Fulfillment centers are large-scale warehouses strategically located to store vast inventories and process high volumes of orders efficiently, often situated on the outskirts of urban areas. Urban hubs are smaller, centrally located facilities designed to facilitate rapid last-mile delivery and improve customer service within dense city environments. Choosing between a fulfillment center and an urban hub depends on balancing storage capacity with delivery speed to optimize supply chain performance.
Table of Comparison
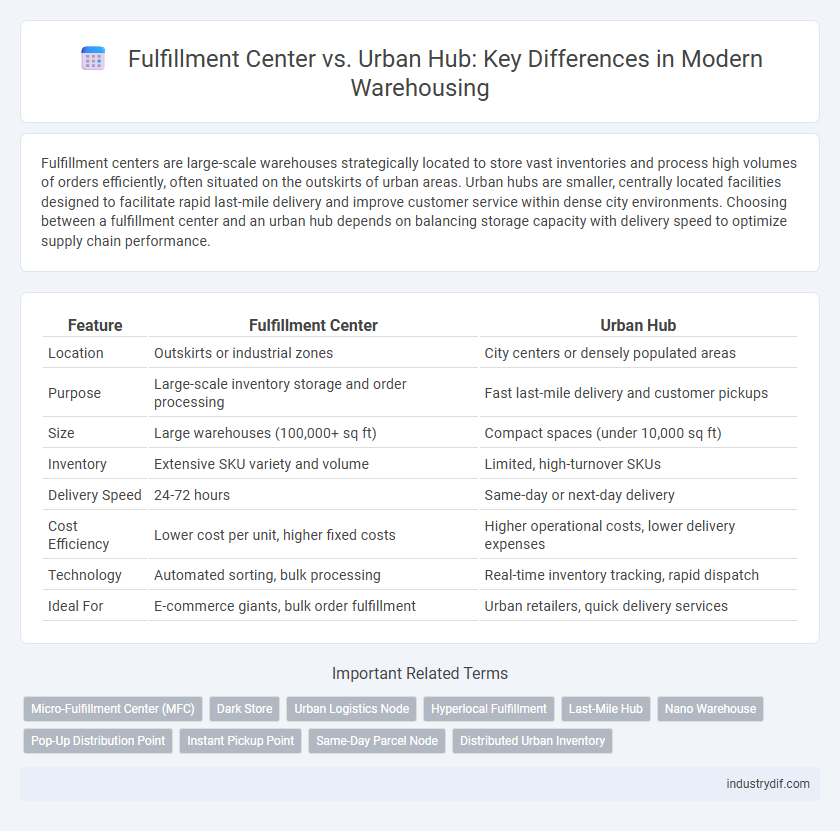
| Feature | Fulfillment Center | Urban Hub |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Outskirts or industrial zones | City centers or densely populated areas |
| Purpose | Large-scale inventory storage and order processing | Fast last-mile delivery and customer pickups |
| Size | Large warehouses (100,000+ sq ft) | Compact spaces (under 10,000 sq ft) |
| Inventory | Extensive SKU variety and volume | Limited, high-turnover SKUs |
| Delivery Speed | 24-72 hours | Same-day or next-day delivery |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower cost per unit, higher fixed costs | Higher operational costs, lower delivery expenses |
| Technology | Automated sorting, bulk processing | Real-time inventory tracking, rapid dispatch |
| Ideal For | E-commerce giants, bulk order fulfillment | Urban retailers, quick delivery services |
Overview of Fulfillment Centers and Urban Hubs
Fulfillment centers are large-scale warehouses designed to store inventory, process orders, and manage shipping logistics for e-commerce businesses. Urban hubs are smaller, strategically located facilities within city limits that enable faster last-mile delivery and improved customer convenience. Both types of distribution centers play crucial roles in optimizing supply chain efficiency and meeting consumer demand in different geographic and logistical contexts.
Key Differences Between Fulfillment Centers and Urban Hubs
Fulfillment centers are large-scale warehouses designed for high-volume storage and order processing, typically located in suburban areas to maximize space and efficiency. Urban hubs are smaller, strategically positioned facilities within city centers aimed at speeding up last-mile delivery and enhancing customer accessibility. Key differences include scale, location purpose, and operational focus, with fulfillment centers prioritizing inventory management and order accuracy, while urban hubs emphasize rapid distribution and proximity to end consumers.
Location Strategies: Suburban vs Urban Placement
Fulfillment centers are typically located in suburban areas to leverage larger spaces, lower land costs, and easier access to highways for efficient distribution. Urban hubs prioritize central city placement to reduce last-mile delivery times and meet growing consumer demand for fast shipping within densely populated regions. Strategic placement balances operational efficiency in suburban fulfillment centers with the immediacy of urban hubs for optimized supply chain networks.
Operational Scale and Throughput Comparison
Fulfillment centers typically operate on a large-scale basis, handling vast inventories with throughput capacities reaching hundreds of thousands of orders per day due to extensive automation and optimized storage solutions. Urban hubs focus on smaller operational scales, designed for rapid last-mile delivery within dense city areas, processing tens of thousands of orders daily with an emphasis on speed rather than volume. Throughput in fulfillment centers emphasizes bulk processing efficiency, while urban hubs prioritize agility and responsiveness to meet immediate consumer demand.
Technology and Automation in Both Models
Fulfillment centers leverage advanced robotics, AI-driven inventory management, and automated sorting systems to optimize large-scale order processing and reduce fulfillment times. Urban hubs integrate compact automation technologies such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and real-time data analytics to enhance last-mile delivery efficiency in densely populated areas. Both models utilize cloud-based platforms and IoT sensors to streamline operations, but fulfillment centers prioritize high-throughput automation while urban hubs focus on agility and rapid response to local demand.
