Distribution centers are large-scale facilities designed to store and ship a broad range of products to various retail locations or customers, emphasizing high volume and extensive inventory management. Micro-fulfillment centers are compact, automated warehouses located closer to urban areas, prioritizing rapid order processing and last-mile delivery efficiency. Both play crucial roles in supply chain optimization, with micro-fulfillment centers addressing the demand for speed in e-commerce.
Table of Comparison
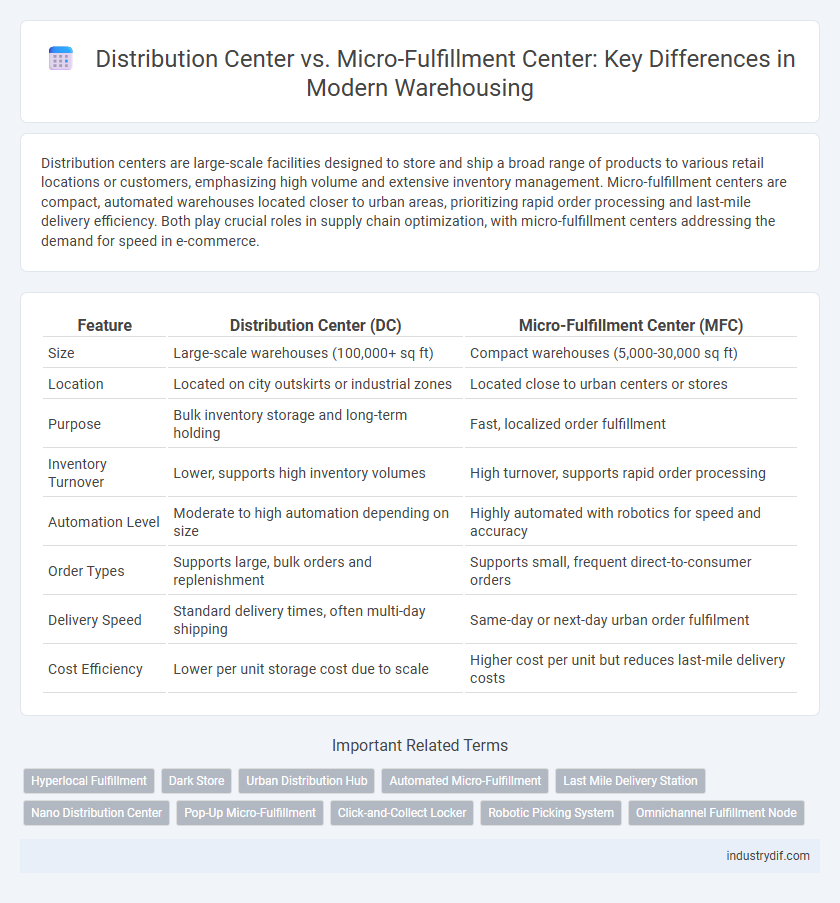
| Feature | Distribution Center (DC) | Micro-Fulfillment Center (MFC) |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Large-scale warehouses (100,000+ sq ft) | Compact warehouses (5,000-30,000 sq ft) |
| Location | Located on city outskirts or industrial zones | Located close to urban centers or stores |
| Purpose | Bulk inventory storage and long-term holding | Fast, localized order fulfillment |
| Inventory Turnover | Lower, supports high inventory volumes | High turnover, supports rapid order processing |
| Automation Level | Moderate to high automation depending on size | Highly automated with robotics for speed and accuracy |
| Order Types | Supports large, bulk orders and replenishment | Supports small, frequent direct-to-consumer orders |
| Delivery Speed | Standard delivery times, often multi-day shipping | Same-day or next-day urban order fulfilment |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower per unit storage cost due to scale | Higher cost per unit but reduces last-mile delivery costs |
Definition of Distribution Center
A distribution center is a large warehouse facility designed to store products from multiple suppliers, manage inventory, and efficiently facilitate the sorting and shipping of goods to retail locations or directly to customers. It serves as a critical hub in supply chain logistics, enabling bulk storage and bulk handling with advanced inventory management systems to optimize order fulfillment. Distribution centers typically operate with high-capacity storage, cross-docking capabilities, and sophisticated technology to streamline large-scale product flow across diverse channels.
