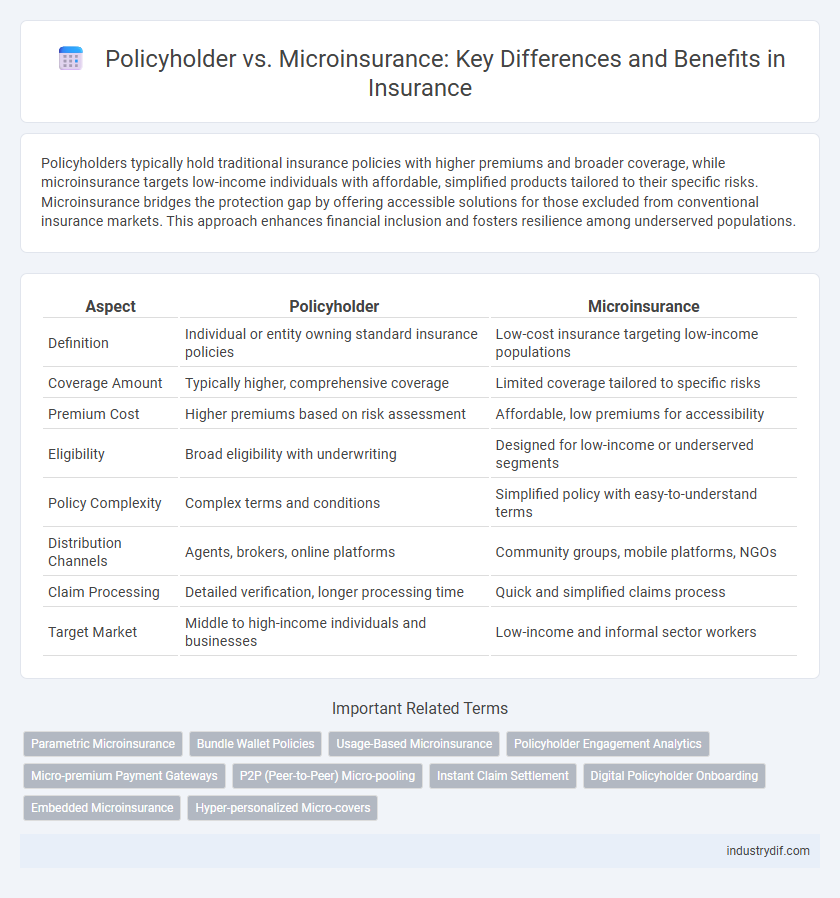
Policyholders typically hold traditional insurance policies with higher premiums and broader coverage, while microinsurance targets low-income individuals with affordable, simplified products tailored to their specific risks. Microinsurance bridges the protection gap by offering accessible solutions for those excluded from conventional insurance markets. This approach enhances financial inclusion and fosters resilience among underserved populations.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Policyholder | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual or entity owning standard insurance policies | Low-cost insurance targeting low-income populations |
| Coverage Amount | Typically higher, comprehensive coverage | Limited coverage tailored to specific risks |
| Premium Cost | Higher premiums based on risk assessment | Affordable, low premiums for accessibility |
| Eligibility | Broad eligibility with underwriting | Designed for low-income or underserved segments |
| Policy Complexity | Complex terms and conditions | Simplified policy with easy-to-understand terms |
| Distribution Channels | Agents, brokers, online platforms | Community groups, mobile platforms, NGOs |
| Claim Processing | Detailed verification, longer processing time | Quick and simplified claims process |
| Target Market | Middle to high-income individuals and businesses | Low-income and informal sector workers |
Defining Policyholder and Microinsurance
A policyholder is an individual or entity that owns an insurance policy and holds the contractual rights to benefits and claims under the agreement. Microinsurance is a specialized form of insurance designed to provide affordable coverage to low-income individuals or underserved populations, addressing risks that traditional insurance policies may not cover. Understanding the distinction between a policyholder as the insured party and microinsurance as a targeted, accessible product is critical for expanding financial protection in developing markets.
Key Differences Between Policyholders and Microinsurance
Policyholders typically hold standard insurance policies with higher premiums and comprehensive coverage, while microinsurance targets low-income individuals with affordable, limited protection for specific risks. The primary difference lies in accessibility and scale; microinsurance is designed to meet the financial constraints and unique needs of underserved populations, often featuring simpler terms and faster claim processes. Policyholders usually engage in long-term contracts with formal insurers, whereas microinsurance emphasizes community-based or mobile platforms to promote widespread adoption.
Eligibility Criteria for Policyholder and Microinsurance
Eligibility criteria for policyholders typically include age limits, income levels, and health status, ensuring coverage is appropriate and sustainable. Microinsurance targets low-income individuals often excluded from traditional policies, with simplified requirements like minimal documentation and flexible premium payments. This approach increases accessibility, providing essential coverage to vulnerable populations in emerging markets.
Coverage Scope: Traditional Insurance vs Microinsurance
Traditional insurance policies typically offer extensive coverage with higher sums insured, targeting individuals or businesses able to pay substantial premiums. Microinsurance focuses on providing limited, essential coverage designed for low-income populations, emphasizing affordability and accessibility with lower premiums and simplified claims processes. The coverage scope in microinsurance often addresses specific risks such as health, crop failure, or natural disasters, contrasting with the broader protection found in traditional insurance products.
