Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing minimizes inventory by producing goods only as needed, reducing waste and lowering storage costs. Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing enhances flexibility by continuously adjusting production schedules based on real-time market demand and supply chain conditions. This adaptive approach improves responsiveness to customer needs and mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
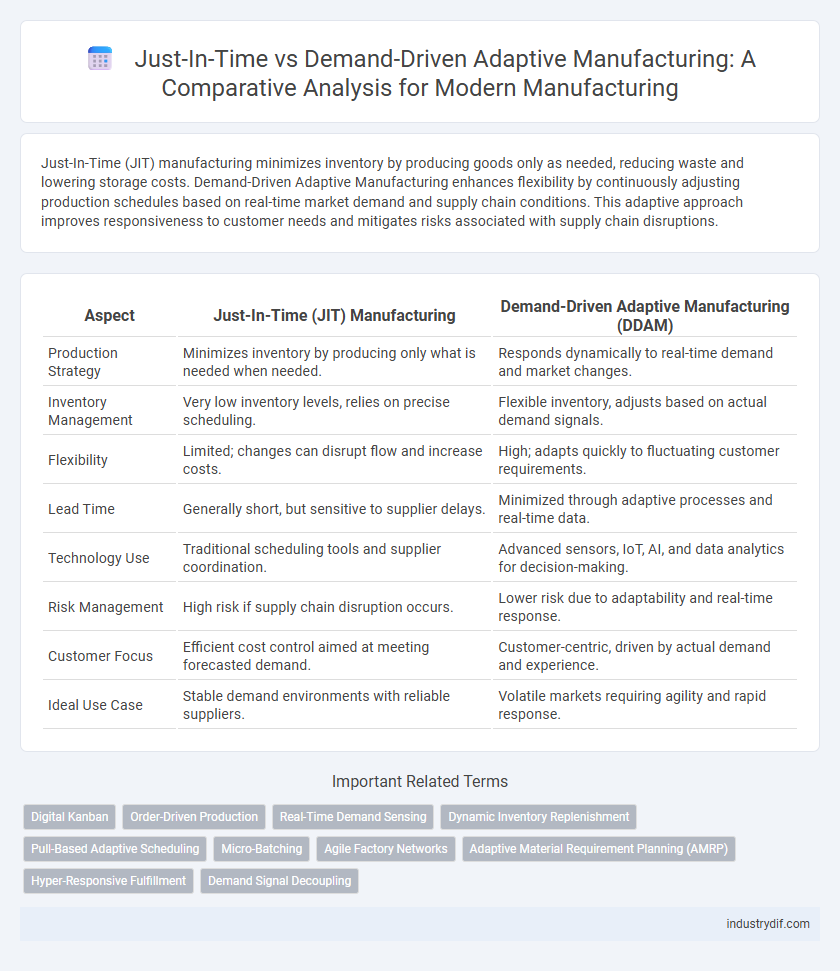
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Just-In-Time (JIT) Manufacturing | Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing (DDAM) |
|---|---|---|
| Production Strategy | Minimizes inventory by producing only what is needed when needed. | Responds dynamically to real-time demand and market changes. |
| Inventory Management | Very low inventory levels, relies on precise scheduling. | Flexible inventory, adjusts based on actual demand signals. |
| Flexibility | Limited; changes can disrupt flow and increase costs. | High; adapts quickly to fluctuating customer requirements. |
| Lead Time | Generally short, but sensitive to supplier delays. | Minimized through adaptive processes and real-time data. |
| Technology Use | Traditional scheduling tools and supplier coordination. | Advanced sensors, IoT, AI, and data analytics for decision-making. |
| Risk Management | High risk if supply chain disruption occurs. | Lower risk due to adaptability and real-time response. |
| Customer Focus | Efficient cost control aimed at meeting forecasted demand. | Customer-centric, driven by actual demand and experience. |
| Ideal Use Case | Stable demand environments with reliable suppliers. | Volatile markets requiring agility and rapid response. |
Introduction to Just-In-Time and Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing
Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing minimizes inventory by synchronizing production schedules with demand, reducing waste and improving efficiency. Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing (DDAM) integrates real-time data and flexible processes to dynamically adjust production in response to fluctuating market needs. Both approaches aim to optimize resource use, but DDAM offers enhanced responsiveness and agility through advanced analytics and automation.
