Annual premiums typically require a larger upfront payment, providing comprehensive coverage tailored to long-term needs, whereas microinsurance offers affordable, smaller-scale policies aimed at low-income individuals or short-term protection. Microinsurance often focuses on essential risks such as health, crop, or life insurance, making it accessible to those with limited financial resources. Choosing between annual premium plans and microinsurance depends on balancing coverage depth with budget constraints and risk exposure.
Table of Comparison
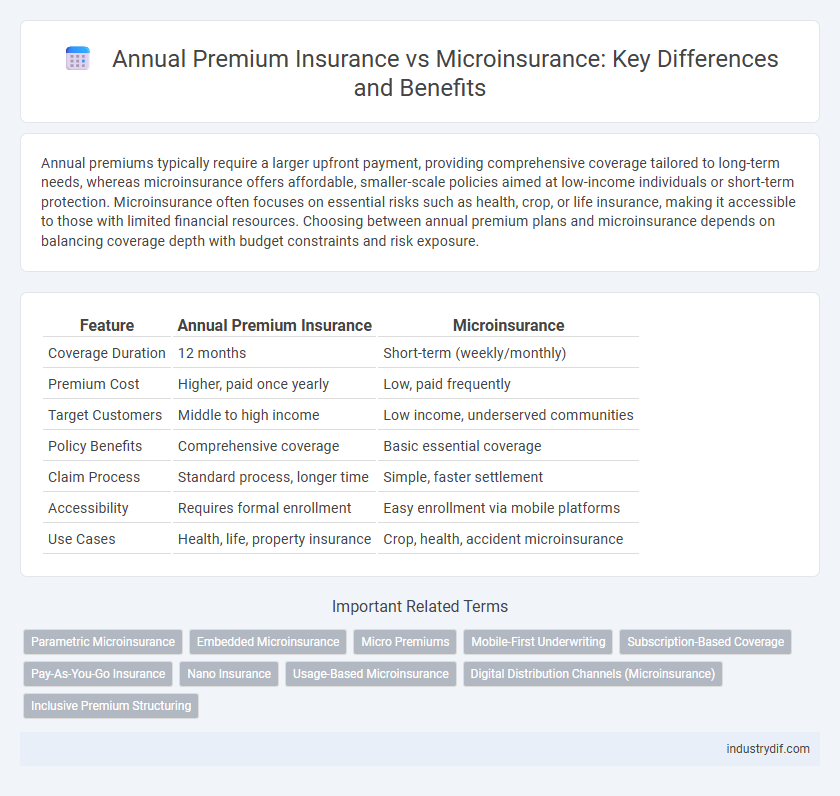
| Feature | Annual Premium Insurance | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Duration | 12 months | Short-term (weekly/monthly) |
| Premium Cost | Higher, paid once yearly | Low, paid frequently |
| Target Customers | Middle to high income | Low income, underserved communities |
| Policy Benefits | Comprehensive coverage | Basic essential coverage |
| Claim Process | Standard process, longer time | Simple, faster settlement |
| Accessibility | Requires formal enrollment | Easy enrollment via mobile platforms |
| Use Cases | Health, life, property insurance | Crop, health, accident microinsurance |
Annual Premium: Definition and Key Features
Annual premium refers to the total amount an insured person pays once a year to maintain an insurance policy, covering risks such as health, auto, or life insurance. Key features of annual premium include fixed payment intervals, premium stability, and comprehensive coverage options for longer policy terms. This payment structure often offers discounts compared to monthly payments and simplifies budgeting for policyholders.
What is Microinsurance?
Microinsurance is a type of insurance designed specifically to meet the needs and budgets of low-income individuals, offering affordable coverage for health, life, property, and agriculture risks. It typically features lower premiums and smaller coverage limits compared to traditional annual premium insurance, making it accessible for vulnerable populations. Microinsurance products often emphasize simplicity, quick claims processing, and minimal paperwork to ensure inclusivity and financial protection for underserved communities.
Coverage Scope: Annual Premium vs Microinsurance
Annual premium insurance typically offers extensive coverage scopes, including comprehensive protection for health, property, or life with higher coverage limits and broader risk inclusion. Microinsurance, designed for low-income individuals, provides limited coverage focused on specific risks like health emergencies or crop damage with affordable premiums and simplified terms. The narrower coverage scope of microinsurance caters to immediate, essential needs, contrasting with the wide-ranging protections available through annual premium policies.
Target Markets and Customer Segments
Annual premium insurance targets middle to high-income individuals and businesses seeking comprehensive coverage with higher policy limits and long-term protection. Microinsurance serves low-income populations, informal workers, and underserved communities by offering affordable, flexible, and simplified insurance plans tailored to limited financial capacity and specific local risks. Both models address distinct customer segments, optimizing coverage accessibility based on economic status and insurance awareness levels.
Cost Comparison: Affordability and Premium Structures
Annual premiums typically involve higher, fixed payments suited for extensive coverage, while microinsurance offers lower, flexible premiums tailored to individuals with limited income. Microinsurance structures emphasize affordability and accessibility, making it a viable option in emerging markets where traditional insurance premiums may be prohibitive. Cost comparison reveals microinsurance's strategic role in expanding financial protection by aligning premium costs with the economic capacity of low-income populations.
