Drill and blast techniques in mining involve drilling holes into rock and using explosives to break it apart, offering rapid fragmentation and efficiency in hard rock conditions. Electric rock cutting, on the other hand, utilizes advanced machinery to mechanically cut rock with precision, reducing vibration and environmental impact. Choosing between these methods depends on factors like rock type, operational safety, environmental regulations, and project scale.
Table of Comparison
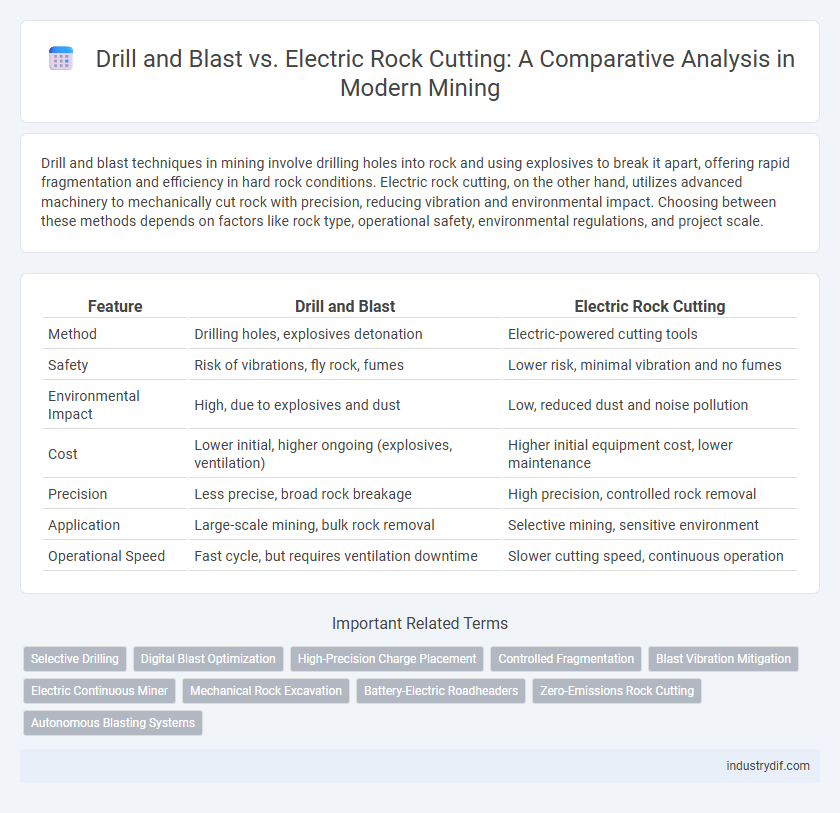
| Feature | Drill and Blast | Electric Rock Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Drilling holes, explosives detonation | Electric-powered cutting tools |
| Safety | Risk of vibrations, fly rock, fumes | Lower risk, minimal vibration and no fumes |
| Environmental Impact | High, due to explosives and dust | Low, reduced dust and noise pollution |
| Cost | Lower initial, higher ongoing (explosives, ventilation) | Higher initial equipment cost, lower maintenance |
| Precision | Less precise, broad rock breakage | High precision, controlled rock removal |
| Application | Large-scale mining, bulk rock removal | Selective mining, sensitive environment |
| Operational Speed | Fast cycle, but requires ventilation downtime | Slower cutting speed, continuous operation |
Overview of Drill and Blast vs Electric Rock Cutting
Drill and Blast remains the dominant mining technique due to its cost-effectiveness and ability to handle hard rock in large-scale operations, utilizing explosives to fracture rock for easier removal. Electric Rock Cutting offers a quieter, dust-free alternative with lower vibration, ideal for underground mines emphasizing environmental and safety standards. Both methods impact productivity and operational costs, with the choice often influenced by rock type, mine depth, and regulatory requirements.
Historical Development of Mining Extraction Methods
Drill and blast mining, first developed in the early 19th century, revolutionized extraction by using explosives to fragment rock, enhancing productivity in both surface and underground mines. Electric rock cutting emerged in the mid-20th century as a cleaner, safer alternative, utilizing high-powered electric cutters to reduce vibration and environmental impact while improving precision in hard rock excavation. These developments reflect the mining industry's evolution from explosive-driven techniques to more controlled, energy-efficient methods optimized for safety and operational efficiency.
Technology and Equipment Comparison
Drill and blast technology relies on explosives to fracture rock, using heavy-duty drilling rigs and blasting equipment that offer high fragmentation efficiency but generate significant vibration and dust. Electric rock cutting employs advanced machinery such as electric cutting heads and precision sensors, enabling quieter, cleaner, and more controlled excavation with lower environmental impact. While drill and blast suits large-scale operations requiring rapid advancement, electric rock cutting excels in urban or sensitive environments demanding minimal disturbance.
Operational Safety Considerations
Drill and blast operations pose significant risks such as flyrock, dust, and vibration, necessitating strict safety protocols including exclusion zones and robust ventilation systems. Electric rock cutting reduces airborne pollutants and eliminates explosive hazards, offering a safer alternative with lower noise levels and fewer ground vibrations. However, the reliance on high-powered electrical equipment requires comprehensive insulation and grounding measures to prevent electrical accidents.
