Investment banking relies on centralized institutions to facilitate complex financial transactions such as mergers, acquisitions, and underwriting, offering regulatory oversight and risk mitigation. Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer financial services without intermediaries, increasing transparency and accessibility. The choice between investment banking and DeFi hinges on factors like regulatory environment, security preferences, and the need for innovation in financial products.
Table of Comparison
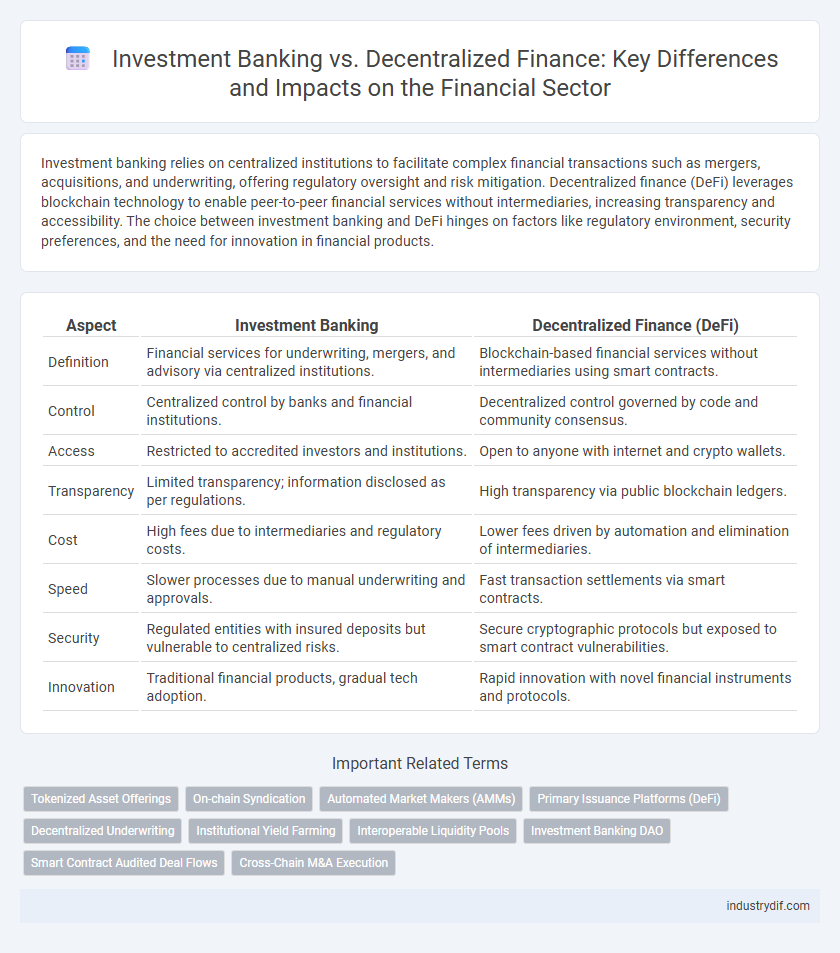
| Aspect | Investment Banking | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial services for underwriting, mergers, and advisory via centralized institutions. | Blockchain-based financial services without intermediaries using smart contracts. |
| Control | Centralized control by banks and financial institutions. | Decentralized control governed by code and community consensus. |
| Access | Restricted to accredited investors and institutions. | Open to anyone with internet and crypto wallets. |
| Transparency | Limited transparency; information disclosed as per regulations. | High transparency via public blockchain ledgers. |
| Cost | High fees due to intermediaries and regulatory costs. | Lower fees driven by automation and elimination of intermediaries. |
| Speed | Slower processes due to manual underwriting and approvals. | Fast transaction settlements via smart contracts. |
| Security | Regulated entities with insured deposits but vulnerable to centralized risks. | Secure cryptographic protocols but exposed to smart contract vulnerabilities. |
| Innovation | Traditional financial products, gradual tech adoption. | Rapid innovation with novel financial instruments and protocols. |
Introduction to Investment Banking and Decentralized Finance
Investment banking involves financial institutions facilitating large-scale capital raising, mergers, acquisitions, and advisory services for corporations and governments using centralized intermediaries. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology and smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer financial services without traditional intermediaries, promoting transparency and accessibility. The contrast highlights investment banking's reliance on regulated entities and centralized control versus DeFi's open-source, decentralized protocols reshaping modern finance.
