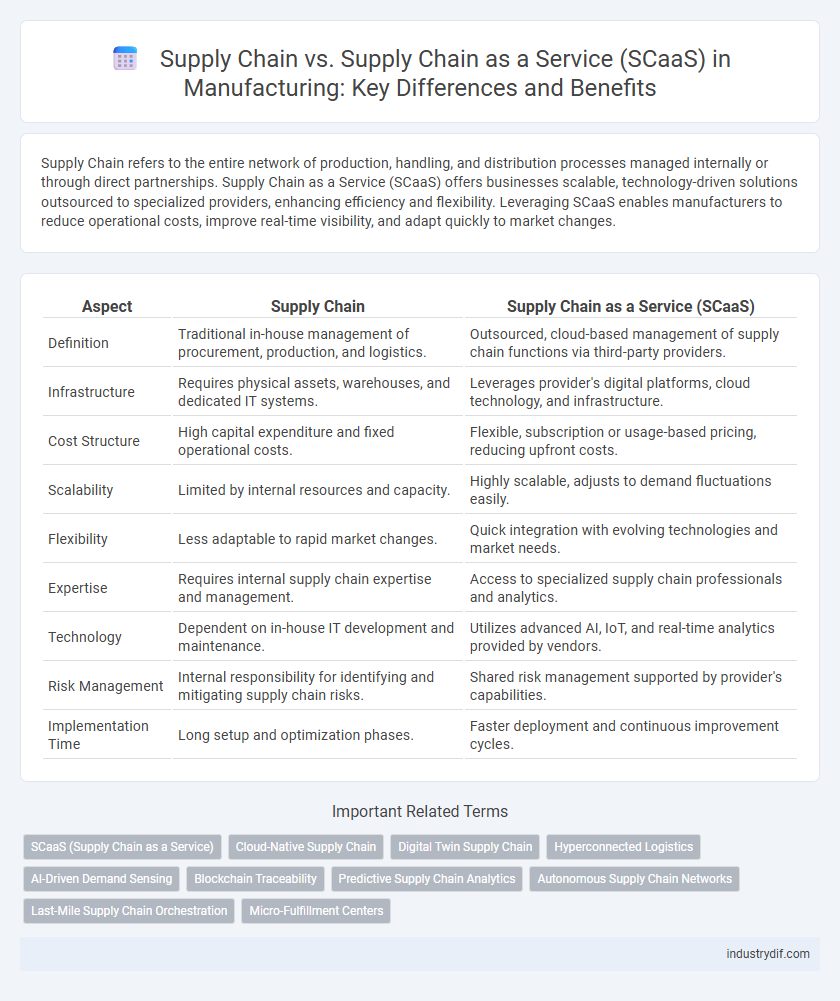
Supply Chain refers to the entire network of production, handling, and distribution processes managed internally or through direct partnerships. Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) offers businesses scalable, technology-driven solutions outsourced to specialized providers, enhancing efficiency and flexibility. Leveraging SCaaS enables manufacturers to reduce operational costs, improve real-time visibility, and adapt quickly to market changes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Supply Chain | Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional in-house management of procurement, production, and logistics. | Outsourced, cloud-based management of supply chain functions via third-party providers. |
| Infrastructure | Requires physical assets, warehouses, and dedicated IT systems. | Leverages provider's digital platforms, cloud technology, and infrastructure. |
| Cost Structure | High capital expenditure and fixed operational costs. | Flexible, subscription or usage-based pricing, reducing upfront costs. |
| Scalability | Limited by internal resources and capacity. | Highly scalable, adjusts to demand fluctuations easily. |
| Flexibility | Less adaptable to rapid market changes. | Quick integration with evolving technologies and market needs. |
| Expertise | Requires internal supply chain expertise and management. | Access to specialized supply chain professionals and analytics. |
| Technology | Dependent on in-house IT development and maintenance. | Utilizes advanced AI, IoT, and real-time analytics provided by vendors. |
| Risk Management | Internal responsibility for identifying and mitigating supply chain risks. | Shared risk management supported by provider's capabilities. |
| Implementation Time | Long setup and optimization phases. | Faster deployment and continuous improvement cycles. |
Defining Traditional Supply Chain
A traditional supply chain involves the end-to-end process of sourcing raw materials, manufacturing products, and distributing them to customers, typically managed internally by a company. This model requires significant investment in infrastructure, inventory management, and logistics coordination to ensure seamless operations. Companies rely on in-house teams and legacy systems to control procurement, production scheduling, and delivery, often facing challenges with scalability and agility.
