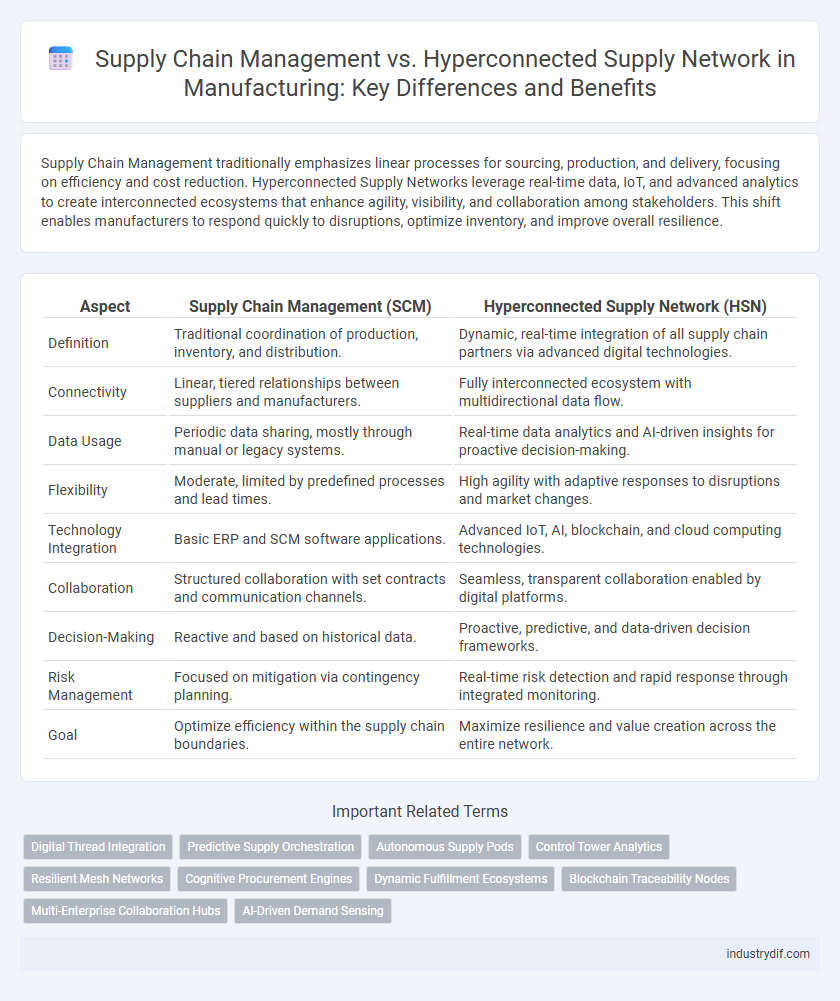
Supply Chain Management traditionally emphasizes linear processes for sourcing, production, and delivery, focusing on efficiency and cost reduction. Hyperconnected Supply Networks leverage real-time data, IoT, and advanced analytics to create interconnected ecosystems that enhance agility, visibility, and collaboration among stakeholders. This shift enables manufacturers to respond quickly to disruptions, optimize inventory, and improve overall resilience.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Supply Chain Management (SCM) | Hyperconnected Supply Network (HSN) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional coordination of production, inventory, and distribution. | Dynamic, real-time integration of all supply chain partners via advanced digital technologies. |
| Connectivity | Linear, tiered relationships between suppliers and manufacturers. | Fully interconnected ecosystem with multidirectional data flow. |
| Data Usage | Periodic data sharing, mostly through manual or legacy systems. | Real-time data analytics and AI-driven insights for proactive decision-making. |
| Flexibility | Moderate, limited by predefined processes and lead times. | High agility with adaptive responses to disruptions and market changes. |
| Technology Integration | Basic ERP and SCM software applications. | Advanced IoT, AI, blockchain, and cloud computing technologies. |
| Collaboration | Structured collaboration with set contracts and communication channels. | Seamless, transparent collaboration enabled by digital platforms. |
| Decision-Making | Reactive and based on historical data. | Proactive, predictive, and data-driven decision frameworks. |
| Risk Management | Focused on mitigation via contingency planning. | Real-time risk detection and rapid response through integrated monitoring. |
| Goal | Optimize efficiency within the supply chain boundaries. | Maximize resilience and value creation across the entire network. |
Defining Supply Chain Management in Manufacturing
Supply Chain Management in manufacturing involves the coordination of materials, information, and finances as products move from supplier to manufacturer to distributor to retailer to consumer. It emphasizes optimizing processes such as procurement, production planning, inventory management, and logistics to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Effective supply chain management ensures timely delivery of raw materials, minimizes disruptions, and aligns production schedules with market demand.
