Bulk storage facilities offer extensive space designed for high-volume inventory, ideal for businesses needing cost-effective solutions for large quantities of goods. Urban warehousing provides proximity to metropolitan markets, enabling faster delivery times and improved last-mile logistics. Choosing between the two depends on balancing storage capacity with distribution speed and accessibility.
Table of Comparison
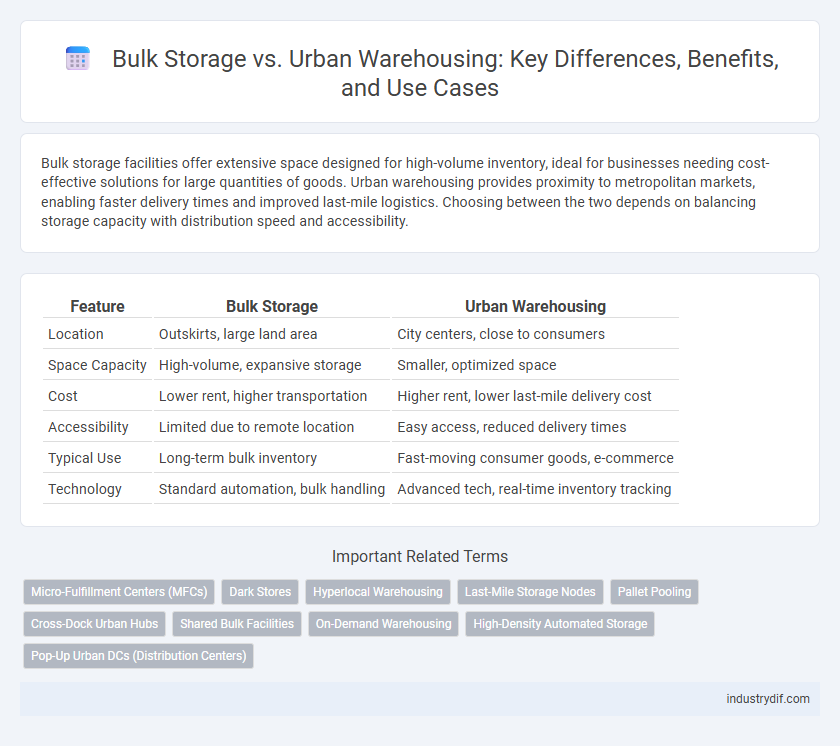
| Feature | Bulk Storage | Urban Warehousing |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Outskirts, large land area | City centers, close to consumers |
| Space Capacity | High-volume, expansive storage | Smaller, optimized space |
| Cost | Lower rent, higher transportation | Higher rent, lower last-mile delivery cost |
| Accessibility | Limited due to remote location | Easy access, reduced delivery times |
| Typical Use | Long-term bulk inventory | Fast-moving consumer goods, e-commerce |
| Technology | Standard automation, bulk handling | Advanced tech, real-time inventory tracking |
Introduction to Bulk Storage and Urban Warehousing
Bulk storage involves storing large quantities of goods in expansive facilities typically located in suburban or rural areas, optimizing cost efficiency and space utilization. Urban warehousing focuses on smaller, strategically positioned storage spaces within city limits to ensure rapid delivery and better access to end consumers. These two warehousing models cater to different supply chain needs, balancing between volume capacity and proximity to demand centers.
Defining Bulk Storage: Key Features
Bulk storage in warehousing refers to the large-scale storage of goods, typically characterized by vast open spaces designed to accommodate high volumes of homogeneous products. Key features include high shelving units, pallet racking systems, and minimal handling requirements to optimize space utilization and inventory management. This method contrasts with urban warehousing by prioritizing capacity and efficiency over proximity to end consumers.
What is Urban Warehousing?
Urban warehousing refers to strategically located storage facilities within or near city centers, designed to facilitate rapid distribution and last-mile delivery. Unlike bulk storage warehouses typically situated in suburban or rural areas with large-scale capacity, urban warehouses prioritize proximity to end consumers over volume. These facilities leverage advanced inventory management and technology to optimize space and meet the increasing demand for fast e-commerce fulfillment in densely populated areas.
Location and Accessibility Differences
Bulk storage facilities are typically located in peripheral industrial zones with ample space for large-scale inventory, prioritizing cost efficiency over proximity. Urban warehousing is strategically situated within city centers to ensure rapid delivery and high accessibility, catering to last-mile logistics demands. The location of urban warehouses allows for enhanced connectivity to transportation networks and consumer markets compared to bulk storage hubs.
Space Utilization and Layout Comparison
Bulk storage facilities maximize space utilization by using high-density shelving and pallet stacking systems, enabling storage of large quantities of goods in expansive warehouse footprints. Urban warehousing prioritizes compact layouts with multiple smaller units strategically located near city centers to reduce last-mile delivery times, often sacrificing some space efficiency for accessibility. The layout in bulk storage emphasizes vertical storage and wide aisles for forklifts, whereas urban warehouses optimize for quick inventory turnover and flexible configurations within limited square footage.
Inventory Management Approaches
Bulk storage utilizes centralized, large-scale facilities optimized for high-volume inventory, enabling efficient stock rotation and minimizing handling costs through palletized systems. Urban warehousing employs decentralized, smaller facilities closer to end consumers, allowing for faster order fulfillment and real-time inventory tracking using advanced warehouse management systems (WMS). Inventory management in urban warehousing relies heavily on demand forecasting and dynamic replenishment to reduce stockouts and optimize space utilization in limited areas.
