Six Sigma emphasizes reducing defects and variability in manufacturing processes through statistical analysis and DMAIC methodology, ensuring high-quality outputs. Process mining leverages data from event logs to visualize, analyze, and optimize real-time workflows, identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies. While Six Sigma targets process improvement through structured problem-solving, process mining provides a data-driven foundation for continuous process discovery and optimization.
Table of Comparison
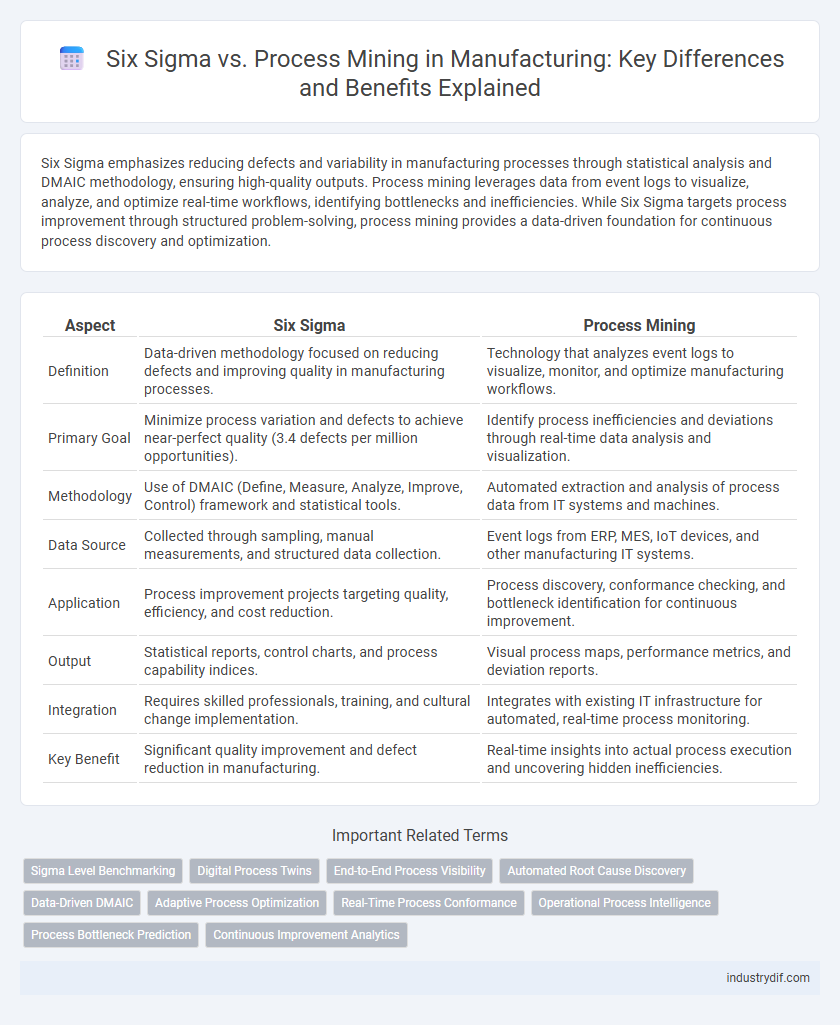
| Aspect | Six Sigma | Process Mining |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data-driven methodology focused on reducing defects and improving quality in manufacturing processes. | Technology that analyzes event logs to visualize, monitor, and optimize manufacturing workflows. |
| Primary Goal | Minimize process variation and defects to achieve near-perfect quality (3.4 defects per million opportunities). | Identify process inefficiencies and deviations through real-time data analysis and visualization. |
| Methodology | Use of DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) framework and statistical tools. | Automated extraction and analysis of process data from IT systems and machines. |
| Data Source | Collected through sampling, manual measurements, and structured data collection. | Event logs from ERP, MES, IoT devices, and other manufacturing IT systems. |
| Application | Process improvement projects targeting quality, efficiency, and cost reduction. | Process discovery, conformance checking, and bottleneck identification for continuous improvement. |
| Output | Statistical reports, control charts, and process capability indices. | Visual process maps, performance metrics, and deviation reports. |
| Integration | Requires skilled professionals, training, and cultural change implementation. | Integrates with existing IT infrastructure for automated, real-time process monitoring. |
| Key Benefit | Significant quality improvement and defect reduction in manufacturing. | Real-time insights into actual process execution and uncovering hidden inefficiencies. |
Introduction to Six Sigma and Process Mining
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aimed at improving manufacturing quality by identifying and eliminating defects, reducing process variation, and enhancing overall efficiency through rigorous statistical analysis. Process Mining leverages event logs from manufacturing systems to visualize, analyze, and optimize production workflows, uncovering bottlenecks and deviations in real-time. Both Six Sigma and Process Mining empower manufacturers to enhance operational performance, with Six Sigma emphasizing defect reduction and Process Mining focusing on process transparency and continuous improvement.
