Manual handling in warehousing relies heavily on human labor for tasks such as lifting, moving, and sorting goods, which can increase the risk of injuries and reduce efficiency. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) enhance operational productivity by automating repetitive tasks, reducing errors, and promoting safer work environments. Integrating AMRs into warehouse processes optimizes inventory management, accelerates order fulfillment, and lowers labor costs.
Table of Comparison
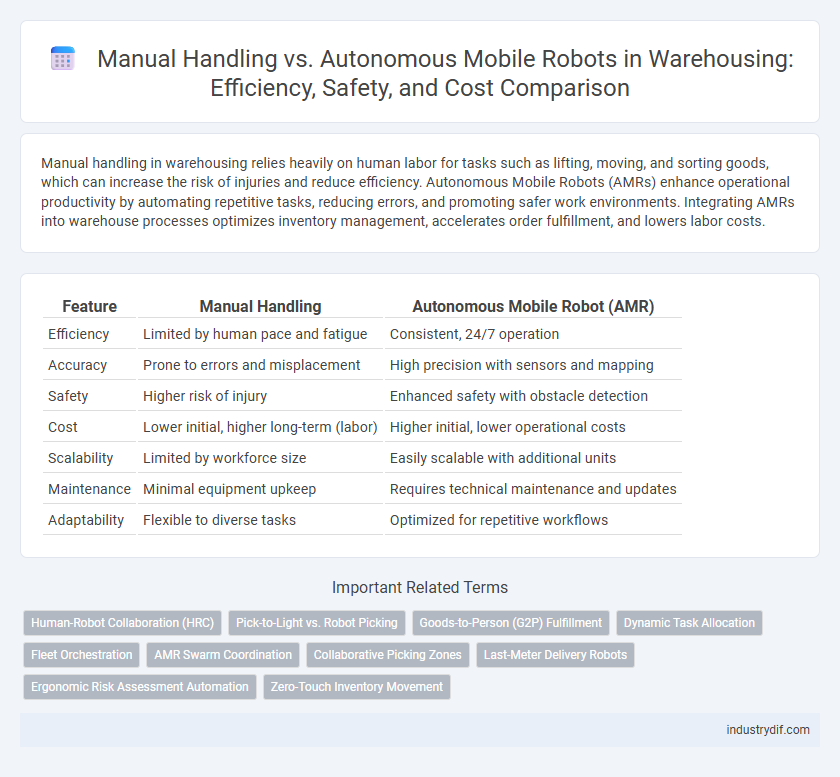
| Feature | Manual Handling | Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR) |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Limited by human pace and fatigue | Consistent, 24/7 operation |
| Accuracy | Prone to errors and misplacement | High precision with sensors and mapping |
| Safety | Higher risk of injury | Enhanced safety with obstacle detection |
| Cost | Lower initial, higher long-term (labor) | Higher initial, lower operational costs |
| Scalability | Limited by workforce size | Easily scalable with additional units |
| Maintenance | Minimal equipment upkeep | Requires technical maintenance and updates |
| Adaptability | Flexible to diverse tasks | Optimized for repetitive workflows |
Introduction to Manual Handling and Autonomous Mobile Robots
Manual handling in warehousing involves physical tasks such as lifting, carrying, and moving goods, which can lead to fatigue and injury risks for workers. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) use advanced sensors and navigation systems to transport items efficiently, reducing human labor and increasing operational safety. Implementing AMRs enhances productivity by automating repetitive tasks while minimizing workplace accidents linked to manual handling.
Key Differences Between Manual and Automated Warehousing
Manual warehousing relies on human labor for tasks such as picking, sorting, and transporting goods, which often leads to increased labor costs, slower processing times, and higher risk of workplace injuries. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) integrate advanced sensors, AI, and machine learning to navigate warehouse environments independently, improving operational efficiency, accuracy, and safety while reducing human error. Key differences include scalability, with AMRs offering consistent performance and faster throughput compared to the variable pace of manual workflows, and cost-effectiveness over time due to reduced labor dependency and minimized downtime.
Efficiency: Human Labor vs. Autonomous Mobile Robots
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) in warehousing outperform manual handling by significantly increasing efficiency through faster item retrieval and reduced human error rates. AMRs operate continuously without fatigue, enabling consistent throughput and optimized inventory management compared to the variable pace of human labor. Data from industry reports show AMRs can improve operational efficiency by up to 40%, resulting in lower labor costs and higher order accuracy.
Safety Considerations in Manual vs. AMR Warehousing
Manual handling in warehousing presents significant safety risks, including musculoskeletal injuries from repetitive lifting and potential accidents due to human error. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) enhance safety by reducing worker exposure to hazardous environments and minimizing manual lifting tasks, thereby decreasing injury rates. Integration of AMRs requires safety protocols such as robot navigation systems and emergency stop features to ensure seamless human-robot coexistence on the warehouse floor.
Scalability and Flexibility: Which Solution Prevails?
Manual handling offers immediate adaptability in diverse warehousing tasks but struggles to scale efficiently as order volumes increase, leading to higher labor costs and inconsistency. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) provide unparalleled scalability by seamlessly integrating with warehouse management systems and optimizing routes, allowing for rapid adjustment to fluctuating inventory demands. The flexibility and data-driven precision of AMRs ultimately surpass manual handling in large-scale operations seeking sustainable growth and efficiency.
