Conventional forklifts require skilled operators to manually handle loading and unloading tasks, increasing labor costs and safety risks in warehousing environments. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) enhance efficiency by autonomously transporting goods, reducing human error and streamlining inventory management. Implementing AGVs leads to improved operational accuracy and consistent productivity compared to traditional forklift use.
Table of Comparison
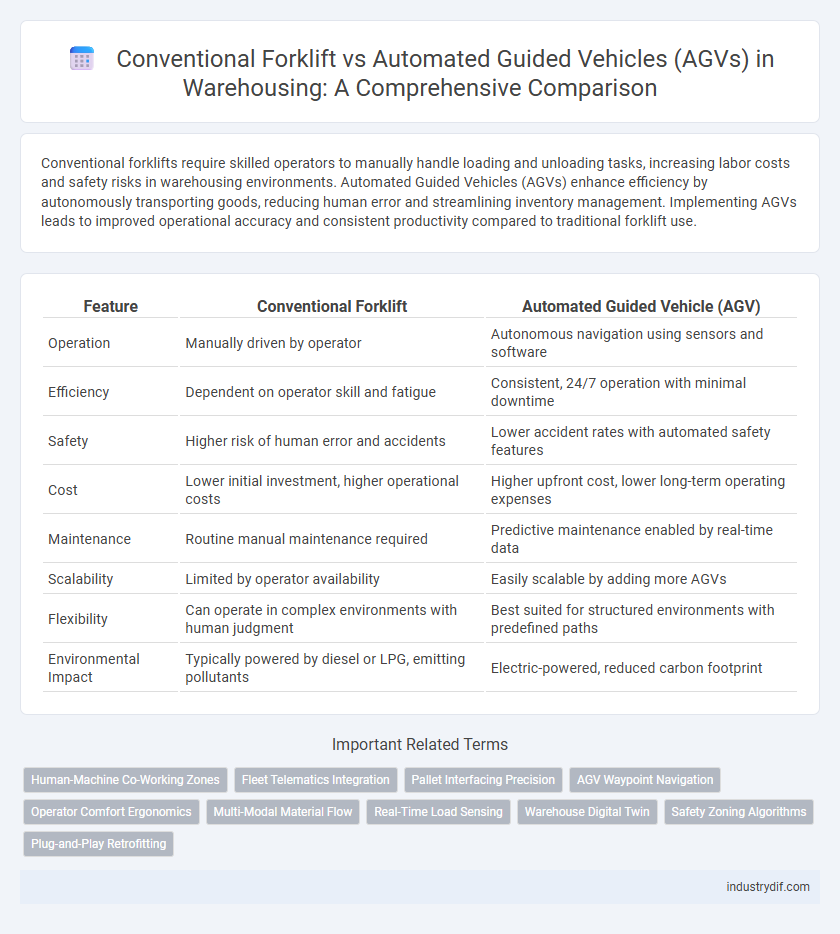
| Feature | Conventional Forklift | Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Manually driven by operator | Autonomous navigation using sensors and software |
| Efficiency | Dependent on operator skill and fatigue | Consistent, 24/7 operation with minimal downtime |
| Safety | Higher risk of human error and accidents | Lower accident rates with automated safety features |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, higher operational costs | Higher upfront cost, lower long-term operating expenses |
| Maintenance | Routine manual maintenance required | Predictive maintenance enabled by real-time data |
| Scalability | Limited by operator availability | Easily scalable by adding more AGVs |
| Flexibility | Can operate in complex environments with human judgment | Best suited for structured environments with predefined paths |
| Environmental Impact | Typically powered by diesel or LPG, emitting pollutants | Electric-powered, reduced carbon footprint |
Introduction to Conventional Forklifts and Automated Guided Vehicles
Conventional forklifts are manually operated industrial trucks designed for lifting and transporting materials within warehouses, offering flexibility and control through human operation. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are driverless, computer-controlled machines that navigate predefined paths to move goods, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Both technologies play crucial roles in modern warehousing, balancing manual dexterity with automation for optimized material handling.