Impact on Last-Mile Delivery Efficiency
Fulfillment centers typically handle large-scale inventory storage and order processing, enabling bulk shipment to regional distribution points, which can result in longer last-mile delivery times. Urban hubs, located closer to densely populated areas, optimize last-mile delivery by reducing transit distances, enhancing speed and reducing transportation costs. Leveraging urban hubs significantly improves delivery efficiency by facilitating same-day or next-day shipping through proximity to end consumers.
Cost Structures and Economic Considerations
Fulfillment centers typically demand higher capital investment due to larger facility sizes and extensive inventory storage, leading to increased fixed costs but benefiting from economies of scale. Urban hubs incur lower real estate and storage expenses as they focus on rapid last-mile delivery with limited inventory, resulting in higher variable costs per order. Companies must balance these economic trade-offs by evaluating order volume, delivery speed requirements, and urban real estate market trends to optimize overall cost efficiency in warehousing strategy.
Inventory Management Approaches
Fulfillment centers leverage centralized inventory management systems that optimize stock levels for high-volume processing and cost efficiency, utilizing advanced automation and real-time tracking to streamline order fulfillment. Urban hubs employ decentralized inventory strategies focused on rapid replenishment and last-mile delivery optimization, often integrating local demand data to maintain agile stock levels. Both approaches use inventory visibility tools, but fulfillment centers prioritize bulk storage accuracy while urban hubs emphasize dynamic, location-specific inventory adjustments.
Suitability for Different Business Models
Fulfillment centers are ideally suited for large-scale e-commerce businesses requiring bulk storage, efficient order processing, and regional distribution capabilities. Urban hubs cater to businesses focusing on fast delivery within metropolitan areas, offering smaller storage space but enhanced last-mile logistics efficiency. The choice depends on order volume, delivery speed priorities, and customer location density.
Future Trends in Warehousing: Fulfillment Centers vs Urban Hubs
Future trends in warehousing highlight a shift from large-scale fulfillment centers towards more strategically located urban hubs to meet growing consumer demand for faster delivery. Urban hubs leverage proximity to dense metropolitan areas to optimize last-mile logistics, reducing shipping times and costs while enhancing customer satisfaction. Advanced technologies such as automation, AI-driven inventory management, and sustainable energy solutions are increasingly integrated into both fulfillment centers and urban hubs to maximize efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Fulfillment Center (MFC)
Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs) optimize urban logistics by enabling rapid order processing and reducing last-mile delivery times within densely populated areas. These compact warehouses efficiently integrate automation technology to handle high-volume e-commerce demand, distinguishing them from traditional fulfillment centers and larger urban hubs.
Dark Store
Dark stores, a specialized type of urban hub, function as localized fulfillment centers that prioritize rapid order processing and last-mile delivery in densely populated areas. These facilities optimize inventory management and streamline e-commerce fulfillment by combining retail storage with advanced picking technologies, significantly reducing delivery times compared to traditional fulfillment centers.
Urban Logistics Node
Urban logistics nodes streamline last-mile delivery by serving as compact fulfillment centers within city limits, reducing transit times and transportation costs. These hubs optimize urban warehousing by leveraging proximity to consumers and integrating advanced inventory management for faster order processing.
Hyperlocal Fulfillment
Fulfillment centers are large-scale warehouses designed for bulk storage and rapid order processing, while urban hubs are strategically located smaller facilities focused on hyperlocal fulfillment to ensure faster last-mile delivery and reduced transportation costs. Hyperlocal fulfillment leverages urban hubs to optimize inventory proximity to customers, enhancing delivery speed and customer satisfaction in densely populated areas.
Last-Mile Hub
Fulfillment centers are large-scale warehouses specializing in storing vast inventories and processing bulk orders, while urban hubs function as compact last-mile hubs positioned close to consumers to expedite final delivery stages. Last-mile hubs optimize delivery speed and reduce transportation costs by decentralizing inventory storage and enabling same-day or next-day shipping within metropolitan areas.
Nano Warehouse
Nano warehouses represent a transformative approach in warehousing by serving as compact fulfillment centers strategically located within urban hubs to expedite last-mile delivery. These micro-fulfillment centers leverage automation and real-time inventory management, significantly reducing delivery times and enhancing operational efficiency in densely populated areas.
Pop-Up Distribution Point
Pop-up distribution points in fulfillment centers enable rapid order processing with extensive inventory storage, supporting high-volume e-commerce demands. Urban hubs prioritize proximity to customers for faster last-mile delivery but offer limited storage, making pop-up locations ideal for temporary spikes in local demand.
Instant Pickup Point
Fulfillment centers are large-scale warehouses designed for bulk storage and order processing, while urban hubs are smaller facilities strategically located in city centers to enable rapid delivery and instant pickup points. Instant pickup points at urban hubs significantly reduce last-mile delivery time, enhancing customer convenience and supporting same-day order fulfillment.
Same-Day Parcel Node
Fulfillment centers specialize in large-scale inventory storage and order processing, optimizing efficiency for nationwide distribution, while urban hubs function as same-day parcel nodes positioned within city limits to expedite last-mile delivery and reduce transit times. Same-day parcel nodes leverage urban hubs to boost rapid parcel sorting and dispatching, enhancing customer satisfaction through faster delivery windows.
Distributed Urban Inventory
Distributed urban inventory enhances fulfillment centers by decentralizing stock across multiple urban hubs, reducing last-mile delivery times and transportation costs. This networked approach supports rapid order fulfillment, improving customer satisfaction through increased product availability and expedited shipping in densely populated areas.
Fulfillment Center vs Urban Hub Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com