Cost Analysis: Upfront Investments and Operational Expenses
Manual handling in warehousing typically demands lower upfront investment but incurs higher operational expenses due to labor costs, injury risks, and reduced efficiency. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) require significant initial capital for acquisition, integration, and staff training but offer long-term savings by minimizing labor expenses, lowering error rates, and increasing throughput. Evaluating total cost of ownership highlights that AMRs can reduce overall warehousing costs by optimizing workflows and decreasing reliance on manual labor over time.
Impact on Workforce and Job Roles
Manual handling in warehousing often leads to physical strain, repetitive injuries, and labor-intensive tasks that limit workforce efficiency and job satisfaction. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) significantly reduce these risks by automating material transport, allowing employees to focus on higher-value roles that require decision-making and oversight. The integration of AMRs shifts job roles from manual labor to operational management, maintenance, and system monitoring, fostering workforce upskilling and improved productivity.
Technology Integration and Infrastructure Requirements
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) require advanced technology integration including sensors, navigation software, and real-time data processing systems, contrasting with manual handling's reliance on basic tools and human labor. AMRs demand significant infrastructure upgrades such as wireless networks, charging stations, and optimized warehouse layouts to support seamless operation. Investing in AMR technology enhances efficiency and accuracy but necessitates thorough infrastructure planning to fully leverage automation benefits.
Maintenance and Downtime Comparisons
Manual handling in warehousing requires minimal maintenance but often leads to higher downtime due to worker fatigue and potential injuries. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) demand regular software updates and hardware inspections, which reduce unexpected breakdowns and improve overall uptime. While AMRs involve scheduled maintenance costs, their consistent operation significantly lowers downtime compared to manual labor.
Future Trends in Warehousing Automation
Future trends in warehousing automation emphasize a shift from manual handling to autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to increase efficiency and reduce workplace injuries. AMRs enable real-time inventory management and seamless integration with warehouse management systems (WMS), driving operational accuracy and productivity. The adoption of AI-powered navigation and advanced sensors in AMRs is expected to further optimize logistics workflows and minimize human error in complex warehouse environments.
Related Important Terms
Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC)
Human-robot collaboration (HRC) in warehousing enhances efficiency by combining manual handling's flexibility with autonomous mobile robots' precision and endurance, reducing worker strain and increasing throughput. Integrating advanced sensors and AI enables seamless interaction, ensuring safety and optimizing task allocation between humans and robots.
Pick-to-Light vs. Robot Picking
Pick-to-Light systems enhance manual handling efficiency by guiding workers with visual indicators to accurately pick items, reducing errors and increasing order fulfillment speed. Robot picking using Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) automates the retrieval process through AI-driven navigation and object recognition, significantly boosting throughput and minimizing labor costs in high-volume warehousing operations.
Goods-to-Person (G2P) Fulfillment
Manual handling in Warehousing for Goods-to-Person (G2P) Fulfillment often leads to increased labor costs, slower order processing, and higher risk of worker injury. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) dramatically improve efficiency by autonomously transporting goods directly to workers, enhancing speed, accuracy, and reducing physical strain in warehouse operations.
Dynamic Task Allocation
Dynamic task allocation in warehousing significantly improves efficiency by assigning manual handling tasks based on real-time workload and human availability, optimizing labor resources and reducing bottlenecks. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) enhance this process by autonomously adapting to changing environments and task priorities, seamlessly integrating with manual operators to streamline operations and increase throughput.
Fleet Orchestration
Fleet orchestration in warehousing enhances efficiency by coordinating autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to optimize task allocation, reduce idle time, and streamline inventory movement compared to manual handling methods. Integrating AI-driven fleet management systems enables real-time tracking, dynamic route planning, and scalable automation, significantly improving throughput and operational accuracy.
AMR Swarm Coordination
Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR) swarm coordination enhances warehousing efficiency by enabling multiple robots to communicate and collaborate in real-time, optimizing task allocation and route planning without human intervention. This technological advancement reduces manual handling risks, increases throughput, and supports scalable, flexible warehouse operations with improved accuracy and reduced downtime.
Collaborative Picking Zones
Collaborative picking zones enhance efficiency by integrating Manual Handling with Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), enabling workers to focus on complex tasks while robots transport goods seamlessly. This synergy reduces physical strain, minimizes errors, and accelerates order fulfillment in modern warehouses.
Last-Meter Delivery Robots
Last-meter delivery robots enhance warehouse efficiency by reducing manual handling errors, improving load consistency, and accelerating parcel-to-customer workflows. Autonomous mobile robots equipped with advanced sensors and AI enable precise navigation, minimizing workplace injuries and optimizing last-meter logistics in complex warehouse environments.
Ergonomic Risk Assessment Automation
Ergonomic risk assessment automation in warehousing significantly reduces manual handling hazards by leveraging Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) to perform repetitive and strenuous tasks, minimizing workers' exposure to musculoskeletal disorders. Integrating AMRs with advanced sensor systems enables continuous monitoring and real-time ergonomic data analysis, enhancing workplace safety and operational efficiency.
Zero-Touch Inventory Movement
Zero-touch inventory movement leverages Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) to minimize human involvement, boosting operational efficiency and reducing labor costs in warehousing. Unlike manual handling, which is prone to errors and injuries, AMRs provide consistent, accurate, and safe transport of goods, streamlining inventory management and enhancing productivity.
Manual Handling vs Autonomous Mobile Robot Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com