Health insurance provides comprehensive coverage for medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription medications, typically through fixed monthly premiums. Usage-based insurance, often employed in auto and health sectors, adjusts premiums based on the insured's actual behaviors, such as driving habits or physical activity levels, promoting personalized risk assessment and potential cost savings. Choosing between them depends on the need for predictable coverage versus flexible, behavior-driven pricing models.
Table of Comparison
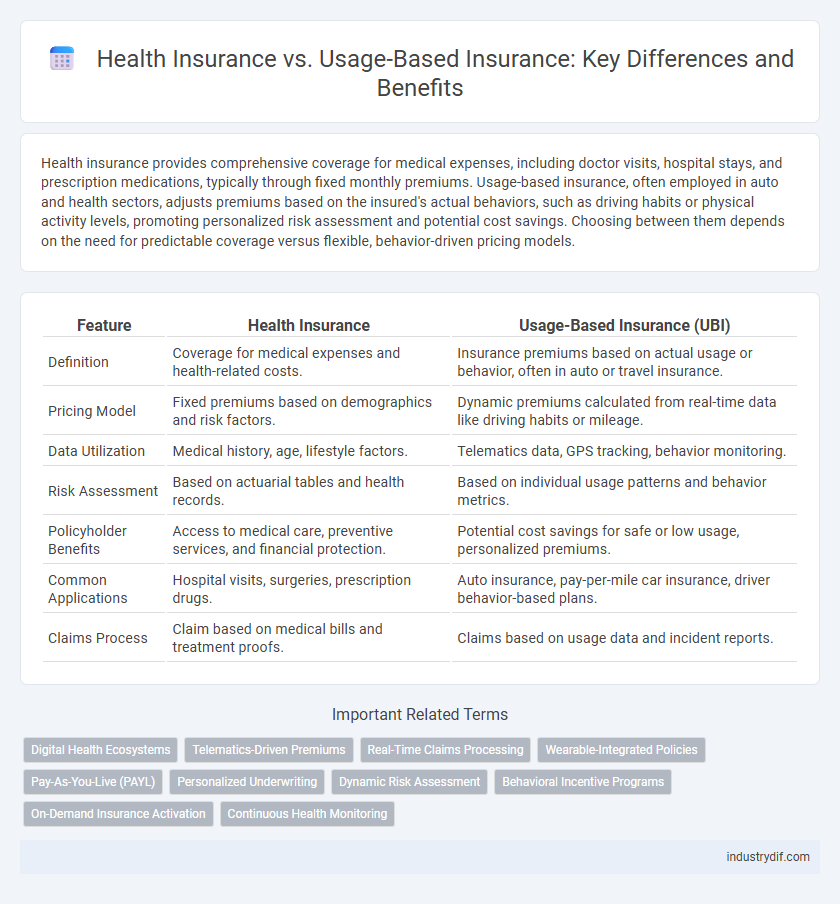
| Feature | Health Insurance | Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coverage for medical expenses and health-related costs. | Insurance premiums based on actual usage or behavior, often in auto or travel insurance. |
| Pricing Model | Fixed premiums based on demographics and risk factors. | Dynamic premiums calculated from real-time data like driving habits or mileage. |
| Data Utilization | Medical history, age, lifestyle factors. | Telematics data, GPS tracking, behavior monitoring. |
| Risk Assessment | Based on actuarial tables and health records. | Based on individual usage patterns and behavior metrics. |
| Policyholder Benefits | Access to medical care, preventive services, and financial protection. | Potential cost savings for safe or low usage, personalized premiums. |
| Common Applications | Hospital visits, surgeries, prescription drugs. | Auto insurance, pay-per-mile car insurance, driver behavior-based plans. |
| Claims Process | Claim based on medical bills and treatment proofs. | Claims based on usage data and incident reports. |
Understanding Health Insurance: Coverage and Benefits
Health insurance provides comprehensive coverage for medical expenses including hospitalization, prescription drugs, preventive care, and specialist visits, ensuring financial protection against unexpected health costs. Plans often include benefits such as wellness programs, chronic disease management, and mental health support, tailored to promote overall well-being. Understanding specific policy terms like deductibles, copayments, and out-of-pocket maximums is crucial to maximizing coverage and minimizing healthcare expenses.
