Industrial automation integrates programmable machines and control systems to streamline manufacturing processes, boosting efficiency and consistency. Lights-out manufacturing takes automation further by enabling fully unmanned production facilities that operate continuously without human intervention. This approach reduces labor costs and minimizes errors, driving higher productivity and operational savings.
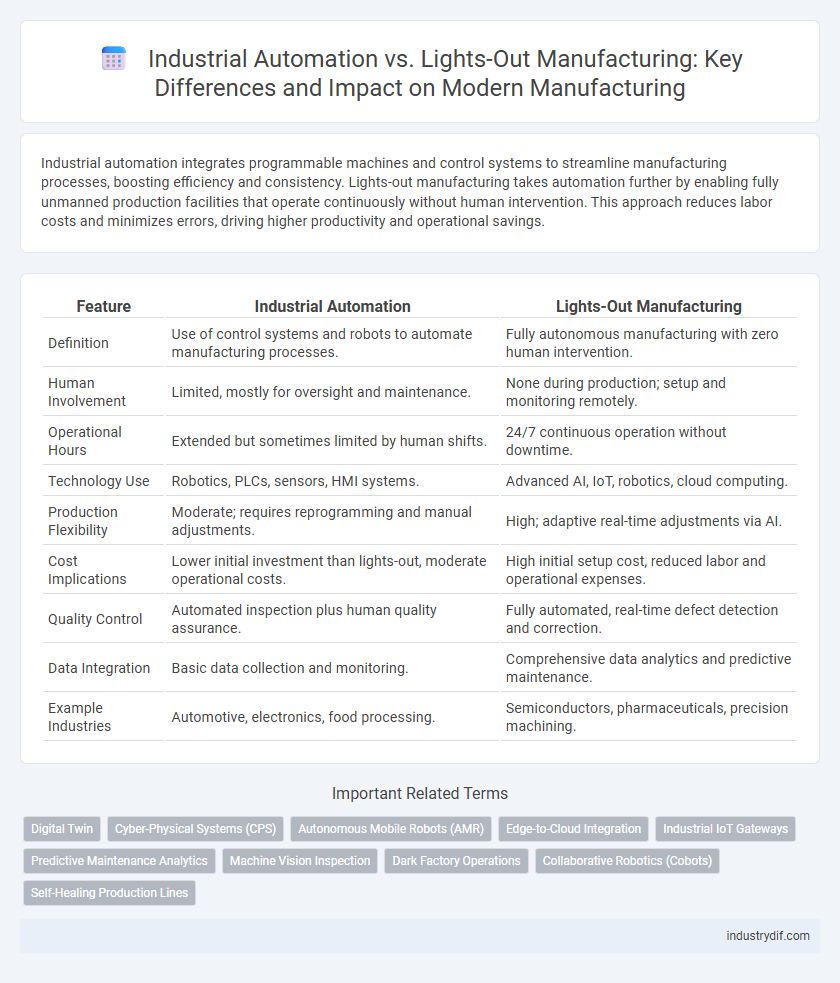
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Industrial Automation | Lights-Out Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of control systems and robots to automate manufacturing processes. | Fully autonomous manufacturing with zero human intervention. |
| Human Involvement | Limited, mostly for oversight and maintenance. | None during production; setup and monitoring remotely. |
| Operational Hours | Extended but sometimes limited by human shifts. | 24/7 continuous operation without downtime. |
| Technology Use | Robotics, PLCs, sensors, HMI systems. | Advanced AI, IoT, robotics, cloud computing. |
| Production Flexibility | Moderate; requires reprogramming and manual adjustments. | High; adaptive real-time adjustments via AI. |
| Cost Implications | Lower initial investment than lights-out, moderate operational costs. | High initial setup cost, reduced labor and operational expenses. |
| Quality Control | Automated inspection plus human quality assurance. | Fully automated, real-time defect detection and correction. |
| Data Integration | Basic data collection and monitoring. | Comprehensive data analytics and predictive maintenance. |
| Example Industries | Automotive, electronics, food processing. | Semiconductors, pharmaceuticals, precision machining. |
Understanding Industrial Automation: Key Concepts
Industrial automation involves the use of control systems, such as robots and computer software, to perform manufacturing processes with minimal human intervention. Key concepts include Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs), and sensors that enable real-time monitoring and precise control of machinery. Lights-out manufacturing extends automation by operating facilities entirely without human presence, relying heavily on advanced robotics and autonomous systems for increased efficiency and reduced labor costs.