Overview of Micro-Fulfillment Center
Micro-fulfillment centers are compact, automated facilities designed to expedite order fulfillment by placing inventory closer to end consumers, significantly reducing last-mile delivery times. These centers utilize advanced robotics and AI-driven inventory management systems to efficiently handle high volumes of small, frequent orders in urban areas. Unlike traditional distribution centers, micro-fulfillment centers prioritize speed and space optimization, enabling retailers to meet growing e-commerce demand with enhanced agility.
Key Differences Between Distribution Center and Micro-Fulfillment Center
Distribution centers handle large volumes of inventory and serve wide geographic regions with bulk shipments, while micro-fulfillment centers focus on rapid order processing in urban areas using automation to support last-mile delivery. Distribution centers typically cover tens of thousands of square feet and prioritize storage capacity, whereas micro-fulfillment centers occupy smaller spaces, often integrated within retail stores or urban warehouses, emphasizing speed and efficiency. The key operational difference lies in the scale and purpose: distribution centers optimize for distribution and stock management, whereas micro-fulfillment centers optimize for rapid, localized e-commerce fulfillment.
Operational Workflow Comparison
Distribution centers typically manage large-scale inventory with slower, batch-based order processing to handle high volumes across broad geographic regions. Micro-fulfillment centers utilize automated systems and robotics to enable rapid, smaller order fulfillment closer to end customers, enhancing speed and accuracy. Workflow in distribution centers emphasizes bulk storage and outbound shipping, whereas micro-fulfillment centers focus on real-time inventory picking and last-mile delivery efficiency.
Storage Capacity and Footprint Analysis
Distribution centers typically offer large storage capacities ranging from hundreds of thousands to millions of square feet, designed to handle bulk inventory and support high-volume order fulfillment. Micro-fulfillment centers, on the other hand, have a significantly smaller footprint, often under 50,000 square feet, optimized for rapid processing of local orders with dense storage systems like automated shelving. The smaller physical footprint of micro-fulfillment centers enables efficient urban placement, reducing last-mile delivery times but limiting overall storage capacity compared to traditional distribution centers.
Location Strategy: Urban vs. Rural Placement
Distribution centers are typically located in rural or suburban areas to leverage larger spaces and lower land costs, enabling bulk storage and efficient long-haul transportation. Micro-fulfillment centers prioritize urban placement near dense customer bases to facilitate rapid order processing and last-mile delivery. The strategic location choice directly impacts operational efficiency, delivery speed, and overall supply chain responsiveness in warehousing logistics.
Technology and Automation Utilization
Distribution centers leverage large-scale warehouse management systems (WMS) and automated conveyor belts to handle high-volume order processing and bulk inventory storage efficiently. Micro-fulfillment centers prioritize advanced robotics, AI-driven picking systems, and real-time inventory tracking to enable rapid order fulfillment within urban or retail environments. Both facility types integrate IoT devices and data analytics platforms to optimize inventory accuracy and reduce labor costs, but micro-fulfillment centers emphasize compact, speed-focused automation tailored for last-mile delivery demands.
Cost Implications and Return on Investment
Distribution centers typically involve higher initial capital expenditures due to larger facility sizes and extensive labor requirements, impacting the overall cost structure. Micro-fulfillment centers, leveraging automation and proximity to end consumers, offer reduced last-mile delivery expenses and faster inventory turnover, enhancing return on investment. Businesses must weigh the scalability and operational efficiencies of distribution centers against the agility and lower overhead costs inherent to micro-fulfillment centers to optimize cost implications and ROI.
Impact on Last-Mile Delivery Efficiency
Distribution centers handle large volumes of inventory with centralized storage, supporting bulk shipments to retail locations but often resulting in longer last-mile delivery times. Micro-fulfillment centers are strategically located near urban areas, enabling faster order processing and reduced delivery distances, significantly enhancing last-mile delivery efficiency. Leveraging micro-fulfillment reduces transportation costs and accelerates delivery speeds, meeting growing consumer demand for quick fulfillment.