Core Principles of Just-In-Time Manufacturing
Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing centers on minimizing inventory and reducing waste by producing items only as they are needed, guided by precise demand signals. Its core principles include continuous flow, pull production, and waste elimination, which collectively streamline operations and improve efficiency. JIT relies heavily on strong supplier relationships and accurate forecasting to synchronize production with actual customer demand.
Fundamentals of Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing
Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing (DDAM) prioritizes real-time demand signals to optimize production schedules, minimizing inventory and enhancing responsiveness compared to traditional Just-In-Time (JIT) methods. DDAM integrates advanced data analytics, IoT sensors, and AI-driven algorithms to dynamically adjust workflows, ensuring alignment with actual customer demand rather than forecast-based schedules. This approach reduces lead times, lowers operational costs, and improves supply chain agility by enabling seamless adaptation to market fluctuations.
Inventory Management: JIT vs Demand-Driven Approaches
Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory management minimizes stock levels by synchronizing production schedules with supplier deliveries, reducing holding costs but risking supply chain disruptions. Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing leverages real-time data and flexible workflows to adjust inventory dynamically, enhancing responsiveness to market fluctuations and lowering the risk of stockouts or excess inventory. This approach improves supply chain resilience and aligns production closely with actual customer demand patterns.
Flexibility and Responsiveness to Market Changes
Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing emphasizes inventory reduction and streamlined production schedules but often lacks flexibility when sudden market shifts occur. Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing leverages real-time data and advanced analytics to rapidly adjust production volumes and product variants, enhancing responsiveness to dynamic customer demands. This approach improves operational agility, minimizing lead times and reducing the risk of stockouts or overproduction in volatile markets.
Technology Integration in Adaptive Manufacturing
Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing leverages advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and real-time data integration to optimize production processes and respond dynamically to market fluctuations. Unlike traditional Just-In-Time methods, which rely on fixed schedules and forecasts, adaptive manufacturing systems continuously adjust operations based on live demand signals, minimizing waste and enhancing efficiency. This technology integration enables seamless communication across supply chains, ensuring agility and robustness in production workflows.
Benefits and Risks of Just-In-Time Systems
Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing minimizes inventory costs by synchronizing production schedules closely with demand, reducing waste and improving cash flow. However, JIT systems face risks such as supply chain disruptions, which can halt production due to minimal inventory buffers. This approach requires highly reliable suppliers and precise demand forecasting to maintain operational efficiency and avoid costly delays.
Scalability and Customization in Demand-Driven Manufacturing
Demand-driven adaptive manufacturing excels in scalability by dynamically adjusting production volumes in real-time based on fluctuating customer demand patterns. This approach enhances customization capabilities, allowing manufacturers to produce highly tailored products without compromising efficiency or increasing lead times. Unlike traditional Just-In-Time systems, demand-driven manufacturing leverages advanced data analytics and flexible automation to seamlessly scale operations and meet diverse consumer requirements with precision.
Impact on Supply Chain Resilience
Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing minimizes inventory costs by aligning production closely with demand but increases vulnerability to disruptions due to limited buffer stock. Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing enhances supply chain resilience by integrating real-time demand signals and flexibility, enabling rapid response to fluctuations and unforeseen events. This adaptive approach reduces lead times and mitigates risks associated with supplier delays and market volatility more effectively than traditional JIT systems.