What is a Hyperconnected Supply Network?
A Hyperconnected Supply Network (HSN) integrates advanced digital technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain to enable real-time data exchange and seamless collaboration among all supply chain stakeholders. Unlike traditional Supply Chain Management (SCM) which focuses on linear processes, HSN emphasizes dynamic connectivity, visibility, and agility across a decentralized ecosystem. This transformation enhances predictive analytics, accelerates decision-making, and drives resilience in complex manufacturing environments.
Key Differences Between SCM and HSN
Supply Chain Management (SCM) primarily focuses on optimizing the flow of goods, information, and finances from suppliers to customers through a linear process, emphasizing inventory control, demand forecasting, and supplier coordination. Hyperconnected Supply Network (HSN) leverages advanced digital technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain to create a dynamic, real-time interconnected system enabling enhanced visibility, agility, and collaboration across multiple stakeholders. Key differences include SCM's structured, sequential approach versus HSN's decentralized, data-driven ecosystem that supports rapid decision-making and risk mitigation in complex manufacturing environments.
Benefits of Traditional Supply Chain Management
Traditional Supply Chain Management offers streamlined processes that enhance inventory control, reduce operational costs, and improve supplier relationships, resulting in predictable and efficient production cycles. It provides clear accountability and structured workflows, which simplify risk management and compliance with industry standards. Established communication channels and centralized decision-making contribute to operational stability and long-term strategic planning.
Advantages of Hyperconnected Supply Networks
Hyperconnected supply networks enhance real-time data exchange across multiple stakeholders, improving visibility and responsiveness throughout the manufacturing process. These networks leverage advanced IoT sensors, AI analytics, and cloud platforms to optimize inventory levels, reduce lead times, and mitigate risks from disruptions. Compared to traditional supply chain management, hyperconnected systems enable more agile decision-making and foster seamless collaboration, driving higher operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Digital Transformation in Manufacturing Supply Chains
Digital transformation in manufacturing supply chains shifts traditional supply chain management towards hyperconnected supply networks by integrating IoT, AI, and real-time data analytics to enhance visibility and responsiveness. Hyperconnected supply networks enable seamless collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, reducing lead times and improving demand forecasting accuracy. This evolution supports agile production processes, lowers operational costs, and drives innovation through end-to-end digital synchronization.
Role of Real-Time Data in Modern Supply Networks
Real-time data drives increased visibility and agility in hyperconnected supply networks by enabling instantaneous decision-making across global suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. Unlike traditional supply chain management systems that rely on periodic updates, hyperconnected networks leverage continuous data streams to optimize inventory levels, forecast demand accurately, and respond promptly to disruptions. This dynamic integration of IoT sensors, AI analytics, and cloud platforms transforms supply networks into adaptive ecosystems, enhancing efficiency and resilience.
Challenges in Adopting Hyperconnected Supply Networks
Challenges in adopting hyperconnected supply networks include data integration complexities across diverse platforms and real-time communication demands that strain existing IT infrastructure. Ensuring cybersecurity and maintaining data privacy become critical as more interconnected nodes increase vulnerability to cyberattacks. Additionally, fostering collaboration among multiple stakeholders requires overcoming organizational silos and aligning technological capabilities with strategic supply chain objectives.
Impact on Operational Efficiency and Agility
Supply Chain Management (SCM) traditionally emphasizes linear processes and supplier relationships, which can limit responsiveness and operational efficiency in dynamic manufacturing environments. Hyperconnected Supply Networks leverage real-time data integration and digital communication between all stakeholders, significantly enhancing agility and decision-making speed. This networked approach enables manufacturers to adapt quickly to disruptions, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall operational performance.