Cost Structures in Bulk vs Urban Warehousing
Bulk storage facilities typically offer lower cost per square foot due to economies of scale and location in less expensive, peripheral areas, making them ideal for high-volume, low-cost inventory. Urban warehousing incurs higher costs driven by premium real estate prices, increased labor expenses, and stricter regulatory compliance, but offers advantages in faster delivery times and proximity to end consumers. The cost structure differences significantly impact supply chain strategies, influencing decisions on inventory placement, transportation expenses, and service level commitments.
Technology and Automation Trends
Bulk storage facilities increasingly adopt advanced automation technologies such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and robotic palletizers to enhance inventory management and throughput efficiency. Urban warehousing leverages IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics to optimize space utilization and facilitate real-time tracking in constrained city environments. Integration of warehouse management systems (WMS) combined with machine learning algorithms enables both bulk and urban warehouses to improve predictive maintenance and demand forecasting.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bulk storage facilities typically consume more land and energy due to their large-scale operations, leading to higher carbon emissions compared to urban warehousing. Urban warehousing reduces transportation distances by being closer to end consumers, significantly lowering greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to sustainable last-mile delivery. Implementing energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy sources in both bulk and urban warehouses enhances sustainability and reduces overall environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Warehousing Model for Your Business
Bulk storage offers cost-effective solutions with large capacity and lower storage costs per unit, ideal for businesses managing high volumes of inventory with less frequent access needs. Urban warehousing provides proximity to customers, enabling faster delivery times and enhanced last-mile logistics, suitable for companies prioritizing speed and flexibility in dense metropolitan areas. Selecting the right warehousing model depends on balancing inventory volume, delivery speed requirements, and geographic market coverage to optimize supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs)
Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs) optimize urban warehousing by enabling rapid order processing and minimizing last-mile delivery times in densely populated areas, contrasting with bulk storage facilities that prioritize large-scale inventory holding in suburban locations. MFCs leverage automation and compact layouts to enhance e-commerce fulfillment efficiency, addressing the growing demand for faster delivery in urban settings.
Dark Stores
Dark stores, a key component of urban warehousing, enable rapid, localized fulfillment by storing goods in smaller, strategically positioned facilities within city limits, contrasting with bulk storage that relies on large, centralized warehouses often located in suburban or rural areas. This shift towards dark stores supports faster delivery times and enhanced inventory efficiency for e-commerce and omnichannel retail operations in densely populated urban environments.
Hyperlocal Warehousing
Hyperlocal warehousing, a subset of urban warehousing, enables rapid delivery by strategically positioning inventory closer to end consumers within dense urban areas, contrasting with bulk storage that centralizes large volumes in remote facilities. This approach enhances supply chain efficiency through reduced last-mile costs and faster order fulfillment, essential for meeting the growing demands of e-commerce and same-day delivery services.
Last-Mile Storage Nodes
Bulk storage facilities are typically large, centralized warehouses located on city outskirts designed to handle high volumes of inventory, while urban warehousing strategically places smaller storage nodes within metropolitan areas to facilitate faster last-mile delivery. Last-mile storage nodes in urban warehousing reduce transit times and logistics costs by positioning goods closer to end consumers, enhancing efficiency in e-commerce and retail supply chains.
Pallet Pooling
Bulk storage offers high-capacity, cost-efficient solutions ideal for long-term inventory management, while urban warehousing emphasizes rapid order fulfillment and proximity to end customers. Pallet pooling enhances both models by enabling shared, reusable pallets that reduce handling costs, improve supply chain sustainability, and streamline inventory turnover across centralized or decentralized warehouse locations.
Cross-Dock Urban Hubs
Cross-dock urban hubs in warehousing optimize the flow of goods by minimizing storage time and facilitating rapid distribution directly from inbound to outbound transportation, which contrasts with bulk storage facilities designed primarily for long-term inventory holding. These hubs enhance urban supply chain efficiency by reducing last-mile delivery costs and improving responsiveness to consumer demand in dense metropolitan areas.
Shared Bulk Facilities
Shared bulk facilities in urban warehousing optimize space utilization by consolidating large volumes of goods in centrally located warehouses, reducing transportation costs and improving last-mile delivery efficiency. These facilities leverage economies of scale and advanced inventory management systems to meet the high demand density in urban areas while minimizing environmental impact.
On-Demand Warehousing
On-demand warehousing offers flexible, scalable solutions contrasting traditional bulk storage by utilizing underused urban spaces to meet fluctuating inventory demands. This model enhances supply chain agility through real-time capacity access, reduced transportation costs, and improved last-mile delivery efficiency in densely populated markets.
High-Density Automated Storage
High-density automated storage in bulk storage facilities maximizes space utilization through advanced mechanization and robotics, enabling efficient handling of large inventory volumes with minimal footprint. Urban warehousing leverages compact, technology-driven solutions to optimize limited city space, enhancing rapid order fulfillment and reducing last-mile delivery times.
Pop-Up Urban DCs (Distribution Centers)
Pop-up urban distribution centers (DCs) optimize urban warehousing by offering flexible, temporary storage solutions closer to high-demand markets, reducing last-mile delivery costs and transit times compared to traditional bulk storage facilities. These urban DCs leverage smaller footprint spaces in dense city areas, enhancing supply chain responsiveness and supporting e-commerce growth with faster order fulfillment.
Bulk Storage vs Urban Warehousing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com