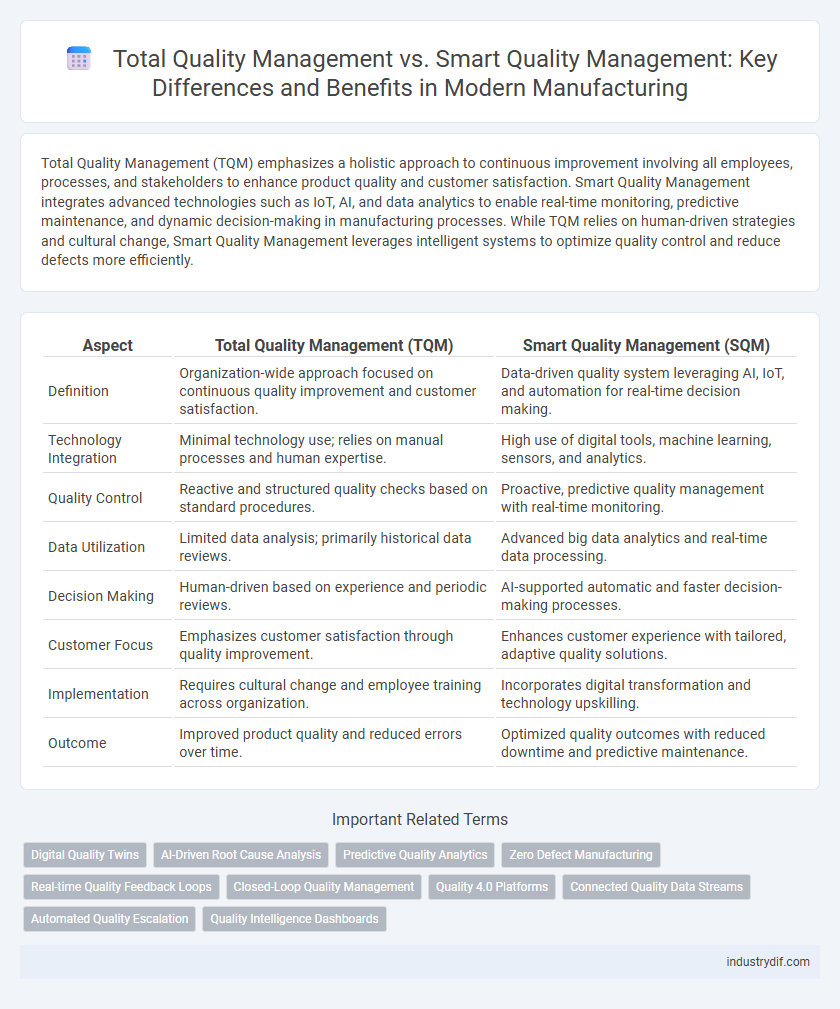
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes a holistic approach to continuous improvement involving all employees, processes, and stakeholders to enhance product quality and customer satisfaction. Smart Quality Management integrates advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and data analytics to enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and dynamic decision-making in manufacturing processes. While TQM relies on human-driven strategies and cultural change, Smart Quality Management leverages intelligent systems to optimize quality control and reduce defects more efficiently.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Total Quality Management (TQM) | Smart Quality Management (SQM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organization-wide approach focused on continuous quality improvement and customer satisfaction. | Data-driven quality system leveraging AI, IoT, and automation for real-time decision making. |
| Technology Integration | Minimal technology use; relies on manual processes and human expertise. | High use of digital tools, machine learning, sensors, and analytics. |
| Quality Control | Reactive and structured quality checks based on standard procedures. | Proactive, predictive quality management with real-time monitoring. |
| Data Utilization | Limited data analysis; primarily historical data reviews. | Advanced big data analytics and real-time data processing. |
| Decision Making | Human-driven based on experience and periodic reviews. | AI-supported automatic and faster decision-making processes. |
| Customer Focus | Emphasizes customer satisfaction through quality improvement. | Enhances customer experience with tailored, adaptive quality solutions. |
| Implementation | Requires cultural change and employee training across organization. | Incorporates digital transformation and technology upskilling. |
| Outcome | Improved product quality and reduced errors over time. | Optimized quality outcomes with reduced downtime and predictive maintenance. |
Understanding Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a holistic approach to manufacturing that emphasizes continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and employee involvement across all organizational levels. It integrates quality principles into every process, ensuring defect prevention and waste reduction while fostering a culture of collaboration. Key TQM tools include statistical process control, root cause analysis, and employee training to maintain consistent product quality and operational efficiency.