Key Differences Between Conventional Forklifts and AGVs
Conventional forklifts require manual operation by skilled drivers, whereas Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) navigate warehouse environments using pre-programmed routes and sensors, enabling hands-free operation. Forklifts offer flexibility for varied tasks and terrain, while AGVs provide consistent, repeatable movements with reduced risk of human error and accidents. AGVs typically improve efficiency and safety by integrating with warehouse management systems, contrasting with the higher labor costs and training demands associated with conventional forklifts.
Operational Efficiency Comparison
Conventional forklifts require manual operation, leading to variability in productivity and increased labor costs, while Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) deliver consistent performance with reduced human error and lower operational expenses. AGVs optimize warehouse logistics by enabling continuous operation and precise load handling, enhancing throughput and minimizing downtime. The integration of AGVs supports scalable workflows, improving order fulfillment speed and overall warehouse efficiency compared to traditional forklift systems.
Safety Features and Risk Factors
Conventional forklifts pose higher risks of operator injury and accidents due to limited visibility and manual control, while Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) incorporate advanced safety sensors, collision avoidance systems, and controlled navigation to minimize workplace hazards. AGVs reduce human error by following predefined paths and real-time obstacle detection, enhancing operational safety in warehouses. Despite higher upfront costs, AGVs significantly decrease risks related to forklift tip-overs, pedestrian collisions, and load mishandling compared to traditional forklifts.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Savings
Conventional forklifts require a lower initial investment, typically ranging from $20,000 to $50,000 per unit, while automated guided vehicles (AGVs) can cost upwards of $100,000 due to advanced sensors and control systems. Despite the high upfront cost, AGVs offer significant long-term savings by reducing labor expenses, minimizing accidents, and increasing operational efficiency through continuous, precise automation. Over time, companies adopting AGVs can achieve a lower total cost of ownership compared to conventional forklifts, especially in large-scale warehouse operations with high throughput requirements.
Flexibility and Scalability in Warehousing Operations
Conventional forklifts offer high flexibility due to their ability to navigate complex layouts and handle diverse load types without extensive reprogramming. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) provide scalable solutions that can easily expand through additional units integrated into a warehouse management system for synchronized operations. AGVs enhance workflow scalability while conventional forklifts maintain operational adaptability in dynamic warehousing environments.
Technological Requirements and Integration
Conventional forklifts demand minimal technological infrastructure, primarily requiring manual operation and basic safety systems, which simplifies initial integration but limits scalability in automated environments. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) necessitate advanced technological frameworks including navigation systems like LiDAR or magnetic tape, real-time data processing, and seamless integration with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) for efficient path planning and operational coordination. Implementing AGVs involves substantial investment in sensor technology, software, and connectivity infrastructure to ensure smooth interoperability and enhance overall warehouse automation efficiency.
Workforce Implications and Training Needs
Conventional forklifts require operators with specialized training in manual driving skills, safety protocols, and equipment maintenance, leading to ongoing workforce development costs and potential labor shortages. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) shift workforce needs toward technical roles in programming, monitoring, and maintenance, reducing manual handling but increasing demand for skilled technicians and digital literacy. Transitioning to AGVs necessitates comprehensive training programs focused on automation systems, software troubleshooting, and remote operation management to ensure operational efficiency and safety compliance.
Maintenance and Downtime Considerations
Conventional forklifts require frequent manual maintenance such as engine checks, oil changes, and brake inspections, leading to higher downtime due to human error or wear and tear. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) feature predictive maintenance systems that reduce unexpected failures and optimize scheduling, significantly minimizing operational disruptions. Investing in AGVs can lead to lower overall maintenance costs and enhanced productivity by decreasing downtime associated with manual forklift upkeep.
