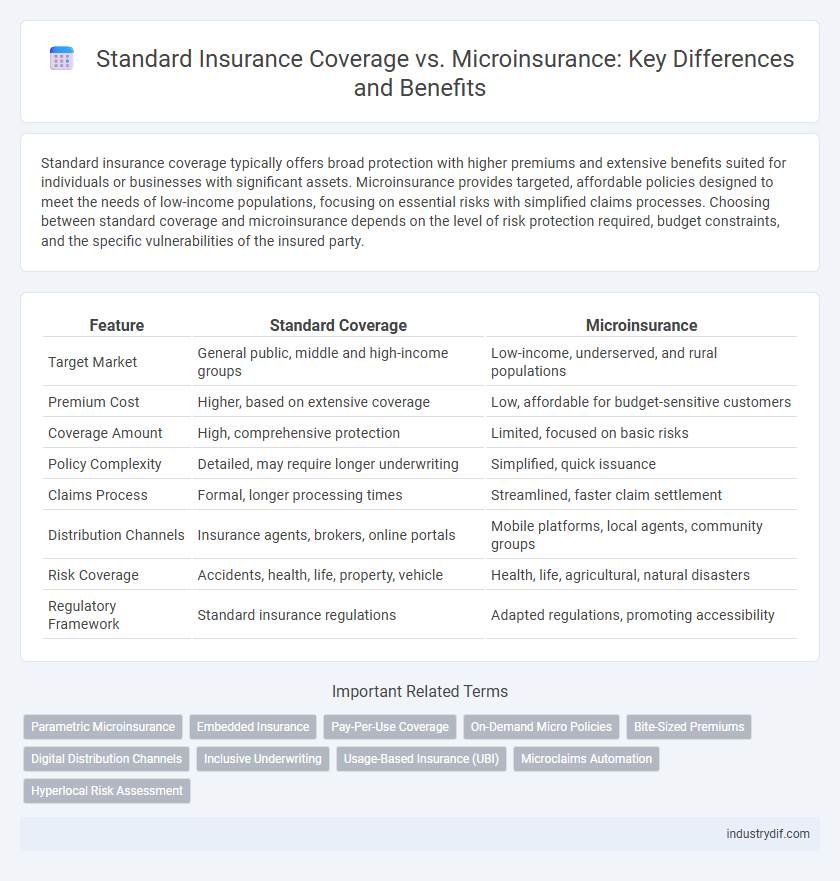
Standard insurance coverage typically offers broad protection with higher premiums and extensive benefits suited for individuals or businesses with significant assets. Microinsurance provides targeted, affordable policies designed to meet the needs of low-income populations, focusing on essential risks with simplified claims processes. Choosing between standard coverage and microinsurance depends on the level of risk protection required, budget constraints, and the specific vulnerabilities of the insured party.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Standard Coverage | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Target Market | General public, middle and high-income groups | Low-income, underserved, and rural populations |
| Premium Cost | Higher, based on extensive coverage | Low, affordable for budget-sensitive customers |
| Coverage Amount | High, comprehensive protection | Limited, focused on basic risks |
| Policy Complexity | Detailed, may require longer underwriting | Simplified, quick issuance |
| Claims Process | Formal, longer processing times | Streamlined, faster claim settlement |
| Distribution Channels | Insurance agents, brokers, online portals | Mobile platforms, local agents, community groups |
| Risk Coverage | Accidents, health, life, property, vehicle | Health, life, agricultural, natural disasters |
| Regulatory Framework | Standard insurance regulations | Adapted regulations, promoting accessibility |
Overview of Standard Coverage and Microinsurance
Standard coverage provides comprehensive protection with higher premiums and extensive policies typically designed for individuals or businesses seeking broad risk management. Microinsurance offers affordable, simplified insurance products targeting low-income or underserved populations, focusing on essential risks with lower coverage limits. Both serve crucial roles in risk mitigation but differ significantly in accessibility, cost, and coverage scope.
Key Differences Between Standard Coverage and Microinsurance
Standard coverage offers comprehensive protection with higher premiums and extensive benefits tailored for broader risk exposure, while microinsurance provides affordable, limited coverage designed for low-income individuals with specific, smaller-scale risks. Standard policies typically require detailed underwriting and offer longer-term contracts, whereas microinsurance features simplified enrollment processes and short-term coverage cycles to maximize accessibility. The key differences lie in target demographics, cost structures, coverage scope, and claim processing complexities.
Eligibility Criteria for Standard Coverage vs Microinsurance
Standard coverage typically requires comprehensive eligibility criteria, including proof of income, health assessments, and sometimes a minimum age limit to qualify, reflecting its broader risk assessment scope. Microinsurance offers simplified eligibility conditions, often targeting low-income individuals with minimal documentation and relaxed health requirements to ensure accessibility. The streamlined approval process in microinsurance makes it suitable for underserved populations lacking formal financial records.
Coverage Limits and Benefits
Standard coverage insurance typically offers higher coverage limits and more comprehensive benefits, making it suitable for individuals and businesses with significant risk exposure. Microinsurance provides lower coverage limits tailored to low-income populations, delivering essential benefits that address specific risks like health, crop, or property damage on a smaller financial scale. While standard coverage ensures broader protection through extensive policy options, microinsurance emphasizes affordability and accessibility, often involving simplified claims processes and limited benefit structures.