Future Trends: Evolving from SCM to Hyperconnected Networks
Supply chain management is evolving into hyperconnected supply networks by integrating real-time data analytics, IoT, and AI-driven automation to enhance visibility and responsiveness across production and distribution channels. Future trends emphasize decentralized decision-making and seamless collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers to optimize efficiency and reduce risks. Leveraging blockchain technology ensures transparency and traceability, driving the transformation from traditional SCM frameworks to dynamic, adaptive hyperconnected ecosystems.
Related Important Terms
Digital Thread Integration
Supply Chain Management traditionally emphasizes linear processes focusing on procurement, production, and logistics, whereas Hyperconnected Supply Networks leverage digital thread integration to provide real-time visibility, seamless data flow, and predictive analytics across all nodes. Digital thread integration connects design, manufacturing, and operational data, enabling enhanced collaboration, agility, and responsiveness to market demands.
Predictive Supply Orchestration
Supply Chain Management traditionally focuses on managing linear flows of goods and information between suppliers and customers, relying on historical data for decision-making. Hyperconnected Supply Networks leverage real-time data and advanced analytics to enable predictive supply orchestration, proactively adjusting operations to mitigate disruptions and optimize resource allocation across interconnected partners.
Autonomous Supply Pods
Autonomous Supply Pods revolutionize supply chain management by enabling hyperconnected supply networks that enhance real-time data exchange, predictive analytics, and decentralized decision-making. These intelligent pods improve inventory accuracy, reduce lead times, and optimize logistics through seamless integration across manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution nodes.
Control Tower Analytics
Control Tower Analytics in Supply Chain Management provides centralized visibility and real-time data insights to optimize logistics and inventory control, enhancing decision-making efficiency. In contrast, a Hyperconnected Supply Network leverages advanced analytics across interconnected partners to enable dynamic responsiveness and predictive capabilities, driving greater agility and collaboration throughout the supply chain ecosystem.
Resilient Mesh Networks
Supply Chain Management traditionally centers on linear, sequential processes to coordinate suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, often resulting in limited adaptability to disruptions. Hyperconnected Supply Networks leverage resilient mesh networks that enable real-time data exchange and decentralized decision-making, significantly enhancing responsiveness and robustness against supply chain shocks.
Cognitive Procurement Engines
Cognitive procurement engines leverage AI and advanced analytics to enhance decision-making, enabling hyperconnected supply networks to achieve real-time visibility, agility, and predictive capabilities beyond traditional supply chain management systems. These engines integrate vast data sources, optimize sourcing strategies, and facilitate automated risk management, driving efficiency and resilience in complex manufacturing supply ecosystems.
Dynamic Fulfillment Ecosystems
Supply Chain Management traditionally focuses on linear processes and fixed supplier relationships, whereas Hyperconnected Supply Networks leverage real-time data and advanced IoT technologies to create dynamic fulfillment ecosystems that adapt quickly to demand fluctuations and disruptions. This shift enables seamless collaboration across multiple stakeholders, enhancing agility, transparency, and efficiency in manufacturing operations.
Blockchain Traceability Nodes
Supply Chain Management traditionally relies on centralized systems for tracking and coordination, often resulting in limited transparency and slower response times. Hyperconnected Supply Networks leverage blockchain traceability nodes to enable real-time, immutable data sharing across all stakeholders, enhancing visibility, security, and efficiency in manufacturing supply chains.
Multi-Enterprise Collaboration Hubs
Supply Chain Management traditionally centers on linear, transactional processes, while Hyperconnected Supply Networks leverage Multi-Enterprise Collaboration Hubs to enable real-time data exchange and integrated decision-making across diverse stakeholders. These hubs enhance visibility, agility, and responsiveness by connecting suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers within a dynamic and interconnected ecosystem.
AI-Driven Demand Sensing
AI-driven demand sensing enhances supply chain management by providing real-time, data-driven insights that improve forecast accuracy and inventory optimization. In a hyperconnected supply network, this technology enables seamless communication between suppliers and manufacturers, driving agility and responsiveness through predictive analytics and adaptive decision-making.
Supply Chain Management vs Hyperconnected Supply Network Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com