Asset-backed securities (ABS) represent financial instruments backed by pools of underlying assets, providing investors with predictable cash flows and risk diversification. Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer financial transactions without intermediaries, enhancing transparency and accessibility. While ABS offer traditional security through regulated asset pools, DeFi introduces innovative, programmable financial products that challenge conventional investment structures.
Table of Comparison
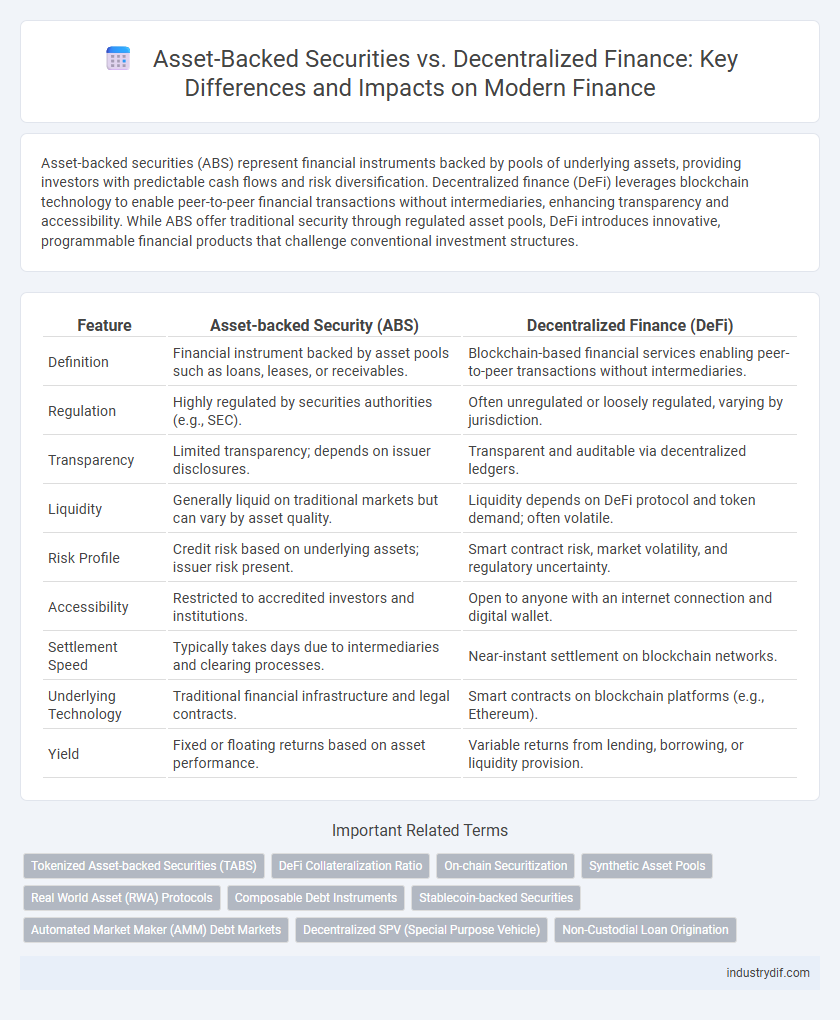
| Feature | Asset-backed Security (ABS) | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial instrument backed by asset pools such as loans, leases, or receivables. | Blockchain-based financial services enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. |
| Regulation | Highly regulated by securities authorities (e.g., SEC). | Often unregulated or loosely regulated, varying by jurisdiction. |
| Transparency | Limited transparency; depends on issuer disclosures. | Transparent and auditable via decentralized ledgers. |
| Liquidity | Generally liquid on traditional markets but can vary by asset quality. | Liquidity depends on DeFi protocol and token demand; often volatile. |
| Risk Profile | Credit risk based on underlying assets; issuer risk present. | Smart contract risk, market volatility, and regulatory uncertainty. |
| Accessibility | Restricted to accredited investors and institutions. | Open to anyone with an internet connection and digital wallet. |
| Settlement Speed | Typically takes days due to intermediaries and clearing processes. | Near-instant settlement on blockchain networks. |
| Underlying Technology | Traditional financial infrastructure and legal contracts. | Smart contracts on blockchain platforms (e.g., Ethereum). |
| Yield | Fixed or floating returns based on asset performance. | Variable returns from lending, borrowing, or liquidity provision. |
Understanding Asset-Backed Securities (ABS)
Asset-backed securities (ABS) are financial instruments backed by a pool of underlying assets such as loans, leases, credit card debt, or receivables, offering investors regular income through asset-generated cash flows. Unlike decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms that use blockchain technology for peer-to-peer transactions, ABS rely on traditional financial structures and credit enhancements to reduce risk. Understanding ABS involves analyzing the credit quality of the asset pool, tranche structures, and the legal framework governing asset transfers and cash flow prioritization.