Defining Smart Quality Management (SQM)
Smart Quality Management (SQM) integrates advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and big data analytics to enhance traditional Total Quality Management (TQM) frameworks in manufacturing. SQM enables real-time quality control, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making, resulting in improved product consistency and reduced defects. By leveraging automation and continuous feedback loops, SQM drives operational efficiency and fosters a proactive quality culture across the production lifecycle.
Core Principles of TQM
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement, customer focus, employee involvement, and process-centered approaches to enhance manufacturing quality. Core principles include a strong commitment to leadership, data-driven decision making, and systematic problem-solving to reduce defects and inefficiencies. In contrast, Smart Quality Management integrates these TQM principles with advanced digital technologies like IoT, AI, and real-time analytics to optimize quality control and predictive maintenance in modern manufacturing environments.
Key Components of SQM
Smart Quality Management (SQM) in manufacturing integrates advanced technologies like IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and real-time data monitoring to enhance product quality and process efficiency. Key components of SQM include automated defect detection, predictive maintenance, and dynamic process control, enabling proactive quality assurance and continuous improvement. Unlike traditional Total Quality Management (TQM), SQM emphasizes digital transformation and data-centric decision-making to achieve higher precision and reduce operational costs.
Human-Centric vs. Data-Driven Approaches
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes a human-centric approach by fostering employee involvement, continuous training, and teamwork to enhance product quality and customer satisfaction. In contrast, Smart Quality Management leverages data-driven technologies such as IoT sensors, AI analytics, and real-time monitoring to optimize manufacturing processes and predict defects with high precision. Integrating human expertise with advanced data analytics creates a balanced strategy that improves operational efficiency and quality outcomes in modern manufacturing environments.
Role of Technology in Quality Management
Total Quality Management (TQM) primarily relies on systematic processes and employee involvement to ensure product quality, while Smart Quality Management leverages advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and big data analytics to enhance real-time monitoring and predictive quality control. The integration of sensors and machine learning algorithms enables Smart Quality Management systems to detect defects early and optimize manufacturing workflows automatically. This technological shift significantly improves accuracy, reduces waste, and accelerates decision-making compared to traditional TQM methods.
Implementation Challenges: TQM vs. SQM
Implementation challenges of Total Quality Management (TQM) in manufacturing often include resistance to cultural change, extensive training requirements, and difficulties in sustaining long-term commitment across all organizational levels. Smart Quality Management (SQM) faces challenges integrating advanced digital technologies like IoT, AI, and big data analytics, requiring significant investment in infrastructure and skilled personnel. Both approaches demand a shift in organizational mindset, but SQM emphasizes technological adoption, making seamless data integration and cybersecurity critical obstacles during execution.
Impact on Manufacturing Efficiency
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and defect reduction, leading to consistent manufacturing efficiency through standardized processes and employee involvement. Smart Quality Management (Smart QM) integrates advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and real-time data analytics to optimize quality control, enabling predictive maintenance and faster decision-making that significantly enhance production throughput. Manufacturing plants adopting Smart QM report up to a 30% increase in operational efficiency compared to traditional TQM approaches.
Quality Assurance and Continuous Improvement
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes systematic quality assurance through standardized processes and employee involvement to drive continuous improvement across manufacturing operations. Smart Quality Management integrates advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and real-time data analytics to enhance quality assurance by enabling predictive maintenance and adaptive process control. This digital approach accelerates continuous improvement cycles by providing actionable insights, reducing defects, and optimizing production efficiency.