Claims Process: Speed and Simplicity
Microinsurance offers a streamlined claims process with faster approvals and minimal documentation compared to traditional annual premium policies, enhancing customer satisfaction. Annual premium insurance often involves more complex procedures and longer waiting times due to detailed verification and higher claim amounts. Simplified claim settlements in microinsurance increase accessibility for low-income populations, promoting financial inclusion and trust in insurance services.
Product Flexibility and Customization
Annual premium insurance policies offer limited flexibility due to fixed coverage terms and higher cost commitments, making them less adaptable to changing customer needs. Microinsurance provides customizable, affordable coverage with flexible payment frequencies and benefit options tailored to low-income or niche markets. This flexibility in microinsurance enhances accessibility and meets diverse risk profiles more effectively than traditional annual premium plans.
Regulatory Considerations in Insurance Types
Regulatory considerations in insurance types significantly impact annual premium policies and microinsurance products, ensuring consumer protection and market stability. Annual premium insurance often faces stringent regulatory frameworks involving solvency margins and detailed disclosures, while microinsurance regulations prioritize accessibility, simplified claims processes, and affordability to serve low-income populations effectively. Compliance with these tailored regulatory standards fosters trust, enhances financial inclusion, and mitigates risks in both traditional and emerging insurance markets.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Model
Annual premium insurance offers comprehensive coverage with higher policy limits and broader benefits, ideal for individuals seeking extensive protection and long-term financial security. Microinsurance provides affordable, targeted coverage designed for low-income populations or specific risks, enabling access to essential protection with minimal financial burden. While annual premiums may involve higher costs and less flexibility, microinsurance often limits coverage scope and sums insured, making it suitable primarily for basic risk mitigation.
Choosing Between Annual Premium and Microinsurance
Choosing between annual premium insurance and microinsurance depends on individual financial capacity and coverage needs, where annual premium plans offer comprehensive protection through larger, less frequent payments, while microinsurance provides affordable, smaller premiums designed for low-income groups with basic coverage. Microinsurance is ideal for those seeking flexible, accessible policies that address immediate risks without long-term financial commitment. Evaluating risk exposure and budget constraints helps determine the optimal insurance product for effective financial security.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Microinsurance
Parametric microinsurance offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional annual premiums by providing instant payouts based on predefined triggers such as weather events or natural disasters, reducing claim processing time and administrative expenses for low-income populations. This innovative model enhances financial inclusion by delivering transparent, affordable, and rapid insurance coverage tailored to specific risks, unlike conventional policies with fixed annual premiums and lengthy claim settlements.
Embedded Microinsurance
Embedded microinsurance integrates affordable, customizable coverage within everyday products and services, offering a streamlined alternative to traditional annual premium policies. This approach enhances accessibility and financial inclusion by providing targeted protection with lower upfront costs compared to conventional insurance models.
Micro Premiums
Microinsurance offers significantly lower annual premiums compared to traditional insurance, making coverage accessible to low-income individuals and small businesses. These micro premiums are tailored to fit limited budgets, ensuring financial protection without the burden of high recurring costs.
Mobile-First Underwriting
Mobile-first underwriting transforms annual premium insurance by enabling faster, data-driven risk assessments through smartphone technology, reducing processing time and enhancing customer accessibility. Microinsurance leverages this approach to deliver affordable, tailored coverage with incremental premiums, expanding protection to underserved populations via digital platforms.
Subscription-Based Coverage
Subscription-based coverage in microinsurance offers flexible, affordable premiums tailored to low-income individuals, contrasting with traditional annual premium models that require lump-sum payments. This approach increases accessibility and continuous protection for underserved populations by allowing incremental payments aligned with fluctuating income streams.
Pay-As-You-Go Insurance
Annual premium insurance requires a lump-sum payment for comprehensive coverage, often posing affordability challenges for low-income individuals. Pay-as-you-go microinsurance offers flexible, usage-based premiums, enhancing financial accessibility while providing essential protection tailored to varying risk exposures.
Nano Insurance
Nano insurance offers ultra-affordable coverage with premiums often below one dollar annually, making it accessible for low-income individuals and micro-entrepreneurs. Unlike traditional annual premiums that require substantial upfront payments, nano insurance provides targeted, short-term protection tailored for specific risks, enhancing financial inclusion in underserved markets.
Usage-Based Microinsurance
Annual premium insurance typically requires a fixed payment regardless of usage patterns, whereas usage-based microinsurance offers flexible, pay-as-you-go coverage tailored to individual risk behaviors and short-term needs. This model leverages telematics and mobile technology to provide affordable, on-demand protection, especially benefiting low-income or underserved populations by aligning cost with actual usage and risk exposure.
Digital Distribution Channels (Microinsurance)
Digital distribution channels for microinsurance leverage mobile apps, SMS, and online platforms to offer low-cost, accessible coverage tailored to underserved populations with annual premiums significantly lower than traditional insurance policies. These technology-driven channels streamline enrollment, claims processing, and customer service, enhancing affordability and convenience while expanding market reach in developing regions.
Inclusive Premium Structuring
Inclusive premium structuring in insurance integrates traditional annual premiums with microinsurance to enhance affordability and accessibility for low-income populations. This approach tailors payment schedules and coverage options, increasing protection while addressing financial constraints and promoting widespread insurance adoption.
Annual Premium vs Microinsurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com