Risk pooling involves collecting premiums from a large group of policyholders to spread financial risk across many individuals, providing stability and predictability in claims payments. Peer-to-peer insurance allows smaller groups of people with similar risk profiles to share insurance costs directly, often resulting in lower premiums and increased transparency. Both models aim to reduce individual risk but differ in structure, with risk pooling relying on traditional insurers and peer-to-peer insurance leveraging community-based networks.
Table of Comparison
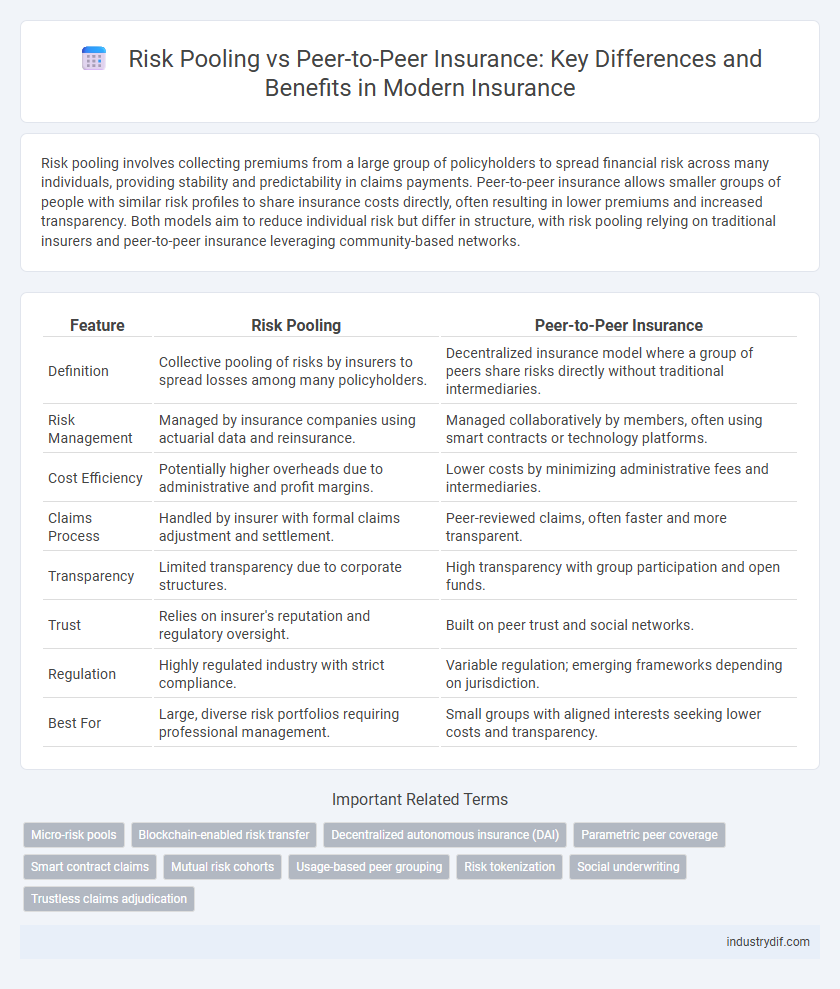
| Feature | Risk Pooling | Peer-to-Peer Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collective pooling of risks by insurers to spread losses among many policyholders. | Decentralized insurance model where a group of peers share risks directly without traditional intermediaries. |
| Risk Management | Managed by insurance companies using actuarial data and reinsurance. | Managed collaboratively by members, often using smart contracts or technology platforms. |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially higher overheads due to administrative and profit margins. | Lower costs by minimizing administrative fees and intermediaries. |
| Claims Process | Handled by insurer with formal claims adjustment and settlement. | Peer-reviewed claims, often faster and more transparent. |
| Transparency | Limited transparency due to corporate structures. | High transparency with group participation and open funds. |
| Trust | Relies on insurer's reputation and regulatory oversight. | Built on peer trust and social networks. |
| Regulation | Highly regulated industry with strict compliance. | Variable regulation; emerging frameworks depending on jurisdiction. |
| Best For | Large, diverse risk portfolios requiring professional management. | Small groups with aligned interests seeking lower costs and transparency. |
Definition of Risk Pooling in Insurance
Risk pooling in insurance refers to the practice of aggregating risks from multiple policyholders to spread potential losses across the entire group, reducing the financial impact on any single member. This traditional method enables insurers to predict claims more accurately by leveraging the law of large numbers, enhancing premium stability and affordability. Peer-to-peer insurance contrasts with risk pooling by connecting individuals who share similar risk profiles to insure each other directly, minimizing administrative costs and fostering community trust.