Defining Lights-Out Manufacturing
Lights-out manufacturing refers to fully automated production processes that operate without human intervention, leveraging robotics, AI, and advanced control systems to optimize efficiency and precision. Unlike standard industrial automation, which may require human oversight for certain tasks, lights-out manufacturing runs continuously in a dark facility, minimizing labor costs and errors. This approach enhances scalability, improves quality consistency, and accelerates production cycles by eliminating manual operations.
Historical Evolution of Automation in Manufacturing
The historical evolution of automation in manufacturing began with mechanization through simple machines in the Industrial Revolution, progressively advancing to industrial automation characterized by programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and robotics in the 20th century. More recently, lights-out manufacturing has emerged as a fully autonomous system operating without human intervention, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, sensors, and real-time data analytics. This paradigm shift reflects a move from semi-automated processes to smart factories emphasizing efficiency, precision, and continuous production.
Core Technologies Driving Industrial Automation
Core technologies driving industrial automation include programmable logic controllers (PLCs), robotics, and advanced sensors that enable real-time data collection and process control. In contrast, lights-out manufacturing builds on these by integrating artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT connectivity to achieve fully autonomous, unattended operations. The synergy of these technologies enhances efficiency, precision, and scalability in modern manufacturing environments.
Lights-Out Manufacturing: Essential Components
Lights-Out Manufacturing relies on fully automated systems, including robotics, sensors, and advanced control software, to operate without human intervention. Key components such as IoT-enabled devices ensure real-time monitoring and data collection, optimizing production efficiency and minimizing downtime. Integration of AI-driven predictive maintenance and adaptive control systems enhances precision and reliability in a lights-out manufacturing environment.
Workforce Implications: Human Roles vs Full Automation
Industrial automation integrates human oversight with mechanized processes, enhancing productivity while maintaining workforce roles in monitoring and decision-making. Lights-out manufacturing eliminates manual intervention entirely, relying on fully autonomous systems to maximize operational efficiency and reduce labor costs. Workforce implications shift from hands-on tasks to advanced skills in system management, maintenance, and programming in these automated environments.
Operational Efficiency: Comparing Productivity Gains
Industrial automation enhances operational efficiency by integrating robotics and control systems to streamline repetitive tasks, reducing human error and increasing throughput. Lights-out manufacturing further amplifies productivity gains through fully autonomous processes that operate without human intervention, enabling continuous 24/7 production. Data shows lights-out facilities achieve up to 30% higher output and 25% lower operational costs compared to conventional industrial automation setups.
Capital Investment and Cost Considerations
Industrial automation requires substantial capital investment in machinery, robotics, and control systems to enhance production efficiency and consistency. Lights-out manufacturing, characterized by fully autonomous operations without human intervention, demands even higher upfront costs for advanced AI, sensor networks, and maintenance infrastructure. Cost considerations for lights-out manufacturing also include long-term savings from reduced labor expenses and minimized downtime, making it a viable strategy for high-volume, continuous production environments.
Scalability and Flexibility in Manufacturing Systems
Industrial automation enhances manufacturing scalability by integrating programmable machinery that adapts to varying production volumes with ease, ensuring consistent output quality. Lights-out manufacturing takes scalability further by enabling fully autonomous, 24/7 operations without human intervention, ideal for high-volume, repetitive tasks. Flexibility in industrial automation allows for quick reprogramming and equipment adjustments, while lights-out systems require advanced AI-driven adaptability to respond dynamically to changing product designs and demand fluctuations.