What is Usage-Based Insurance? Key Features Explained
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) is a health insurance model that customizes premiums based on real-time data collected from policyholders' behavior, such as driving habits or physical activity levels tracked via wearable devices. Key features include dynamic pricing, personalized risk assessments, and incentives for healthier lifestyles or safer behavior, which help reduce claims and promote cost savings. This model leverages telematics and digital health monitoring technologies to enhance accuracy in risk evaluation and improve user engagement.
Comparing Cost Structures: Premiums vs. Pay-as-You-Go
Health insurance typically involves fixed premiums paid monthly or annually, offering predictable costs regardless of individual usage, while usage-based insurance (UBI) employs a pay-as-you-go model where premiums fluctuate based on real-time data such as mileage, driving behavior, or health metrics. The cost structure of health insurance prioritizes risk pooling and actuarial calculations to stabilize premiums across a broad population, whereas UBI leverages telematics and wearable devices to personalize pricing and incentivize healthier behaviors. Usage-based models can lower expenses for low-risk individuals but may introduce cost variability and require continuous monitoring to optimize savings effectively.
Risk Assessment in Health vs. Usage-Based Insurance
Health insurance risk assessment primarily relies on medical history, age, lifestyle factors, and pre-existing conditions to determine premium rates and coverage eligibility. Usage-Based Insurance (UBI), often applied in auto insurance but increasingly explored in health insurance, uses real-time data from wearable devices to monitor behaviors such as physical activity, heart rate, and sleep patterns for dynamic risk evaluation. This data-driven approach allows for personalized premiums reflecting the insured's current health status and behavioral risk factors more accurately than traditional underwriting methods.
Personalization: Tailoring Policies to Individual Needs
Health insurance policies increasingly leverage personalization by analyzing individual health data to tailor coverage and premiums, enhancing affordability and relevance. Usage-based insurance (UBI) employs real-time behavioral data, such as driving habits or lifestyle activities, to customize pricing and benefits for each policyholder. Both approaches prioritize personalized risk assessment, enabling insurers to offer customized plans that better align with individual needs and promote proactive health management.
Technology Integration: Wearables and Telematics in Insurance
Health insurance increasingly integrates wearable technology to monitor real-time health metrics, enabling personalized wellness programs and proactive risk management. Usage-based insurance (UBI) leverages telematics devices to track driving behavior, mileage, and vehicle usage patterns, allowing insurers to offer customized premiums based on actual risk exposure. Both models utilize advanced data analytics and IoT connectivity to enhance policyholder engagement and improve underwriting accuracy.
Data Privacy Concerns: Health vs. Usage-Based Models
Health insurance typically relies on medical records and personal health information, triggering rigorous data privacy regulations like HIPAA to protect sensitive data. Usage-based insurance collects real-time data through telematics devices or mobile apps, raising concerns about continuous location tracking and behavioral monitoring. Consumers often face heightened privacy risks with usage-based models due to extensive data granularity and potential third-party data sharing.
Claims Processes: Traditional vs. Real-Time Submissions
Health insurance claims typically involve a traditional process where policyholders submit detailed documents for reimbursement, often resulting in longer approval times. Usage-based insurance, however, leverages real-time data from telematics or health monitoring devices to enable instant claims submissions and faster settlements. This shift enhances efficiency and accuracy in claims processing by reducing paperwork and enabling proactive fraud detection.
Regulatory Differences: Compliance and Legal Considerations
Health insurance regulations primarily focus on protecting patient rights, requiring compliance with laws such as the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which govern coverage standards and data privacy. Usage-based insurance (UBI), particularly in health applications involving wearable devices, navigates complex legal frameworks concerning data collection consent, accuracy, and discrimination risks under regulations like the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA). Regulatory differences demand insurers ensure transparency, data security, and equitable underwriting practices tailored to each model's compliance obligations.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Health and Usage-Based Insurance
Health insurance is rapidly integrating digital health data and telemedicine to enhance personalized care and risk assessment. Usage-based insurance leverages real-time monitoring through wearable devices and IoT technology to offer dynamic premium adjustments based on individual behavior and health metrics. Future trends indicate a convergence of these models, driven by advanced AI analytics and big data, creating more flexible, tailored health insurance solutions that improve outcomes and reduce costs.