Key Principles of Six Sigma Methodology
Six Sigma methodology revolves around the DMAIC framework--Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control--aimed at reducing defects and variability in manufacturing processes. It emphasizes data-driven decision-making and statistical analysis to enhance process capability and ensure consistent product quality. Process mining complements Six Sigma by uncovering process inefficiencies through event log analysis, enabling more precise identification of improvement areas.
What is Process Mining in Manufacturing?
Process mining in manufacturing leverages data from production systems to visualize, analyze, and optimize manufacturing processes by identifying bottlenecks, deviations, and inefficiencies. Unlike Six Sigma, which focuses on statistical methods to reduce defects and variability, process mining uses real-time event logs to provide a factual, data-driven view of process execution. Integrating process mining enables manufacturers to achieve higher operational transparency, improve cycle times, and enhance quality control through data-backed insights.
Data Requirements: Six Sigma vs Process Mining
Six Sigma relies on structured and high-quality data from controlled experiments and historical process metrics to identify defects and reduce variability in manufacturing. Process Mining requires comprehensive event logs capturing real-time process execution data, including timestamps and system-generated records, to visualize and analyze actual workflows. The data demands of Process Mining are broader and more dynamic, enabling deeper insights into process deviations and inefficiencies beyond traditional statistical analysis.
Core Tools and Techniques Compared
Six Sigma employs core tools such as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control), control charts, and root cause analysis to reduce process variation and defects in manufacturing. Process Mining leverages data-driven techniques including event log analysis, process discovery, and conformance checking to visualize and optimize production workflows in real time. Combining Six Sigma's structured problem-solving methods with Process Mining's data analytics enhances quality control and operational efficiency in manufacturing environments.
Integration with Manufacturing Systems
Six Sigma enhances manufacturing quality by systematically reducing defects through data-driven methodologies integrated with systems like MES and SCADA for real-time monitoring. Process Mining complements this by extracting and visualizing process data from ERP and PLC systems, enabling identification of bottlenecks and deviations in production workflows. Integrating Six Sigma with Process Mining within manufacturing systems drives continuous improvement, optimizes process efficiency, and supports decision-making based on comprehensive, real-time operational insights.
Impact on Quality Improvement
Six Sigma uses statistical tools to reduce defects and variability, achieving up to 99.99966% process accuracy that significantly enhances product quality and consistency. Process Mining leverages real-time data analysis from IT systems to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks, enabling faster resolution of quality issues in manufacturing workflows. Combining Six Sigma's structured methodologies with Process Mining's data-driven insights drives continuous quality improvement and operational excellence in manufacturing environments.
Efficiency and Bottleneck Identification
Six Sigma drives efficiency in manufacturing by using statistical methods to reduce process variation and eliminate defects, leading to consistent quality and cost savings. Process Mining enhances bottleneck identification through data-driven analysis of event logs, uncovering hidden process inefficiencies and real-time performance gaps. Integrating Six Sigma with Process Mining tools accelerates continuous improvement by combining deep analytical insights with structured problem-solving methodologies.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
Implementing Six Sigma in manufacturing often faces challenges such as resistance to cultural change and the need for extensive employee training in statistical methods. Process mining implementation demands high-quality, comprehensive data from various IT systems and integration expertise to accurately map and analyze workflows. Best practices include combining Six Sigma's structured problem-solving approach with process mining's real-time data insights to identify bottlenecks and drive continuous improvement.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Manufacturing Needs
Six Sigma emphasizes reducing defects through statistical analysis and process control, ideal for manufacturing environments aiming to improve quality and consistency. Process Mining offers data-driven insights by analyzing event logs to uncover inefficiencies and bottlenecks in production workflows. Selecting the right approach depends on your facility's current challenges: Six Sigma suits structured defect reduction, while Process Mining excels in identifying hidden process inefficiencies for continuous improvement.