Overview of Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Insurance
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) insurance is a decentralized model where individuals pool their premiums to insure each other, reducing reliance on traditional insurers and minimizing administrative costs. This approach fosters transparency and trust by allowing policyholders to collectively manage claims and share excess premiums. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, P2P insurance enhances efficiency, reduces fraud, and aligns incentives among participants.
Key Differences: Risk Pooling vs Peer-to-Peer Insurance
Risk pooling centralizes premiums from a large group of policyholders to cover losses collectively, spreading risk across the entire pool. Peer-to-peer insurance segments smaller groups of individuals who share similar risk profiles, promoting transparency and potentially lower costs by directly distributing claims among members. Unlike traditional risk pooling, peer-to-peer models leverage community-based trust and technology to enhance control over coverage and claim handling.
Underwriting Practices in Both Models
Risk pooling in traditional insurance relies on actuarial underwriting practices that assess risk based on large population data, enabling predictable premium setting and loss distribution. Peer-to-peer insurance employs underwriting methods emphasizing individual behavior and group dynamics, often using technology-driven data to adjust risks within smaller, trust-based networks. Both models aim to optimize risk assessment but differ in pooling scale and the granularity of underwriting criteria applied.
Claims Management and Settlements
Risk pooling centralizes claims management by aggregating premiums into a common fund to cover losses, enabling efficient settlements through professional underwriting and loss adjustment processes. Peer-to-peer insurance decentralizes claims handling, leveraging social trust and transparency among members to expedite settlements and reduce administrative costs. Both models seek to optimize claims resolution, but peer-to-peer emphasizes member engagement and cost sharing, while traditional risk pooling relies on established insurers' expertise and financial reserves.
Cost Structures and Premium Calculations
Risk pooling in traditional insurance spreads risk across a large group, resulting in standardized premium calculations based on actuarial data and statistical models. Peer-to-peer insurance structures costs by grouping individuals with similar risk profiles, enabling more personalized premiums and reducing administrative expenses through direct member interactions. This often lowers overall premiums and increases transparency compared to conventional insurance, where fixed overheads and profit margins influence pricing.
Technology’s Role in P2P and Traditional Insurance
Technology in peer-to-peer insurance leverages blockchain and smart contracts to increase transparency, automate claims processing, and reduce administrative costs. Traditional insurance relies on centralized databases and legacy IT systems, often leading to slower claim settlements and higher operational expenses. The integration of AI and machine learning in both models enhances risk assessment and fraud detection, but P2P insurance uniquely empowers policyholders through decentralized platforms that foster trust and community-based risk sharing.
Advantages of Risk Pooling
Risk pooling in insurance maximizes risk diversification by aggregating a large number of policyholders, which stabilizes premiums and reduces individual financial exposure. It enhances predictability of losses, enabling insurers to allocate resources more efficiently and maintain solvency during high claim periods. This traditional approach benefits from established regulatory frameworks and widespread acceptance, providing greater security and trust among insured individuals.
Benefits and Challenges of P2P Insurance
Peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance offers the benefit of increased transparency and reduced costs by directly connecting policyholders who share similar risk profiles, fostering trust and potentially lowering premiums through collective risk sharing. Challenges include regulatory uncertainties and the difficulty of managing diverse risk appetites within small groups, which can lead to liquidity issues or coverage gaps. Despite these hurdles, P2P insurance promotes community-driven accountability and may improve customer satisfaction compared to traditional risk pooling models.