What is Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS)?
Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) is a cloud-based model that allows manufacturers to outsource supply chain management functions, leveraging external expertise and technology for real-time visibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. Unlike traditional supply chains that require in-house resources and infrastructure, SCaaS integrates advanced analytics, IoT, and AI-driven optimization to enhance operational agility and reduce lead times. This service-based approach supports just-in-time inventory, reduces capital expenditure, and improves end-to-end supply chain responsiveness in a dynamic manufacturing environment.
Key Differences: Traditional Supply Chain vs SCaaS
Traditional supply chain management involves in-house oversight of procurement, production, and distribution processes, requiring extensive capital investment and internal resources. Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) leverages cloud-based platforms and third-party providers to offer scalable, flexible solutions with real-time data analytics and enhanced visibility. SCaaS reduces operational costs and improves responsiveness compared to traditional supply chains by integrating advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain for optimized supply chain processes.
Benefits of Supply Chain as a Service
Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) offers enhanced flexibility and scalability compared to traditional supply chain models, allowing manufacturers to quickly adapt to market fluctuations without large capital investments. Leveraging cloud-based platforms and advanced analytics, SCaaS improves real-time visibility, optimizes inventory management, and reduces operational costs through outsourced expertise. This approach accelerates innovation cycles and enhances overall supply chain resilience by integrating third-party logistics, procurement, and warehousing services into a seamless, on-demand solution.
Challenges of Adopting SCaaS
Adopting Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) introduces challenges including integration complexities with existing legacy systems, potential data security risks, and dependence on third-party providers for critical supply chain functions. Manufacturers must address interoperability issues to maintain seamless operations and ensure real-time visibility across multi-tier supply networks. Additionally, balancing cost efficiencies with the need for customization and control remains a significant hurdle in SCaaS adoption.
Technology’s Role in SCaaS Transformation
Technology drives the transformation from traditional Supply Chain management to Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) by enabling real-time data integration, advanced analytics, and cloud-based platforms that enhance visibility and scalability. IoT devices, AI-powered predictive tools, and blockchain ensure seamless collaboration and secure transactions across global networks. These innovations reduce operational costs, improve responsiveness, and foster agility in manufacturing supply chains.
Cost Implications: Traditional Supply Chain vs SCaaS
Traditional supply chains often involve significant capital expenditure for infrastructure, technology, and labor, leading to higher upfront costs and ongoing maintenance expenses. Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) shifts these costs to a variable pricing model, reducing capital investment and aligning expenses with actual usage, which improves cash flow and scalability. Leveraging cloud-based platforms and outsourced logistics in SCaaS minimizes overhead and enables manufacturers to optimize supply chain efficiency while controlling operational costs more effectively.
Scalability and Flexibility in Manufacturing Supply Chains
Manufacturing supply chains benefit from Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) by offering enhanced scalability and flexibility, enabling rapid adjustment to demand fluctuations and production changes without significant capital investment. Traditional supply chains often face limitations in scaling operations quickly due to fixed infrastructure and resource constraints, whereas SCaaS integrates cloud-based solutions and third-party logistics to streamline inventory management and distribution. This dynamic approach supports manufacturers in optimizing operational efficiency and responding agilely to market shifts.
Risk Management: Conventional vs SCaaS Models
Traditional supply chain models often face challenges in risk management due to limited visibility and slower response times to disruptions. Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) enhances risk mitigation by leveraging real-time data analytics, cloud-based platforms, and flexible resources to quickly adapt to supply chain disruptions. SCaaS models also enable proactive identification of potential risks, reducing downtime and improving overall resilience across manufacturing processes.