Productivity and Efficiency Metrics
Drill and Blast techniques typically achieve higher fragmentation rates, enabling faster mucking and loading cycles, which boosts overall productivity in hard rock mining. Electric Rock Cutting offers enhanced precision with reduced vibration and dust emissions, improving operational efficiency and worker safety while minimizing equipment downtime. Efficiency metrics favor Electric Rock Cutting in environments requiring controlled blasting and lower environmental impact, whereas Drill and Blast remains optimal for large-scale, high-throughput tunneling projects.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Electric rock cutting significantly reduces airborne dust and noise pollution compared to traditional drill and blast methods in mining, benefiting local air quality and worker health. The elimination of explosives decreases the risk of vibrations affecting surrounding ecosystems and infrastructure, leading to a more stable mining environment. Energy consumption and carbon emissions are also lower with electric rock cutting, making it a more environmentally sustainable option for extracting minerals.
Cost Analysis and Investment Factors
Drill and blast mining involves higher operational costs due to explosives procurement, ventilation, and extensive equipment maintenance, while electric rock cutting demands significant upfront investment in specialized cutting machinery but offers lower ongoing energy costs and reduced environmental impact. Electric rock cutting increases productivity by minimizing vibration and overbreak, which translates to cost savings in ground support and rehabilitation compared to drill and blast methods. Investment decisions hinge on factors such as ore hardness, underground ventilation capacity, energy prices, and regulatory compliance related to blasting emissions and worker safety.
Application Suitability by Geological Conditions
Drill and blast methods excel in hard, fractured rock formations where precision and high fragmentation are essential for efficient ore extraction. Electric rock cutting is more suitable for soft to medium-strength, layered sedimentary rocks, offering reduced vibration and dust, minimizing environmental impact. Geological conditions such as rock hardness, fracturing, and layer orientation critically influence the choice between these techniques to optimize operational safety and productivity.
Workforce Skills and Training Requirements
Drill and blast methods demand skilled operators with expertise in handling explosives and precise drilling techniques, requiring extensive safety and technical training programs. Electric rock cutting technology necessitates a workforce trained in advanced machinery operation, electrical systems, and remote controls, emphasizing continuous upskilling to adapt to evolving equipment. Both methods involve specialized training, but electric rock cutting often requires more technical proficiency in digital interfaces and maintenance protocols.
Future Trends in Hard Rock Extraction Technologies
Electric rock cutting technologies offer cleaner, more precise alternatives to traditional drill and blast methods, reducing environmental impact and enhancing worker safety. Advancements in automation and AI integration in electric cutting systems improve operational efficiency and real-time rock characterization. Future trends emphasize hybrid approaches combining electric cutting and controlled blasting to optimize extraction speed and cost-effectiveness in hard rock mining.
Related Important Terms
Selective Drilling
Selective drilling in mining enhances precision by targeting specific ore zones, reducing dilution and improving resource recovery compared to conventional drill and blast methods. Electric rock cutting offers a quieter, dust-free alternative, enabling more controlled excavation with minimal damage to surrounding rock structures, optimizing selective extraction processes.
Digital Blast Optimization
Digital Blast Optimization enhances Drill and Blast efficiency by leveraging advanced software to design precise blast patterns and monitor fragmentation in real-time, reducing explosive waste and improving rock breakage quality. Electric Rock Cutting offers a quieter, dust-free alternative but lacks the scalable, data-driven optimization capabilities that digital blasting technologies provide for maximizing operational productivity in mining.
High-Precision Charge Placement
High-precision charge placement in drill and blast mining ensures controlled fragmentation and minimizes ground vibration, enhancing safety and ore recovery. Electric rock cutting offers an alternative by providing precise, dust-free excavation without explosive use, but typically has slower advance rates compared to optimized blast patterns.
Controlled Fragmentation
Controlled fragmentation in drill and blast mining enables precise rock breakage through tailored explosive energy distribution, reducing overbreak and minimizing ground vibration. Electric rock cutting, by contrast, achieves controlled fragmentation mechanically with diamond or carbide tools, offering finer control and less environmental impact but generally slower advance rates compared to blasting.
Blast Vibration Mitigation
Blast vibration mitigation in drill and blast mining relies on controlled explosive energy and blast design to minimize ground and structural impact, leveraging techniques such as optimal charge distribution and delay timing. Electric rock cutting offers reduced vibration levels by mechanically fracturing rock with precision, significantly lowering the risk of damage to nearby infrastructure and improving overall site safety.
Electric Continuous Miner
Electric continuous miners offer a safer and more efficient alternative to traditional drill and blast methods by eliminating blasting vibrations and reducing airborne dust and emissions. These machines enhance productivity through continuous material extraction, lowering operational costs and environmental impact in underground mining operations.
Mechanical Rock Excavation
Mechanical rock excavation methods such as electric rock cutting offer precise control and reduced vibration compared to traditional drill and blast techniques, enhancing safety and minimizing environmental impact. Electric rock cutting delivers consistent rock fragmentation without explosive use, leading to lower operational costs and improved productivity in underground mining operations.
Battery-Electric Roadheaders
Battery-electric roadheaders offer a cleaner and quieter alternative to traditional drill and blast methods in mining by using precise electric rock cutting technology that reduces dust and vibration. This approach enhances operational efficiency, improves worker safety, and lowers environmental impact compared to explosive-based extraction techniques.
Zero-Emissions Rock Cutting
Zero-emissions rock cutting using electric technology drastically reduces environmental impact by eliminating diesel fumes and particulate emissions associated with traditional drill and blast methods. This approach enhances worker safety, improves air quality in underground mines, and supports sustainable mining operations by leveraging advanced electric machinery and battery-powered rock cutting systems.
Autonomous Blasting Systems
Autonomous blasting systems in mining offer precise control and increased safety compared to traditional drill and blast methods by integrating AI-driven sensors and automated charge placement. Electric rock cutting presents a quieter, dust-free alternative with reduced environmental impact, but autonomous blasting systems provide superior fragmentation efficiency and operational scalability in large-scale mining operations.
Drill and Blast vs Electric Rock Cutting Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com