Future Trends in Quality Management
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction through standardized processes, while Smart Quality Management integrates AI, IoT, and data analytics to enable real-time monitoring and predictive quality control in manufacturing. Future trends in quality management prioritize automation, machine learning-driven defect detection, and adaptive quality systems that proactively address production anomalies. This shift towards intelligent quality management enhances efficiency, reduces waste, and fosters agile responses to dynamic market demands.
Related Important Terms
Digital Quality Twins
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes a comprehensive, continuous improvement approach across all manufacturing processes, while Smart Quality Management (SQM) integrates advanced digital technologies such as Digital Quality Twins to enhance real-time monitoring, predictive analysis, and adaptive control of product quality. Digital Quality Twins create virtual replicas of physical products and manufacturing processes, enabling manufacturers to simulate, detect, and resolve quality issues proactively, leading to higher efficiency, reduced defects, and optimized production workflows.
AI-Driven Root Cause Analysis
Total Quality Management relies heavily on human expertise for root cause analysis, while Smart Quality Management leverages AI-driven algorithms to identify defects and process inefficiencies in real-time, enhancing accuracy and speed. AI-driven root cause analysis utilizes machine learning models to detect patterns and anomalies in manufacturing data, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime significantly.
Predictive Quality Analytics
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement through employee involvement and process standardization, while Smart Quality Management leverages Predictive Quality Analytics to use real-time data and machine learning algorithms for anticipating defects and optimizing production quality. Predictive Quality Analytics enhances decision-making by detecting potential quality issues before they occur, reducing downtime and improving yield in manufacturing operations.
Zero Defect Manufacturing
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and employee involvement to achieve defect-free production, while Smart Quality Management leverages advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and real-time data analytics to enable Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM). Implementing ZDM through Smart Quality Management significantly reduces waste, enhances product reliability, and accelerates decision-making processes in manufacturing environments.
Real-time Quality Feedback Loops
Total Quality Management emphasizes continuous improvement through comprehensive process control, whereas Smart Quality Management integrates real-time quality feedback loops using IoT sensors and AI analytics to detect defects instantly. These advanced feedback mechanisms enable manufacturers to reduce downtime, enhance product consistency, and accelerate decision-making for superior quality outcomes.
Closed-Loop Quality Management
Total Quality Management (TQM) focuses on continuous improvement and employee involvement to enhance product quality, while Smart Quality Management integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and big data analytics for real-time monitoring and predictive analysis. Closed-Loop Quality Management in Smart Quality Management enables automated feedback systems that instantly detect defects, analyze root causes, and implement corrective actions, optimizing manufacturing processes and reducing downtime.
Quality 4.0 Platforms
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and employee involvement across production processes, while Smart Quality Management leverages Quality 4.0 platforms integrating AI, IoT, and big data analytics for real-time quality monitoring and predictive insights. Quality 4.0 platforms enable manufacturers to optimize defect detection, enhance supply chain transparency, and drive data-driven decisions, transforming traditional TQM frameworks into intelligent, adaptive quality ecosystems.
Connected Quality Data Streams
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes comprehensive quality control through standardized processes, whereas Smart Quality Management leverages connected quality data streams to enable real-time analytics and predictive insights. Integrating IoT sensors and advanced data platforms creates continuous feedback loops that enhance decision-making, reduce defects, and optimize manufacturing efficiency.
Automated Quality Escalation
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement through manual quality checks and employee involvement, while Smart Quality Management integrates Automated Quality Escalation using AI and IoT sensors to detect defects in real-time, drastically reducing response times and minimizing production downtime. Automated Quality Escalation enhances predictive analytics and root cause analysis, enabling manufacturers to implement proactive corrections and maintain consistent product standards with higher precision.
Quality Intelligence Dashboards
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and employee involvement, while Smart Quality Management leverages Quality Intelligence Dashboards to provide real-time data visualization, predictive analytics, and actionable insights for proactive decision-making. These dashboards integrate IoT sensors and AI algorithms to monitor production processes, identify defects early, and optimize quality control, enhancing manufacturing efficiency and reducing costs.
Total Quality Management vs Smart Quality Management Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com