Premium Costs: Standard Coverage vs Microinsurance
Standard insurance coverage typically involves higher premium costs due to broader protection scopes and higher payout limits, making it suitable for extensive asset and risk management. Microinsurance offers significantly lower premiums by focusing on specific, low-cost risks, providing affordable coverage for low-income individuals or small businesses. This cost-efficient model enables wider access to insurance without compromising essential financial protection.
Application and Enrollment Process
Standard coverage typically requires extensive documentation, medical exams, and a lengthy underwriting process, making application and enrollment more complex and time-consuming. Microinsurance offers a simplified application, often through mobile platforms or community-based distribution, designed for quick enrollment with minimal paperwork. This streamlined process targets low-income populations, allowing broader access to essential insurance products with faster approval times.
Claims Process and Settlement Timelines
Standard coverage typically involves a comprehensive claims process with detailed documentation, often leading to longer settlement timelines that can span weeks or months. Microinsurance emphasizes simplified claims procedures designed for quick verification and minimal paperwork, enabling settlements to be processed within days. Faster turnaround in microinsurance supports low-income clients by providing timely financial relief while standard coverage prioritizes thorough risk assessment and coverage validation.
Target Customer Segments
Standard coverage primarily targets middle to upper-income individuals and businesses seeking comprehensive protection with higher premiums and extensive benefits. Microinsurance is designed for low-income populations, informal sector workers, and underserved communities, offering affordable, tailored policies with limited coverage. These distinct target segments reflect their differing risk appetites, financial capacities, and insurance accessibility needs.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance
Standard coverage insurance typically adheres to comprehensive regulatory frameworks that demand strict compliance with capital requirements, reporting standards, and consumer protection laws to ensure policyholder security. Microinsurance, designed for low-income populations, often operates under tailored regulatory provisions that emphasize simplified product structures, reduced premiums, and accessible claims processes while maintaining essential compliance to prevent exploitation. Regulatory bodies are increasingly adopting flexible approaches to balance consumer protection with market innovation in both insurance models.
Future Trends in Standard Coverage and Microinsurance
Future trends in standard coverage emphasize digital transformation, personalized policies, and integration of AI-driven risk assessments to enhance customer experience and underwriting accuracy. Microinsurance is projected to expand rapidly in emerging markets due to mobile technology penetration, providing affordable, tailored protection to low-income populations with streamlined claims processes. Both sectors are expected to leverage blockchain for transparency and efficiency, driving innovation and inclusivity in the insurance industry.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Microinsurance
Parametric microinsurance provides tailored, event-triggered payouts based on predefined parameters, offering faster claims processing and greater transparency compared to standard coverage's indemnity-based approach. This model enhances affordability and accessibility for low-income populations by minimizing administrative costs and reducing claim disputes through objective triggers like weather data or crop yield indices.
Embedded Insurance
Embedded insurance integrates standard coverage directly into product offerings, providing seamless protection without separate purchase processes. Microinsurance targets low-income clients with affordable, tailored policies, often embedded in everyday transactions to enhance accessibility and financial inclusion.
Pay-Per-Use Coverage
Pay-per-use coverage in microinsurance offers flexible, cost-effective protection by charging premiums based on actual usage or risk exposure, unlike standard coverage which typically involves fixed premiums regardless of usage. This model enhances affordability and accessibility for low-income individuals and those with irregular insurance needs, promoting broader financial inclusion.
On-Demand Micro Policies
On-demand micro policies offer flexible, low-cost insurance coverage tailored for short-term needs, contrasting with standard coverage that typically involves long-term, comprehensive plans with higher premiums. These microinsurance products leverage digital platforms to provide instant access and customizable protection, particularly benefiting underserved segments seeking affordable risk management solutions.
Bite-Sized Premiums
Standard coverage typically involves higher premiums and comprehensive protection, making it accessible primarily to those with stable incomes; microinsurance offers bite-sized premiums tailored for low-income individuals, providing essential coverage without financial strain. This model enhances affordability and inclusivity by allowing consumers to pay small, manageable amounts while still safeguarding against common risks.
Digital Distribution Channels
Standard coverage traditionally relies on agents and brokers, limiting accessibility, while microinsurance leverages digital distribution channels such as mobile apps and online platforms to reach underserved populations efficiently. Digital ecosystems enable microinsurance products to offer affordable, tailored policies with seamless enrollment and claims processing, expanding insurance penetration in emerging markets.
Inclusive Underwriting
Inclusive underwriting in microinsurance leverages simplified risk assessment and community-based data to extend coverage to underserved populations traditionally excluded by standard coverage criteria. This approach reduces barriers by accommodating lower premiums and flexible terms, thereby enhancing financial inclusion and protection for low-income or high-risk individuals.
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI)
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) leverages telematics and real-time data to provide personalized premiums based on individual driving behavior, distinguishing it from traditional Standard Coverage that relies on general risk categories. Microinsurance offers affordable, targeted UBI policies designed for low-income or niche markets, increasing accessibility and tailored risk management.
Microclaims Automation
Microclaims automation streamlines claims processing in microinsurance by leveraging AI and mobile technology to quickly verify and settle small-value claims, reducing operational costs and enhancing customer satisfaction. This contrasts with standard coverage, where claims often require manual assessment and longer turnaround times due to higher claim complexity and larger claim amounts.
Hyperlocal Risk Assessment
Standard coverage often relies on broad risk models that may overlook hyperlocal factors, while microinsurance integrates granular data for precise hyperlocal risk assessment. This approach enables tailored policies that address specific community vulnerabilities, enhancing protection and affordability in localized markets.
Standard Coverage vs Microinsurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com