Premium pricing involves paying a fixed amount based on risk assessments and coverage levels, providing predictable costs regardless of actual usage. Usage-based pricing adjusts premiums according to real-time data, such as mileage or driving behavior, offering personalized rates that reward safe practices. Choosing between these models depends on individual preferences for cost stability or potential savings tied to usage patterns.
Table of Comparison
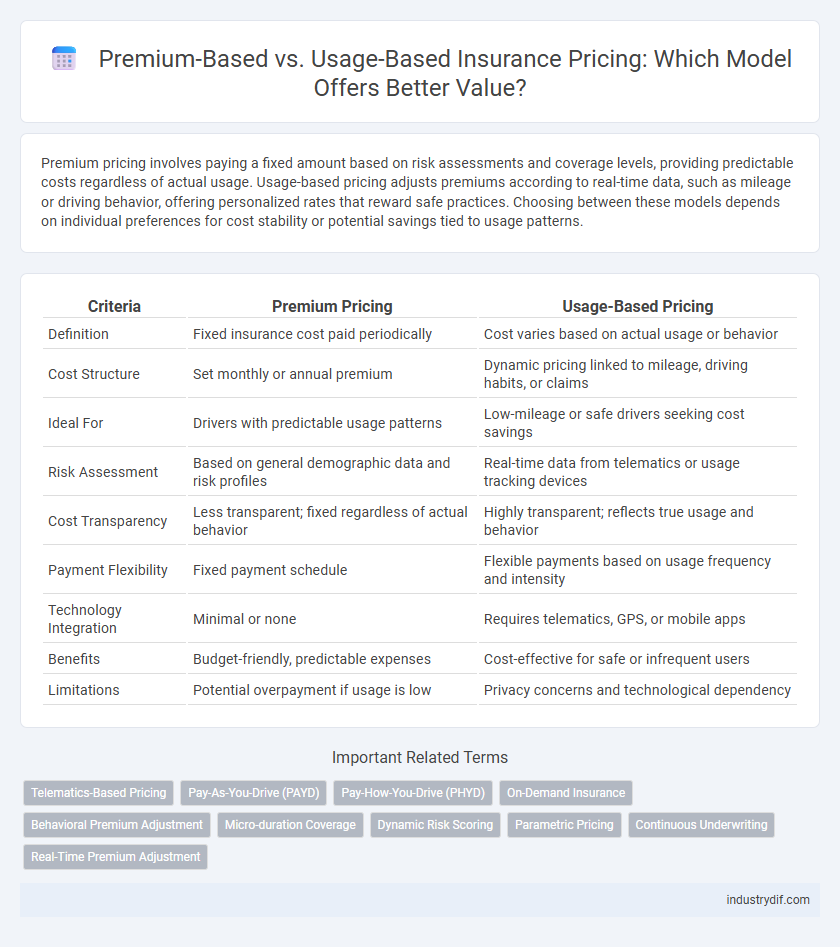
| Criteria | Premium Pricing | Usage-Based Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed insurance cost paid periodically | Cost varies based on actual usage or behavior |
| Cost Structure | Set monthly or annual premium | Dynamic pricing linked to mileage, driving habits, or claims |
| Ideal For | Drivers with predictable usage patterns | Low-mileage or safe drivers seeking cost savings |
| Risk Assessment | Based on general demographic data and risk profiles | Real-time data from telematics or usage tracking devices |
| Cost Transparency | Less transparent; fixed regardless of actual behavior | Highly transparent; reflects true usage and behavior |
| Payment Flexibility | Fixed payment schedule | Flexible payments based on usage frequency and intensity |
| Technology Integration | Minimal or none | Requires telematics, GPS, or mobile apps |
| Benefits | Budget-friendly, predictable expenses | Cost-effective for safe or infrequent users |
| Limitations | Potential overpayment if usage is low | Privacy concerns and technological dependency |
Introduction to Insurance Pricing Models
Insurance pricing models primarily include traditional premium-based and modern usage-based approaches, each leveraging distinct risk assessment techniques. Premium-based pricing calculates fixed payments based on factors like age, location, and historical claims, while usage-based pricing utilizes telematics data to adjust costs according to actual driving behavior. Usage-based insurance enables more personalized risk evaluation, promoting cost savings and incentivizing safer habits.
Defining Premium-Based Pricing
Premium-based pricing in insurance refers to a fixed cost model where policyholders pay a predetermined amount regularly, typically monthly or annually, regardless of actual usage or risk fluctuations. This pricing structure relies heavily on actuarial data, underwriting assessments, and risk factors such as age, location, and driving history to calculate the premium. By providing predictable costs, premium-based pricing offers financial stability for both insurers and insureds while incentivizing risk mitigation through policy adjustments.
Understanding Usage-Based Pricing
Usage-based pricing in insurance calculates premiums based on real-time driving behavior and actual vehicle usage, leveraging telematics technology to monitor factors like mileage, speed, and braking patterns. This model provides more personalized risk assessment compared to traditional flat-rate premiums, aligning costs with individual driving habits. Data collected through usage-based pricing enables insurers to offer dynamic discounts and incentivize safer driving, enhancing both cost efficiency and risk management.
Key Differences Between Premium and Usage-Based Pricing
Premium pricing sets a fixed insurance cost based on risk factors such as age, location, and claims history, providing predictability in monthly payments. Usage-based pricing calculates costs dynamically using real-time data like mileage, driving behavior, or device tracking, often rewarding low-risk behavior with discounts. Key differences include pricing transparency, cost flexibility, and the degree to which individual risk directly influences the insured's premium.