Future Trends in Manufacturing Strategies
Future manufacturing trends highlight a shift from traditional Just-In-Time (JIT) systems to Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing (DDAM), emphasizing real-time data integration and enhanced supply chain responsiveness. DDAM leverages advanced AI, IoT, and machine learning to dynamically adjust production schedules based on fluctuating market demand and supply conditions. This strategy reduces inventory costs, mitigates risks of supply chain disruptions, and supports greater customization and scalability in manufacturing processes.
Related Important Terms
Digital Kanban
Digital Kanban revolutionizes Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing by enabling real-time inventory control and minimizing waste through dynamic signal-based replenishment. Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing leverages Digital Kanban to enhance responsiveness and flexibility, aligning production schedules closely with actual customer demand and reducing lead times effectively.
Order-Driven Production
Order-Driven Production in Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing emphasizes minimizing inventory by producing goods strictly based on confirmed customer orders, reducing waste and lead times. Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing enhances this by incorporating real-time demand signals and predictive analytics, enabling dynamic adjustment of production schedules to meet fluctuating customer needs more efficiently.
Real-Time Demand Sensing
Real-time demand sensing in demand-driven adaptive manufacturing uses advanced analytics and IoT data to continuously monitor customer demand, enabling immediate production adjustments and reducing inventory costs. In contrast, Just-In-Time relies on predefined schedules and forecasts, which can lead to delays and stockouts when unexpected demand fluctuations occur.
Dynamic Inventory Replenishment
Dynamic inventory replenishment in Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing outperforms traditional Just-In-Time systems by continuously adjusting stock levels based on real-time demand signals and supply chain disruptions. This approach minimizes inventory holding costs and reduces stockouts, enhancing overall operational efficiency and responsiveness in manufacturing processes.
Pull-Based Adaptive Scheduling
Pull-based adaptive scheduling in demand-driven adaptive manufacturing dynamically adjusts production workflows based on real-time customer demand signals, minimizing inventory costs and reducing lead times compared to traditional just-in-time systems that rely on forecast-based supply triggers. Integrating IoT sensors and AI algorithms enables enhanced responsiveness and flexibility, allowing manufacturers to optimize resource allocation and swiftly adapt to market fluctuations.
Micro-Batching
Micro-batching in Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing minimizes inventory by synchronizing production with demand but can lead to inefficiencies under volatile market conditions. Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing leverages micro-batching with real-time data analytics to dynamically adjust batch sizes, enhancing responsiveness and reducing waste.
Agile Factory Networks
Agile factory networks enable demand-driven adaptive manufacturing by dynamically reallocating production resources across multiple sites, reducing lead times and minimizing inventory costs compared to traditional just-in-time systems. This decentralized approach enhances responsiveness to market fluctuations through real-time data integration, optimizing supply chain efficiency and boosting overall manufacturing agility.
Adaptive Material Requirement Planning (AMRP)
Adaptive Material Requirement Planning (AMRP) in Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing leverages real-time data and predictive analytics to dynamically adjust inventory levels, contrasting with the static schedules of traditional Just-In-Time (JIT) systems. By responding fluidly to actual demand fluctuations, AMRP minimizes stockouts and excess inventory, enhancing production efficiency and reducing lead times across manufacturing supply chains.
Hyper-Responsive Fulfillment
Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing minimizes inventory by synchronizing production with demand, but Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing (DDAM) enhances hyper-responsive fulfillment through real-time data integration and flexible supply chains, enabling rapid adjustments to market fluctuations. DDAM leverages advanced analytics and IoT technologies to optimize resource allocation, reduce lead times, and improve customer satisfaction by responding instantly to changing consumer demands.
Demand Signal Decoupling
Demand Signal Decoupling in Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing isolates the true customer demand from production processes, enabling real-time responsiveness and reducing inventory waste compared to traditional Just-In-Time systems. This approach enhances supply chain agility by synchronizing manufacturing with actual market demand signals, improving delivery performance and minimizing stockouts.
Just-In-Time vs Demand-Driven Adaptive Manufacturing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com