Related Important Terms
Digital Health Ecosystems
Health insurance within digital health ecosystems leverages data from wearable devices and telemedicine to provide personalized coverage and proactive care, enhancing patient outcomes and cost efficiency. Usage-based insurance models analyze real-time health behaviors and biometric data to dynamically adjust premiums and incentivize healthier lifestyles, fostering a data-driven approach to risk assessment.
Telematics-Driven Premiums
Telematics-driven premiums in health insurance leverage real-time data from wearable devices and mobile apps to personalize coverage and incentivize healthier behaviors, reducing overall costs and improving risk assessment accuracy. Usage-based insurance models collect granular health metrics such as activity levels, heart rate, and sleep patterns, enabling insurers to tailor premiums dynamically based on individual lifestyle and medical conditions.
Real-Time Claims Processing
Health insurance benefits from real-time claims processing by accelerating reimbursements and reducing administrative errors through advanced data analytics. Usage-Based Insurance leverages telematics and real-time data to dynamically adjust premiums and streamline claim validation for personalized coverage.
Wearable-Integrated Policies
Wearable-integrated health insurance policies leverage real-time biometric data to customize premiums and promote preventive care, enhancing risk assessment accuracy compared to traditional health insurance. Usage-based insurance models utilize data from wearable devices to incentivize healthy behaviors and reduce claims by offering dynamic pricing based on individual activity patterns.
Pay-As-You-Live (PAYL)
Pay-As-You-Live (PAYL) health insurance offers personalized premiums based on real-time lifestyle data, promoting healthier behaviors and cost savings compared to traditional health insurance models that rely on fixed rates and historical risk assessments. By leveraging wearable devices and continuous health monitoring, PAYL policies enable dynamic pricing and incentivize preventive care, reducing overall claims and enhancing patient outcomes.
Personalized Underwriting
Health insurance is increasingly adopting personalized underwriting by leveraging extensive medical histories and lifestyle data to tailor premiums and coverage effectively. Usage-based insurance (UBI) utilizes real-time behavior metrics such as driving patterns or wellness activities to dynamically adjust policies, enhancing accuracy in risk assessment and pricing.
Dynamic Risk Assessment
Health insurance typically relies on static risk factors evaluated during policy underwriting, while usage-based insurance integrates dynamic risk assessment by continuously monitoring policyholders' real-time health data or behavior patterns to adjust premiums and coverage. This evolving approach enhances personalized risk management, incentivizing healthier lifestyles and enabling insurers to respond promptly to changes in individual health profiles.
Behavioral Incentive Programs
Health insurance plans with behavioral incentive programs often reward policyholders for engaging in healthy activities such as regular exercise, preventive screenings, and maintaining a balanced diet, thereby promoting long-term wellness and potentially lowering premiums. Usage-based insurance leverages telematics and real-time data to monitor driving behavior, offering discounts or rewards for safe driving habits, which aligns risk assessment with actual user behavior and encourages responsible actions.
On-Demand Insurance Activation
On-demand insurance activation in health insurance allows policyholders to instantly activate coverage only during specific periods of anticipated need, reducing overall premiums. Usage-based insurance leverages real-time data and behavior monitoring to dynamically adjust health coverage costs and benefits based on actual service utilization patterns.
Continuous Health Monitoring
Continuous health monitoring enhances health insurance by providing real-time biometric data such as heart rate, glucose levels, and activity patterns, enabling more accurate risk assessments and personalized premiums. Usage-based insurance leverages similar data from wearable devices to adjust coverage dynamically, promoting proactive health management and potentially lowering overall healthcare costs.
Health Insurance vs Usage-Based Insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com