Factors Influencing Premium-Based Models
Premium-based insurance models are influenced by factors such as the insured individual's age, driving history, credit score, and type of coverage selected, which collectively determine the fixed payment amount. Actuarial data and risk assessments play a crucial role in setting premiums, as insurers evaluate statistical probabilities of claims to balance profitability and competitiveness. Geographic location and vehicle characteristics further refine premium calculations by accounting for regional risk exposure and asset value.
Technologies Enabling Usage-Based Insurance
Telematics devices, GPS tracking, and mobile apps are core technologies enabling usage-based insurance (UBI) by collecting real-time driving data such as speed, distance, and driving behavior. Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms process this data to personalize premiums based on actual risk exposure rather than traditional factors. Connected cars and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors further enhance data accuracy and enable insurers to offer dynamic, behavior-driven pricing models that improve risk assessment and customer engagement.
Pros and Cons of Premium Pricing
Premium pricing in insurance offers the advantage of predictable revenue streams and simplified billing for both insurers and policyholders, fostering financial stability. However, it may lead to higher costs for low-risk customers who end up subsidizing higher-risk individuals, potentially reducing market competitiveness. Fixed premiums can also discourage usage efficiency and fail to incentivize risk-reducing behaviors among insured clients.
Pros and Cons of Usage-Based Pricing
Usage-based pricing in insurance offers personalized premiums by leveraging telematics data, promoting fairer rates for low-mileage and safe drivers while encouraging responsible behavior. This model can reduce costs for cautious customers but may raise privacy concerns and increase complexity in policy management. Insurers face challenges in data accuracy and customer acceptance, yet benefit from enhanced risk assessment and potential fraud detection.
Regulatory Considerations in Insurance Pricing
Regulatory considerations in insurance pricing emphasize the balance between premium and usage-based pricing to prevent discrimination and ensure fairness. Regulators often require transparent methodologies and compliance with anti-discrimination laws, impacting how insurers design usage-based models. Data privacy and consumer consent remain critical concerns, influencing regulatory frameworks that govern the collection and utilization of telematics data in usage-based insurance.
Future Trends in Insurance Pricing Strategies
Future trends in insurance pricing strategies are shifting towards usage-based pricing models powered by telematics and IoT devices, enabling personalized risk assessment and real-time premium adjustments. Traditional premium pricing relies on historical data and broad risk categories, while usage-based insurance offers dynamic pricing that reflects individual driving behavior and lifestyle choices. This evolution enhances customer engagement, improves risk prediction accuracy, and encourages safer behavior among policyholders.
Related Important Terms
Telematics-Based Pricing
Telematics-based pricing leverages real-time driving data, such as speed, braking patterns, and mileage, to tailor insurance premiums more accurately to individual risk profiles. This usage-based pricing model enhances fairness and encourages safer driving by directly linking premium costs to actual behavior rather than traditional demographic factors.
Pay-As-You-Drive (PAYD)
Pay-As-You-Drive (PAYD) insurance offers a usage-based pricing model that calculates premiums based on actual miles driven, promoting fair costs and rewarding low-mileage policyholders with lower premiums. This approach leverages telematics data to enhance risk assessment accuracy and incentivize safer, more economical driving habits.
Pay-How-You-Drive (PHYD)
Pay-How-You-Drive (PHYD) insurance leverages telematics technology to monitor individual driving behaviors such as speed, braking patterns, and mileage, allowing insurers to tailor premiums based on real-time risk assessments. This usage-based pricing model incentivizes safer driving habits while offering policyholders potentially lower premiums compared to traditional fixed-rate insurance plans.
On-Demand Insurance
On-demand insurance leverages usage-based pricing models by charging premiums directly aligned with real-time risk exposure and actual usage patterns, offering customers flexibility and cost-efficiency. This dynamic pricing method contrasts with traditional fixed premiums by providing personalized rates that adjust according to specific behaviors and needs.
Behavioral Premium Adjustment
Behavioral premium adjustment in insurance leverages telematics and driving data to tailor premiums based on individual driving habits, rewarding safer drivers with lower costs. Usage-based pricing enhances risk assessment accuracy, promoting fairness by aligning policyholder premiums directly with real-world behavior and mileage.
Micro-duration Coverage
Micro-duration coverage in insurance offers precise protection for brief periods, enhancing flexibility compared to traditional premium models which rely on fixed, longer-term payments. Usage-based pricing leverages telematics data to adjust costs dynamically, ensuring premiums align closely with actual risk exposure during short coverage intervals.
Dynamic Risk Scoring
Dynamic risk scoring in insurance leverages real-time data from telematics and IoT devices to continuously update premium calculations based on individual driving behavior and risk exposure. This usage-based pricing model enhances pricing accuracy by reflecting actual risk patterns, enabling insurers to offer personalized premiums that incentivize safer habits while improving risk assessment efficiency.
Parametric Pricing
Parametric pricing in insurance sets premiums based on predefined parameters or triggers, such as weather events or flight delays, enabling quicker claim payouts without traditional loss assessments. This model contrasts with usage-based pricing, which calculates premiums according to individual behavior metrics like driving distance or speed, offering more personalized but data-intensive risk evaluation.
Continuous Underwriting
Continuous underwriting enables insurers to adjust premiums dynamically based on real-time risk assessments, enhancing accuracy compared to traditional fixed premium models. Usage-based pricing leverages telematics and data analytics for continuous monitoring, allowing personalized rates that better reflect individual driving behaviors and risk factors.
Real-Time Premium Adjustment
Real-time premium adjustment in usage-based insurance leverages telematics data to dynamically modify policy costs based on actual driving behaviors, enhancing pricing accuracy and fairness. This approach contrasts with traditional fixed premiums by rewarding safer driving trends immediately, reducing risk exposure for insurers and offering cost savings for policyholders.
Premium vs Usage-Based Pricing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com