Related Important Terms
Sigma Level Benchmarking
Six Sigma emphasizes achieving a defect rate of 3.4 defects per million opportunities by improving process capability through statistical analysis, while Process Mining benchmarks sigma levels by extracting real-time event data to identify process inefficiencies and variations. Integrating Process Mining with Six Sigma accelerates sigma level benchmarking accuracy, enabling manufacturers to pinpoint process deviations and drive continuous improvement.
Digital Process Twins
Six Sigma emphasizes reducing process variation through statistical analysis and control, while Process Mining leverages real-time event data to visualize and improve workflows. Digital Process Twins integrate these approaches by creating dynamic, data-driven models that simulate manufacturing processes for continuous optimization and predictive analytics.
End-to-End Process Visibility
Six Sigma enhances manufacturing quality by reducing defects through statistical analysis, while process mining provides comprehensive end-to-end process visibility by extracting real-time data from IT systems to uncover bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Integrating Six Sigma with process mining enables manufacturers to leverage precise process insights and drive continuous improvement across the entire production lifecycle.
Automated Root Cause Discovery
Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects through structured methodologies like DMAIC, while Process Mining leverages real-time data analytics for automated root cause discovery, enabling faster identification of process inefficiencies. Integrating Process Mining with Six Sigma enhances root cause analysis by providing detailed process visualization and data-driven insights, accelerating continuous improvement in manufacturing operations.
Data-Driven DMAIC
Six Sigma's DMAIC framework relies on structured data collection and statistical analysis to identify defects and optimize manufacturing processes, emphasizing measurable improvements through Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control phases. Process Mining complements Six Sigma by automatically extracting event logs from IT systems, offering real-time process visualization and data-driven insights that enhance the accuracy and speed of DMAIC's Analyze and Improve stages.
Adaptive Process Optimization
Six Sigma leverages statistical methods to reduce process variation and defects, while Process Mining utilizes data-driven insights to visualize and analyze real-time workflows for adaptive process optimization. Combining Six Sigma's rigorous control techniques with Process Mining's dynamic process discovery enables manufacturers to continuously refine operations, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness in complex production environments.
Real-Time Process Conformance
Six Sigma leverages statistical analysis to identify and reduce process variation but often relies on historical data, limiting real-time insights for process conformance. Process Mining uses event logs to provide continuous, real-time monitoring of manufacturing workflows, enabling immediate detection and correction of deviations to maintain optimal process standards.
Operational Process Intelligence
Six Sigma leverages statistical analysis to reduce defects and improve manufacturing quality, while Process Mining uses real-time data to visualize and analyze operational workflows for enhanced process transparency. Combining Six Sigma with Process Mining enables operational process intelligence by identifying inefficiencies and providing actionable insights to optimize production performance and reduce cycle times.
Process Bottleneck Prediction
Process Mining leverages real-time data analytics to identify and predict process bottlenecks with higher accuracy compared to traditional Six Sigma methods, which primarily rely on historical data and statistical analysis. Implementing Process Mining in manufacturing enhances bottleneck prediction by providing detailed process visualization and continuous monitoring, enabling proactive decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
Continuous Improvement Analytics
Six Sigma leverages statistical analysis to reduce process variation and defects, driving quality improvements in manufacturing operations. Process Mining provides data-driven insights by visualizing actual workflows from event logs, enabling continuous improvement analytics that identify bottlenecks and optimize process efficiency.
Six Sigma vs Process Mining Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com