Exploring the Fundamentals of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Asset-backed securities (ABS) represent traditional financial instruments secured by underlying assets such as loans or receivables, offering investors predictable cash flows and reduced risk exposure. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) operates on blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer financial services without intermediaries by using smart contracts to automate lending, borrowing, and trading processes. Exploring DeFi fundamentals reveals increased transparency, programmable finance, and enhanced accessibility as core advantages contrasting with the centralized structure of asset-backed securities.
Key Differences Between ABS and DeFi
Asset-backed securities (ABS) are traditional financial instruments secured by underlying assets such as loans or receivables, offering fixed income with regulated structures and centralized credit risk assessment. Decentralized finance (DeFi) operates on blockchain technology, providing peer-to-peer financial services without intermediaries, enabling increased transparency and programmability through smart contracts. Key differences include ABS's reliance on centralized entities for asset verification and risk management, while DeFi leverages decentralization to reduce counterparty risk and enhance access to liquidity.
Risk Assessment: ABS vs DeFi
Asset-backed securities (ABS) rely on traditional credit risk assessments, with performance linked to underlying asset pools and regulatory oversight that mitigates default risk. In contrast, decentralized finance (DeFi) risk assessment involves smart contract vulnerabilities, liquidity fluctuations, and potential for systemic risks due to lack of centralized control. Investors must evaluate ABS for credit quality and legal recourse, while DeFi demands scrutiny of protocol security, token volatility, and market manipulation risks.
Regulatory Landscape in ABS and DeFi
The regulatory landscape for Asset-Backed Securities (ABS) is well-established, governed primarily by financial authorities like the SEC, with strict disclosure, issuer registration, and investor protection requirements that ensure market stability and transparency. In contrast, Decentralized Finance (DeFi) operates in a largely evolving regulatory environment, facing challenges due to its decentralized nature, lack of intermediaries, and cross-jurisdictional operations, which complicates the application of traditional financial regulations. Regulatory bodies are increasingly exploring frameworks to address issues such as anti-money laundering (AML), securities classification, and consumer protection within DeFi, but clarity and standardization remain limited compared to ABS markets.
Transparency and Trust: Traditional vs Decentralized Financing
Asset-backed securities (ABS) provide transparency through regulated disclosures and third-party audits, fostering trust among investors by relying on traditional financial intermediaries. Decentralized finance (DeFi) enhances transparency with blockchain technology, offering real-time, immutable transaction records that eliminate the need for intermediaries and reduce information asymmetry. Trust in DeFi stems from code-driven protocols and smart contracts, contrasting the reliance on institutional reputation and regulatory frameworks in traditional asset-backed securities.
Yield Generation: ABS Returns vs DeFi Yields
Asset-backed securities (ABS) typically offer stable, predictable returns backed by cash flows from underlying assets like loans or receivables, making them attractive for risk-averse investors seeking steady income. In contrast, decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms provide higher yield potentials through liquidity mining, staking, and lending protocols, but come with increased volatility and smart contract risks. Comparing ABS returns with DeFi yields requires careful assessment of risk-adjusted returns, liquidity, and regulatory environment to optimize portfolio yield generation strategies.
Accessibility and Inclusion: DeFi Disrupting Traditional Models
Asset-backed securities (ABS) traditionally rely on centralized intermediaries, limiting accessibility to accredited investors and institutional players. Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms leverage blockchain technology to enable broader participation by reducing barriers, allowing individuals worldwide to access financial products without intermediaries. This inclusivity disrupts traditional models by democratizing access to asset-backed investment opportunities and enhancing financial inclusion.
Technological Infrastructure: Securitization vs Blockchain
Asset-backed securities rely on securitization, a financial process that pools various debt instruments and issues tradable securities backed by these assets, supported by centralized databases and legal frameworks. Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology, utilizing distributed ledgers and smart contracts to enable trustless, transparent transactions without intermediaries. The contrast highlights traditional centralized infrastructure in securitization versus decentralized, automated protocols underpinning DeFi platforms.