Future Trends: Evolution of Supply Chain Management
Future trends in supply chain management highlight the shift from traditional supply chain models to Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS), leveraging cloud-based platforms and real-time data analytics to enhance agility and scalability. Integration of AI, IoT, and blockchain technologies in SCaaS optimizes inventory management, demand forecasting, and transparency across global manufacturing networks. The evolution emphasizes decentralized decision-making, reduced capital expenditure, and enhanced responsiveness to market fluctuations, driving efficiency and sustainability in manufacturing supply chains.
Related Important Terms
SCaaS (Supply Chain as a Service)
Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) revolutionizes traditional manufacturing logistics by offering scalable, cloud-based solutions that enhance visibility, flexibility, and real-time data integration across procurement, production, and distribution channels. SCaaS leverages advanced analytics and IoT technologies to optimize inventory management and demand forecasting, reducing operational costs and improving supply chain resilience.
Cloud-Native Supply Chain
Cloud-native supply chain solutions leverage real-time data integration, scalable cloud infrastructure, and AI-driven analytics to enhance visibility and responsiveness compared to traditional supply chain models. Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) offers manufacturers flexible, on-demand access to advanced logistics, procurement, and inventory management tools without heavy upfront investments, accelerating digital transformation and reducing operational complexity.
Digital Twin Supply Chain
Digital Twin Supply Chain leverages real-time data and simulations to optimize manufacturing operations, offering agility and predictive insights beyond traditional supply chain management. Supply Chain as a Service integrates Digital Twin technology to enhance visibility, reduce risks, and streamline decision-making in complex manufacturing environments.
Hyperconnected Logistics
Hyperconnected logistics transforms traditional manufacturing supply chains by integrating real-time data, IoT devices, and AI-driven analytics to enhance visibility and responsiveness across all supply chain stages. Supply Chain as a Service leverages cloud-based platforms and advanced connectivity to optimize inventory management, reduce lead times, and enable seamless collaboration between manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors.
AI-Driven Demand Sensing
AI-Driven Demand Sensing enhances traditional supply chain operations by leveraging real-time data analytics and machine learning algorithms to predict customer demand accurately, reducing inventory costs and minimizing stockouts. Supply Chain as a Service integrates these advanced AI capabilities into a scalable, cloud-based platform, offering manufacturers agile, data-driven demand forecasting without the need for extensive in-house infrastructure.
Blockchain Traceability
Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) leverages blockchain traceability to enhance transparency, real-time tracking, and data integrity across manufacturing processes, surpassing traditional supply chain models. Blockchain-enabled SCaaS ensures immutable records of product origins, shipment histories, and quality compliance, reducing fraud and improving decision-making efficiency in manufacturing supply chains.
Predictive Supply Chain Analytics
Predictive Supply Chain Analytics enhances traditional supply chains by leveraging advanced data modeling, AI, and machine learning to forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and reduce operational bottlenecks. Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) integrates these predictive capabilities with cloud-based platforms, enabling manufacturers to access real-time insights, improve agility, and streamline end-to-end supply chain management without heavy upfront infrastructure investments.
Autonomous Supply Chain Networks
Autonomous Supply Chain Networks leverage AI and IoT to enable real-time decision-making, enhancing agility and reducing operational costs compared to traditional supply chains. Supply Chain as a Service integrates cloud-based platforms to streamline these autonomous networks, offering scalable, on-demand solutions that optimize inventory management and logistics execution.
Last-Mile Supply Chain Orchestration
Last-mile supply chain orchestration in traditional supply chains often faces challenges such as limited visibility, inefficiencies, and high costs, whereas Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) leverages cloud-based platforms and real-time data analytics to optimize delivery routes, enhance transparency, and reduce operational expenses. SCaaS providers offer scalable solutions integrating advanced technologies like IoT and AI to streamline last-mile logistics, ensuring faster fulfillment and improved customer satisfaction in manufacturing supply networks.
Micro-Fulfillment Centers
Micro-fulfillment centers enhance traditional supply chains by enabling rapid, localized inventory management and reducing delivery times through automation and real-time data integration. Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) leverages these centers to offer scalable, on-demand logistics solutions that optimize inventory flow and improve customer responsiveness in manufacturing operations.
Supply Chain vs Supply Chain as a Service Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com