Choosing the Right Fulfillment Model for Your Business
Choosing the right fulfillment model depends on factors such as order volume, product type, and delivery speed. Distribution centers offer large-scale storage and bulk shipping capabilities ideal for high inventory and wide product ranges. Micro-fulfillment centers optimize last-mile delivery by using automated systems within urban areas, reducing delivery times and costs for e-commerce businesses focused on rapid order fulfillment.
Related Important Terms
Hyperlocal Fulfillment
Distribution centers typically manage large-scale inventory for regional or national distribution, while micro-fulfillment centers are designed for hyperlocal fulfillment, enabling faster delivery within urban areas by using automated systems in smaller spaces. Hyperlocal fulfillment through micro-fulfillment centers reduces last-mile delivery costs and improves order accuracy and speed, meeting growing consumer demand for rapid e-commerce deliveries.
Dark Store
Dark stores serve as specialized micro-fulfillment centers designed to accelerate e-commerce order processing by enabling rapid picking and packing within urban areas. Unlike traditional distribution centers, dark stores optimize last-mile delivery efficiency through automated inventory management and proximity to high-demand customer locations.
Urban Distribution Hub
Urban Distribution Hubs leverage Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs) for faster, last-mile delivery by utilizing automated storage and retrieval systems in compact spaces, contrasting with traditional Distribution Centers (DCs) that operate larger, centralized facilities optimized for bulk storage and regional distribution. MFCs enhance urban logistics efficiency by reducing transportation costs and delivery times, supporting high-demand e-commerce fulfillment in dense metropolitan areas.
Automated Micro-Fulfillment
Automated Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs) leverage advanced robotics and AI-driven systems to streamline inventory storage and order processing within compact urban spaces, offering faster delivery and reduced operational costs compared to traditional large-scale Distribution Centers. These automated MFCs optimize last-mile logistics by enabling high-speed picking and packing, enhancing supply chain efficiency in e-commerce and retail sectors.
Last Mile Delivery Station
Distribution centers serve as large-scale warehousing hubs that store vast inventory and fulfill bulk orders, optimizing supply chain efficiency over broad regional areas. Micro-fulfillment centers function as compact, automated facilities strategically located near urban areas, accelerating last mile delivery by enabling faster, cost-effective order fulfillment and reducing delivery times.
Nano Distribution Center
A Nano Distribution Center (NDC) enhances last-mile delivery efficiency by operating on a smaller scale than traditional Distribution Centers (DCs) and Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs), focusing on hyper-local inventory storage near urban demand hubs. NDCs leverage advanced automation and real-time data analytics to optimize order fulfillment speed and reduce transportation costs, meeting the growing demand for rapid e-commerce delivery.
Pop-Up Micro-Fulfillment
Pop-up micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) are compact, temporary facilities designed to accelerate order processing and last-mile delivery within urban areas, contrasting traditional distribution centers that operate on a larger scale with slower inventory turnover. These pop-up MFCs leverage automation and localized inventory to enhance delivery speed and reduce transportation costs, meeting the growing demand for rapid e-commerce fulfillment.
Click-and-Collect Locker
Click-and-collect lockers in distribution centers support high-volume bulk storage with centralized inventory management, optimizing large-scale order fulfillment and efficient regional distribution. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage these lockers for rapid last-mile delivery and same-day pickup, minimizing transit times and enhancing urban customer convenience.
Robotic Picking System
Robotic picking systems in Distribution Centers enhance large-scale order accuracy and throughput by automating bulk inventory handling and conveyor integration. Micro-Fulfillment Centers utilize compact robotic picking technology to accelerate last-mile delivery and optimize storage density in urban environments.
Omnichannel Fulfillment Node
Distribution centers serve as large-scale omnichannel fulfillment nodes designed for bulk storage and regional order consolidation, optimizing inventory flow across multiple retail channels. Micro-fulfillment centers operate as compact, technology-driven nodes embedded within urban areas to accelerate last-mile delivery and support rapid order fulfillment in dense consumer markets.
Distribution Center vs Micro-Fulfillment Center Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com