Policyholders typically purchase insurance policies directly to protect against specific risks, managing coverage terms and premiums themselves. Embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly within a product or service, offering automatic protection without separate policy management. This approach enhances convenience and reduces friction for consumers compared to traditional policyholder models.
Table of Comparison
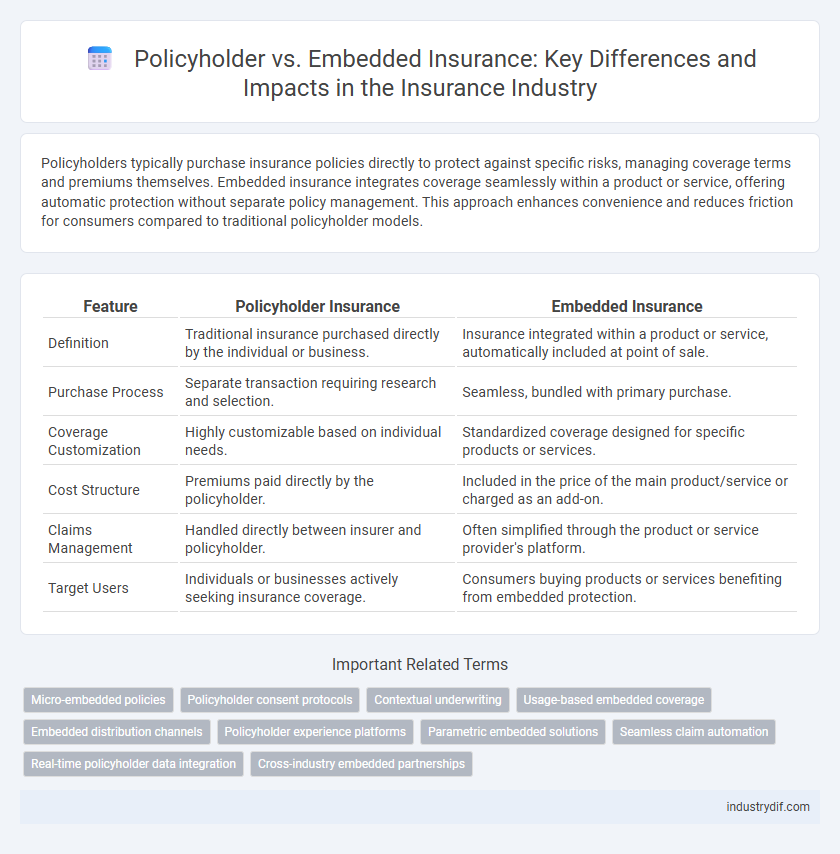
| Feature | Policyholder Insurance | Embedded Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional insurance purchased directly by the individual or business. | Insurance integrated within a product or service, automatically included at point of sale. |
| Purchase Process | Separate transaction requiring research and selection. | Seamless, bundled with primary purchase. |
| Coverage Customization | Highly customizable based on individual needs. | Standardized coverage designed for specific products or services. |
| Cost Structure | Premiums paid directly by the policyholder. | Included in the price of the main product/service or charged as an add-on. |
| Claims Management | Handled directly between insurer and policyholder. | Often simplified through the product or service provider's platform. |
| Target Users | Individuals or businesses actively seeking insurance coverage. | Consumers buying products or services benefiting from embedded protection. |
Defining Policyholder Insurance
Policyholder insurance refers to coverage purchased directly by an individual or entity who owns the insurance policy and assumes the associated rights and responsibilities. This type of insurance grants the policyholder control over policy terms, premium payments, and claims management. Unlike embedded insurance, which is bundled with a product or service, policyholder insurance operates as a standalone contract between the insurer and the insured party.
Understanding Embedded Insurance
Embedded insurance integrates coverage directly within the purchase of products or services, offering policyholders seamless protection without requiring a separate insurance contract. This approach enhances convenience and often results in instant coverage activation, reducing the complexity typically faced by traditional policyholders. Understanding embedded insurance involves recognizing its role in simplifying risk management by embedding policies within everyday transactions.
Key Differences Between Policyholder and Embedded Insurance
Policyholder insurance involves a direct contract between the insurer and the insured, where individuals actively purchase and manage their own policies. Embedded insurance is integrated into the purchase of products or services, offering automatic coverage without separate policy management. The key differences lie in control, convenience, and customization, with policyholders having more choice and embedded insurance providing seamless protection bundled with other transactions.
Advantages of Traditional Policyholder Insurance
Traditional policyholder insurance offers direct control over policy terms, enabling customization to meet individual risk profiles and coverage needs. Policyholders benefit from a well-established claims process and dedicated customer service, ensuring transparency and reliability. This type of insurance often provides broader protection options compared to embedded insurance tied to specific products.
Benefits of Embedded Insurance Solutions
Embedded insurance solutions integrate coverage seamlessly within the purchase of products or services, enhancing convenience for policyholders by eliminating the need for separate insurance transactions. Policyholders benefit from immediate protection tailored to the specific product or service, reducing gaps in coverage and simplifying claims processes. This approach also drives higher adoption rates and customer satisfaction by delivering transparent, cost-effective insurance embedded directly in the consumer journey.