Future Trends: The Convergence of Automation and Lights-Out Facilities
Industrial automation increasingly integrates AI-driven robotics and IoT-enabled systems, enhancing precision and operational efficiency in manufacturing processes. Lights-out manufacturing facilities leverage fully autonomous machines and advanced sensors to enable continuous, unmanned production environments. Future trends indicate a convergence where smart factories combine automated workflows with lights-out capabilities, driving unprecedented productivity, reduced human intervention, and real-time data analytics for predictive maintenance.
Related Important Terms
Digital Twin
Industrial automation integrates sensors, robotics, and control systems to streamline manufacturing processes, while lights-out manufacturing operates fully autonomously without human intervention, relying heavily on digital twin technology to simulate and optimize production environments in real-time. Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling predictive maintenance, performance monitoring, and process optimization essential for efficient, unattended factory operations.
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
Industrial Automation integrates machines and control systems to optimize manufacturing efficiency, whereas Lights-Out Manufacturing employs autonomous Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) capable of operating without human intervention, leveraging real-time data exchange and advanced robotics. CPS in Lights-Out Manufacturing enables seamless coordination between physical processes and digital control, fostering higher precision, reduced downtime, and enhanced adaptability across production lines.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR)
Industrial automation integrates robotics and control systems to streamline manufacturing processes, enhancing productivity and precision; Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) elevate this by enabling lights-out manufacturing through independent navigation, real-time decision-making, and adaptive task execution in complex environments. AMRs optimize material handling and logistics within factories, reducing human intervention and operational costs while increasing flexibility and efficiency in automated production lines.
Edge-to-Cloud Integration
Industrial automation leverages programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and robotics for efficient production, while lights-out manufacturing emphasizes fully autonomous, unmanned factories; edge-to-cloud integration enables real-time data processing and remote monitoring by connecting edge devices with cloud platforms. This integration enhances predictive maintenance and operational agility, reducing downtime and optimizing supply chain responsiveness in smart factories.
Industrial IoT Gateways
Industrial IoT gateways play a crucial role in bridging the gap between legacy manufacturing equipment and modern Industrial Automation systems by enabling seamless data collection, real-time monitoring, and edge processing. Unlike Lights-Out Manufacturing, which relies on fully autonomous, unmanned production lines, Industrial IoT gateways support hybrid environments where human oversight and automation coexist to optimize operational efficiency and predictive maintenance.
Predictive Maintenance Analytics
Predictive maintenance analytics in industrial automation utilizes real-time sensor data and machine learning algorithms to anticipate equipment failures, thereby minimizing downtime and optimizing operational efficiency. Lights-out manufacturing further enhances these capabilities by enabling fully autonomous production processes with minimal human intervention, leveraging advanced predictive analytics to maintain continuous, uninterrupted operations.
Machine Vision Inspection
Industrial automation integrates machine vision inspection to enhance real-time quality control through precise defect detection and measurement accuracy. Lights-out manufacturing leverages advanced machine vision systems for fully autonomous inspection processes, minimizing human intervention and maximizing production efficiency.
Dark Factory Operations
Industrial automation integrates advanced robotics and control systems to streamline manufacturing processes, enhancing efficiency and precision. Dark factory operations take automation further by operating fully unattended production environments with minimal human intervention, relying on AI and IoT for continuous monitoring and maintenance.
Collaborative Robotics (Cobots)
Collaborative robotics (cobots) enhance industrial automation by working safely alongside human operators to optimize production efficiency and flexibility. Lights-out manufacturing relies heavily on cobots to enable fully automated, unattended production processes, reducing downtime and labor costs while maintaining high precision.
Self-Healing Production Lines
Self-healing production lines in industrial automation utilize advanced sensors, AI-driven diagnostics, and real-time data analytics to detect and resolve equipment faults autonomously, minimizing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency. Lights-out manufacturing takes this concept further by enabling fully autonomous facilities operating without human intervention, leveraging self-healing systems to maintain continuous, optimized production cycles.
Industrial Automation vs Lights-Out Manufacturing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com