Future Outlook: Convergence of ABS and DeFi
The future outlook of asset-backed securities (ABS) and decentralized finance (DeFi) indicates a convergence driven by blockchain technology enhancing transparency and liquidity in traditional ABS markets. Integration of smart contracts into ABS issuances can automate payments and reduce intermediaries, increasing efficiency and accessibility for investors. This fusion is poised to revolutionize asset securitization by combining regulatory oversight with decentralized, peer-to-peer finance mechanisms.
Related Important Terms
Tokenized Asset-backed Securities (TABS)
Tokenized Asset-backed Securities (TABS) leverage blockchain technology to enhance liquidity, transparency, and accessibility in traditional asset-backed securities markets, bridging the gap between conventional finance and decentralized finance (DeFi). By digitizing ownership and automating compliance through smart contracts, TABS reduce intermediaries and operational costs while providing real-time asset verification and fractional trading opportunities.
DeFi Collateralization Ratio
DeFi collateralization ratios typically exceed traditional asset-backed security (ABS) standards, often maintaining levels above 150% to mitigate the volatility of underlying crypto assets. Unlike ABS, which rely on static asset pools, DeFi collateralization dynamically adjusts to market fluctuations, thereby enhancing liquidity and risk management in decentralized finance protocols.
On-chain Securitization
On-chain securitization in decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to tokenize asset-backed securities (ABS), enabling enhanced transparency, automated smart contract execution, and increased liquidity compared to traditional ABS markets. This innovative approach reduces intermediaries and settlement times while providing real-time auditability and fractional ownership opportunities on decentralized platforms.
Synthetic Asset Pools
Synthetic asset pools in decentralized finance (DeFi) offer programmable, transparent exposure to real-world assets, contrasting with traditional asset-backed securities (ABS) that rely on underlying physical collateral and centralized entities for valuation and management. These pools utilize smart contracts to create synthetic derivatives, enabling fractional ownership and liquidity without intermediary risk, while ABS depend on legal structures and credit ratings to assess risk and value.
Real World Asset (RWA) Protocols
Asset-backed securities (ABS) traditionally pool real-world assets like mortgages and loans to create structured financial products, whereas decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols increasingly integrate real world asset (RWA) protocols to tokenize these assets on blockchain platforms, enabling enhanced liquidity and transparency. RWA protocols bridge the gap between traditional finance and DeFi by digitizing physical assets, allowing for fractional ownership and programmable smart contracts that facilitate automated, trustless lending and borrowing markets.
Composable Debt Instruments
Asset-backed securities (ABS) represent traditional composable debt instruments secured by pools of tangible assets, offering structured cash flow and credit enhancement features. In contrast, decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to create programmable, interoperable composable debt instruments through smart contracts, enabling automated collateral management and seamless integration across decentralized protocols.
Stablecoin-backed Securities
Stablecoin-backed securities merge asset-backed security principles with decentralized finance by utilizing digital tokens pegged to stable assets, offering liquidity and transparency not typically found in traditional ABS structures. These instruments leverage blockchain technology to enhance trust and efficiency, enabling real-time settlement and reduced counterparty risk in financial markets.
Automated Market Maker (AMM) Debt Markets
Asset-backed securities (ABS) offer traditional debt instruments backed by tangible assets, providing predictable cash flows and risk profiles, while decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages Automated Market Maker (AMM) debt markets to enable permissionless, algorithm-driven lending and borrowing without intermediaries. AMM debt markets optimize liquidity and price discovery through smart contracts, creating dynamic interest rates and real-time asset collateralization unlike the static structures of ABS.
Decentralized SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle)
Decentralized SPVs in finance leverage blockchain technology to facilitate asset-backed securities without traditional intermediaries, enhancing transparency and reducing counterparty risk. Unlike conventional asset-backed securities, decentralized SPVs automate compliance and asset management through smart contracts, driving efficiency and liquidity in decentralized finance ecosystems.
Non-Custodial Loan Origination
Asset-backed securities (ABS) rely on traditional financial institutions to pool and securitize loans, offering investors fixed income through collateralized debt, whereas decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms enable non-custodial loan origination by leveraging smart contracts on blockchain, ensuring transparency and direct peer-to-peer lending without intermediaries. Non-custodial loan origination in DeFi eliminates counterparty risk and promotes greater accessibility, contrasting with the centralized asset management and regulatory oversight typical in ABS markets.
Asset-backed Security vs Decentralized Finance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com