurance policies. Microinsurance typically targets low-income segments with affordable, low-coverage plans, whereas usage-based term insurance appeals to risk-conscious individuals seeking personalized premiums and flexible coverage durations.
Nano Insurance
Nano insurance, a subset of microinsurance, offers highly affordable, short-term coverage tailored to low-income individuals or those needing minimal protection, often with premiums as low as a few cents. Term insurance typically provides larger, long-term coverage with fixed premiums, whereas nano insurance focuses on accessible, on-demand protection for everyday risks in emerging markets.
Instant Issue Term Policy
Instant issue term policies offer quick approval and coverage for higher sum insured amounts compared to microinsurance, which targets low-income individuals with affordable premiums and limited benefits. Term insurance provides longer tenure and comprehensive protection, making it suitable for those seeking substantial financial security without the need for extensive medical underwriting.
Community-Based Microinsurance
Community-based microinsurance provides affordable, tailored coverage designed for low-income groups by leveraging local networks to enhance risk pooling and claim accessibility. Unlike term insurance, which offers fixed-amount protection for a specified duration typically aimed at middle-to-high income individuals, microinsurance emphasizes inclusivity and social protection in underserved communities.
Mobile-Driven Microinsurance Distribution
Mobile-driven microinsurance distribution leverages widespread smartphone penetration and mobile network coverage to deliver affordable, low-premium term insurance policies tailored for low-income populations. This approach enhances accessibility and simplifies premium payments through mobile wallets, differentiating it from traditional term insurance that often relies on conventional sales channels and higher premiums.
On-demand Term Life
On-demand term life insurance offers flexible, short-term coverage tailored to immediate needs, contrasting with microinsurance's affordable, low-sum assured policies designed for low-income groups. This innovative model leverages digital platforms for instant issuance and claims, enhancing accessibility and convenience in the term insurance market.
Term Insurance vs Microinsurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com