Premium Structures: Policyholder vs Microinsurance
Policyholders in traditional insurance often face higher premium structures based on risk assessment, coverage limits, and policy duration, resulting in more customized but costly options. Microinsurance offers significantly lower premiums tailored for low-income individuals, utilizing simplified underwriting and reduced coverage to maintain affordability. This contrast highlights microinsurance's role in expanding accessibility through premium models designed for financial inclusion.
Claims Process: Comparative Analysis
The claims process for policyholders in traditional insurance typically involves complex documentation and longer approval timelines, whereas microinsurance offers streamlined, technology-driven claims handling tailored for low-income clients. Microinsurance platforms leverage mobile-based submissions and automated verification to expedite claim settlements, reducing processing time significantly compared to conventional insurance protocols. This comparative efficiency highlights microinsurance's role in enhancing accessibility and responsiveness for underserved populations during claims resolution.
Accessibility and Distribution Channels
Microinsurance enhances accessibility for low-income policyholders by offering affordable, tailored coverage through mobile platforms and community-based agents. Traditional insurance policyholders often rely on formal channels like brokers and online portals, limiting reach in underserved regions. Expanding digital and agent networks in microinsurance increases distribution efficiency and inclusivity in emerging markets.
Regulatory Frameworks for Policyholder and Microinsurance
Regulatory frameworks for policyholders and microinsurance vary significantly to address their distinct risk profiles and financial capabilities. Policyholder regulations emphasize consumer protection, solvency requirements, and dispute resolution mechanisms to ensure transparency and reliability in traditional insurance. Microinsurance frameworks prioritize simplified procedures, affordability, and inclusivity, often incorporating tailored licensing requirements and relaxed capital standards to facilitate access for low-income populations.
Benefits and Limitations of Microinsurance
Microinsurance offers affordable coverage tailored to low-income policyholders, providing protection against specific risks such as health emergencies, crop failure, or natural disasters. Its benefits include simplified claim processes, lower premiums, and accessibility in underserved markets, promoting financial inclusion. However, microinsurance often features limited coverage amounts, higher relative administrative costs, and potential challenges in awareness and trust among policyholders.
Choosing the Right Insurance Solution
Selecting the right insurance solution involves understanding the policyholder's unique needs alongside microinsurance offerings designed for low-income individuals. Microinsurance provides affordable, accessible coverage with simplified terms, ideal for those underserved by traditional policies. Evaluating risk exposure, coverage scope, and premium affordability helps policyholders determine whether microinsurance or standard insurance better aligns with their financial protection goals.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Microinsurance
Parametric microinsurance offers policyholders streamlined coverage through predefined triggers like weather events, enabling faster claim payouts without traditional loss assessments. This innovative insurance model enhances financial protection for low-income policyholders by reducing administrative costs and improving claim transparency in microinsurance markets.
Bundle Wallet Policies
Bundle wallet policies in microinsurance offer policyholders affordable, flexible coverage options by consolidating multiple insurance products into a single digital wallet. This approach enhances accessibility for low-income individuals, streamlining premium payments and claims management within a unified platform.
Usage-Based Microinsurance
Usage-based microinsurance empowers policyholders by offering personalized coverage tailored to their real-time behavior and risk profiles, enhancing affordability and accessibility. This innovative approach leverages telematics and data analytics to optimize premiums and claims, making insurance more inclusive for low-income individuals.
Policyholder Engagement Analytics
Policyholder engagement analytics in microinsurance leverage real-time data to track customer behavior, preferences, and claim patterns, enabling personalized communication and targeted product offerings that increase retention. Advanced analytics tools assess policyholder interactions across digital platforms, improving risk assessment and driving proactive support strategies tailored to low-income segments.
Micro-premium Payment Gateways
Micro-premium payment gateways enable policyholders to seamlessly manage and pay small insurance premiums, increasing accessibility and affordability for low-income individuals. These gateways leverage mobile money and digital wallets, facilitating real-time transactions and enhancing policyholder engagement in microinsurance schemes.
P2P (Peer-to-Peer) Micro-pooling
P2P micro-pooling in microinsurance enables policyholders to collectively manage risk by pooling small contributions, enhancing affordability and community trust. This decentralized approach reduces administrative costs and increases transparency, empowering individuals with limited resources to access tailored coverage.
Instant Claim Settlement
Microinsurance offers policyholders instant claim settlement through streamlined digital platforms, significantly reducing processing time compared to traditional insurance policies. This rapid payout system enhances financial security for low-income clients by providing immediate access to funds during emergencies.
Digital Policyholder Onboarding
Digital policyholder onboarding in microinsurance leverages mobile technology and data analytics to streamline the enrollment process, reducing barriers for low-income populations and increasing accessibility. This approach enhances real-time identity verification and automated underwriting, resulting in faster policy issuance and improved customer experience.
Embedded Microinsurance
Embedded microinsurance integrates policyholder protection directly within product purchases, offering affordable, tailored coverage without separate enrollment. This approach enhances accessibility for low-income individuals by automatically including insurance benefits, reducing administrative costs and improving risk management in underserved markets.
Hyper-personalized Micro-covers
Hyper-personalized micro-covers offer policyholders tailored insurance solutions that precisely match their unique needs, enhancing affordability and coverage flexibility in microinsurance markets. These innovative products leverage data analytics and real-time risk assessment to deliver customized protection, improving customer satisfaction and policyholder retention.
Policyholder vs Microinsurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com