Future Trends in Warehouse Material Handling
Conventional forklifts continue to be widely used due to their flexibility and lower initial cost, but Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are rapidly advancing with improved navigation systems, AI integration, and enhanced safety features. Future trends in warehouse material handling emphasize the growth of AGVs for increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, and real-time inventory management through IoT connectivity. The industry is moving toward hybrid systems where conventional forklifts are complemented by AGVs for optimized workflow and scalable automation solutions.
Related Important Terms
Human-Machine Co-Working Zones
Human-machine co-working zones in warehousing optimize efficiency by integrating conventional forklifts operated by skilled workers with automated guided vehicles (AGVs) that navigate predefined paths, reducing human error and increasing throughput. These zones require clear safety protocols and advanced sensor technology to ensure seamless collaboration, minimizing accidents while enhancing productivity in mixed operational environments.
Fleet Telematics Integration
Conventional forklifts rely on manual operation with limited telematics capabilities, which restricts real-time fleet management and performance monitoring. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) integrate seamlessly with advanced fleet telematics systems, enabling precise tracking, optimized routing, and enhanced productivity through data-driven decision-making in warehouse operations.
Pallet Interfacing Precision
Conventional forklifts rely heavily on operator skill, resulting in variable pallet interfacing precision and potential for misalignment or damage. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) utilize advanced sensors and navigation systems to achieve consistently high pallet interfacing accuracy, reducing errors and improving warehouse efficiency.
AGV Waypoint Navigation
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) utilize waypoint navigation systems that enable precise, programmable routes for efficient material handling, reducing human error and operational downtime compared to conventional forklifts. This technology improves warehouse productivity by allowing seamless integration with warehouse management systems (WMS) for optimized path planning and real-time adjustments.
Operator Comfort Ergonomics
Conventional forklifts rely heavily on manual operation, often causing operator fatigue and repetitive strain due to constant steering, lifting, and control handling, while automated guided vehicles (AGVs) reduce physical demands by autonomously navigating warehouse paths and minimizing human intervention. Enhanced ergonomics in AGVs contribute to improved operator comfort, lower risk of musculoskeletal disorders, and increased productivity in high-throughput warehousing environments.
Multi-Modal Material Flow
Conventional forklifts provide flexible, human-operated handling suited for varied warehouse tasks, yet Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) optimize multi-modal material flow by seamlessly integrating with conveyor systems, robotic arms, and inventory management software for continuous, efficient movement. AGVs reduce labor costs and human error while enabling synchronized transportation across different warehouse modes, improving throughput and real-time tracking in high-volume distribution centers.
Real-Time Load Sensing
Conventional forklifts rely on operator judgment and limited sensor input, resulting in less precise load handling and potential safety risks, whereas Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) utilize advanced real-time load sensing technologies to monitor weight distribution and optimize stability dynamically. Real-time data from AGVs enhances operational efficiency by reducing load damage, improving safety, and enabling seamless integration with warehouse management systems (WMS).
Warehouse Digital Twin
Conventional forklifts rely on manual operation, creating less data integration and limited real-time accuracy within a Warehouse Digital Twin, while Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) provide continuous data flow and precise movement tracking, enhancing digital twin fidelity and operational efficiency. Incorporating AGVs enables seamless synchronization between physical assets and the digital model, optimizing space utilization, inventory management, and predictive maintenance in smart warehouse environments.
Safety Zoning Algorithms
Conventional forklifts rely heavily on operator skill and basic safety protocols, whereas Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) integrate advanced safety zoning algorithms that dynamically create virtual boundaries to prevent collisions and ensure safe navigation in busy warehouse environments. These algorithms utilize real-time sensor data and predictive modeling to adapt to changing warehouse layouts and human movements, significantly reducing accident risks and improving overall operational safety.
Plug-and-Play Retrofitting
Plug-and-play retrofitting enables conventional forklifts to integrate advanced automation features without extensive infrastructure changes, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. In contrast, automated guided vehicles (AGVs) inherently support plug-and-play deployment, allowing seamless implementation in existing warehouse workflows with minimal disruption.
Conventional Forklift vs Automated Guided Vehicle Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com