Future Trends: Evolving Models in the Insurance Industry
Risk pooling remains a foundational model in traditional insurance, aggregating diverse risks to stabilize premiums and ensure broad coverage. Peer-to-peer insurance increasingly leverages blockchain and AI technologies, promoting transparency, reducing administrative costs, and fostering community-driven claims handling. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach combining risk pooling's financial robustness with peer-to-peer's digital innovation, driving more personalized and efficient insurance solutions.
Related Important Terms
Micro-risk pools
Micro-risk pools in risk pooling aggregate small, homogeneous risks to optimize premium stability and reduce individual exposure, enhancing collective risk management efficiency. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages these micro-risk pools by connecting groups of similar policyholders, promoting transparency, lower costs, and aligned incentives through direct risk sharing without traditional intermediaries.
Blockchain-enabled risk transfer
Blockchain-enabled risk transfer revolutionizes traditional risk pooling by enabling transparent, decentralized peer-to-peer insurance models that reduce intermediaries and fraud. Smart contracts automate claim validation and payouts, enhancing efficiency and lowering costs while empowering policyholders with greater control over risk sharing.
Decentralized autonomous insurance (DAI)
Decentralized autonomous insurance (DAI) leverages blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer insurance models, eliminating traditional intermediaries and enhancing transparency and trust among policyholders. Unlike conventional risk pooling, DAI distributes risk through smart contracts and collective underwriting, optimizing claims management and reducing administrative costs.
Parametric peer coverage
Parametric peer-to-peer insurance leverages predefined triggers based on measurable parameters such as weather data, enabling automated claims payouts without traditional loss assessment, which enhances transparency and reduces administrative costs compared to conventional risk pooling. This model fosters direct risk sharing among peers, aligning incentives and improving efficiency by utilizing smart contracts and real-time data for parametric coverage.
Smart contract claims
Risk pooling in traditional insurance centralizes claims management, while peer-to-peer insurance leverages blockchain-based smart contracts to automate claim verification and payouts, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud. Smart contract claims enable real-time, trustless processing by triggering payments based on pre-defined conditions, revolutionizing risk-sharing mechanisms within decentralized insurance networks.
Mutual risk cohorts
Mutual risk cohorts in insurance create groups of policyholders who share similar risk profiles, enhancing the efficiency of risk pooling by distributing losses among members and reducing reliance on traditional insurers. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages these cohorts to foster transparency and trust, often resulting in lower premiums and more personalized coverage options tailored to the collective risk of the group.
Usage-based peer grouping
Usage-based peer grouping in peer-to-peer insurance leverages telematics and real-time data to create customized risk pools based on individual driving behavior, improving pricing accuracy and fairness. This contrasts with traditional risk pooling, which aggregates risks across broad demographics, often leading to less personalized premiums and potential adverse selection.
Risk tokenization
Risk tokenization transforms traditional risk pooling by converting insurance risk into digital tokens that can be traded or shared among participants, enhancing transparency and liquidity in the insurance market. This approach enables decentralized risk sharing in peer-to-peer insurance models, reducing dependency on centralized insurers and allowing policyholders to directly manage and diversify their risk exposure.
Social underwriting
Social underwriting in risk pooling leverages collective risk distribution across large groups to stabilize premiums and enhance coverage reliability. Peer-to-peer insurance employs social underwriting by enabling policyholders to assess and manage risk collaboratively within trusted communities, reducing fraud and aligning incentives.
Trustless claims adjudication
Risk pooling in traditional insurance relies on centralized authorities to manage claims, whereas peer-to-peer insurance utilizes blockchain technology to enable trustless claims adjudication through smart contracts. This decentralized approach enhances transparency, reduces fraud, and accelerates the settlement process by automatically verifying claims without intermediaries.
Risk pooling vs Peer-to-peer insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com