Customer Experience Comparison
Embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly within the purchase process, offering policyholders immediate protection with minimal friction, enhancing convenience and satisfaction. Traditional policyholders often face complex paperwork and delayed coverage activation, which can diminish overall customer experience. Streamlined embedded insurance solutions leverage real-time data and digital platforms to deliver personalized, hassle-free protection, significantly improving user engagement and trust.
Distribution Channels: Policyholder vs Embedded Models
Distribution channels for policyholder models primarily rely on direct sales, insurance agents, and brokers, enabling policyholders to actively seek and purchase coverage. Embedded insurance integrates protection seamlessly within non-insurance products or services, such as e-commerce platforms or travel bookings, offering insurance automatically at the point of need. The embedded model enhances customer experience by reducing friction, while the policyholder model provides greater transparency and customization in the buying process.
Impact on Claims and Servicing
Policyholders directly manage their insurance claims and servicing, enabling personalized communication and faster resolution. Embedded insurance integrates coverage within products or services, streamlining claims through automated processes but often limiting direct policyholder interaction. This integration impacts the efficiency and transparency of claims handling, shifting responsibilities between insurers and the service providers embedding the insurance.
Regulatory Considerations in Both Models
Regulatory considerations differ significantly between policyholder-driven insurance and embedded insurance models, with traditional policies subject to comprehensive consumer protection and solvency requirements enforced by insurance regulators. Embedded insurance, often integrated within a product or service, faces evolving regulatory scrutiny focusing on transparency, disclosure obligations, and data privacy compliance, particularly under frameworks like the GDPR and PSD2. Both models require strict adherence to anti-money laundering (AML) standards and dispute resolution mechanisms to ensure policyholder rights and market integrity.
Future Trends in Insurance Delivery Models
Policyholders increasingly expect seamless, personalized coverage experiences, driving the adoption of embedded insurance integrated directly within product purchases and services. Future trends indicate a shift towards AI-powered digital platforms that enable real-time policy adjustments and claims processing, enhancing customer convenience and retention. Insurers will prioritize collaboration with tech firms and retailers to embed insurance solutions, transforming traditional distribution channels and meeting evolving consumer demands.
Related Important Terms
Micro-embedded policies
Micro-embedded policies integrate insurance coverage directly into the purchase of products or services, providing seamless protection without requiring separate policyholder engagement. This approach shifts the traditional role of the policyholder by embedding coverage within everyday transactions, enhancing convenience and accessibility.
Policyholder consent protocols
Policyholder consent protocols require explicit agreement before activating embedded insurance within a product or service, ensuring transparency and regulatory compliance. These protocols protect policyholders by mandating clear disclosures and opt-in mechanisms, differentiating traditional insurance policies from automatically included embedded coverage.
Contextual underwriting
Contextual underwriting in insurance leverages real-time data and situational insights to tailor policies directly to the policyholder's specific environment and behavior, enhancing risk assessment accuracy. Embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly within a product or service purchase, enabling contextual underwriting to dynamically adjust terms based on the immediate use case and customer context.
Usage-based embedded coverage
Usage-based embedded insurance integrates coverage directly into products or services, enabling real-time risk assessment and tailored premiums based on actual user behavior, unlike traditional policyholder models requiring separate insurance purchases. This seamless incorporation enhances customer experience by automatically adjusting protection levels and streamlining claims processes within the primary service environment.
Embedded distribution channels
Embedded insurance leverages distribution channels such as e-commerce platforms, ride-sharing apps, and financial services to integrate coverage seamlessly within a primary purchase, enhancing convenience for the policyholder. This approach contrasts traditional policyholder-driven insurance by embedding coverage directly at the point of sale, increasing uptake through frictionless access and improving risk protection alignment with consumers' immediate needs.
Policyholder experience platforms
Policyholder experience platforms streamline communication, claims management, and policy updates, enhancing user satisfaction and engagement in traditional insurance models. Embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly within third-party products but often relies on robust policyholder experience platforms to ensure consistent service quality and real-time support.
Parametric embedded solutions
Parametric embedded insurance integrates seamlessly within products or services, offering policyholders instant, data-driven payouts based on predefined triggers like weather events or flight delays. This model enhances customer experience by reducing claim processing time and providing transparent, objective coverage compared to traditional policyholder-managed insurance.
Seamless claim automation
Seamless claim automation in insurance enhances the policyholder experience by enabling instant verification and settlement using embedded insurance solutions integrated directly within purchase platforms. This integration reduces manual processing, accelerates claims approval, and minimizes errors by leveraging real-time data exchange between insurers and policyholders.
Real-time policyholder data integration
Real-time policyholder data integration enhances embedded insurance by enabling seamless and dynamic risk assessment directly within third-party platforms, improving underwriting accuracy and customer experience. This integration allows insurers to access up-to-date policyholder information instantly, supporting personalized coverage and faster claims processing without traditional policyholder intervention.
Cross-industry embedded partnerships
Cross-industry embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly within products or services from non-insurance companies, enhancing customer experience and expanding market reach without requiring a separate policyholder interaction. This approach leverages partnerships across sectors like retail, automotive, and technology to deliver tailored risk protection embedded at the point of sale, streamlining insurance adoption and driving revenue growth.
Policyholder vs Embedded Insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com