Core Functions of Investment Banking
Investment banking primarily focuses on core functions such as underwriting new debt and equity securities for all types of corporations, facilitating mergers and acquisitions, and providing advisory services for financial restructuring. These institutions play a crucial role in capital raising by connecting issuers with investors and conducting detailed due diligence to assess risks. Unlike decentralized finance, investment banking operates within a highly regulated environment, leveraging traditional financial intermediaries to ensure market stability and investor protection.
Key Principles of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) operates on blockchain technology, eliminating intermediaries by enabling peer-to-peer transactions and programmable smart contracts. Transparency, security through cryptographic consensus, and open access without geographic or institutional barriers are fundamental principles driving DeFi's disruption to traditional investment banking. Protocol composability allows for innovative financial products, enhancing liquidity and efficiency across decentralized ecosystems.
Regulatory Frameworks: Traditional vs Decentralized
Investment banking operates within stringent regulatory frameworks enforced by established authorities such as the SEC and FINRA, ensuring transparency, investor protection, and compliance with financial laws. Decentralized finance (DeFi) challenges traditional regulatory models by utilizing blockchain technology and smart contracts, leading to ambiguous oversight and evolving policies from global regulators aiming to balance innovation with security. The contrast highlights traditional finance's reliance on centralized governance versus DeFi's decentralized and borderless nature, creating ongoing debates over the adequacy and adaptability of existing financial regulations.
Innovation and Technology in Finance
Investment banking leverages advanced algorithms, AI-driven analytics, and blockchain integration to enhance trading efficiency and risk management, while decentralized finance (DeFi) utilizes smart contracts and distributed ledger technology to offer transparent, permissionless financial services without intermediaries. Innovations in investment banking focus on automating complex financial instruments and regulatory compliance, whereas DeFi drives innovation through tokenization, decentralized exchanges, and programmable money. Both sectors harness cutting-edge technology, but DeFi's open-source protocols challenge traditional financial models by democratizing access and enabling peer-to-peer transactions on blockchain networks.
Risk Management: Centralized vs Decentralized Models
Investment banking relies on centralized risk management models that use regulatory oversight, credit assessments, and capital reserves to mitigate financial risks. Decentralized finance (DeFi) employs distributed ledger technology and smart contracts to enable transparent, automated risk controls without intermediaries, but it faces challenges like smart contract vulnerabilities and regulatory uncertainty. Centralized models benefit from human judgment and regulatory frameworks, whereas DeFi emphasizes trustless protocols and algorithmic enforcement, creating distinct risk profiles in each system.
Access and Inclusivity in Financial Services
Investment banking traditionally requires significant capital and rigorous accreditation, limiting access to institutional and high-net-worth clients. Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to offer permissionless, borderless financial services accessible to anyone with an internet connection. This inclusivity fosters greater democratization of capital markets by reducing barriers like geographic restrictions and credit history requirements.
Costs and Efficiency: Comparing Platforms
Investment banking platforms often entail high operational costs due to regulatory compliance, intermediaries, and extensive infrastructure, which can reduce overall efficiency. Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms leverage blockchain technology to minimize intermediaries and automate processes via smart contracts, significantly lowering transaction fees and increasing speed. The cost-efficiency advantage of DeFi platforms offers scalable and transparent alternatives to traditional investment banking systems.
Security Concerns in Investment Banking and DeFi
Investment banking relies heavily on centralized security protocols, which can be vulnerable to internal fraud and cyberattacks targeting large institutions. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms offer increased transparency through blockchain technology but face risks like smart contract vulnerabilities and insufficient regulation. Both sectors must enhance cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive financial data and maintain investor trust.
The Future Landscape: Synergies and Challenges
Investment banking is evolving through the integration of decentralized finance (DeFi) technologies, which promise increased transparency, reduced intermediaries, and faster transaction settlements. Synergies between traditional banking infrastructures and blockchain protocols create opportunities for innovative financial products, yet challenges such as regulatory uncertainty, scalability, and cybersecurity risks persist. The future landscape of finance will likely witness hybrid models combining centralized authority and decentralized networks to optimize efficiency and trust.
Related Important Terms
Tokenized Asset Offerings
Tokenized asset offerings in decentralized finance (DeFi) enable fractional ownership, increased liquidity, and 24/7 global trading absent traditional intermediaries, contrasting with investment banking's structured, heavily regulated processes for asset issuance and underwriting. DeFi leverages blockchain technology to democratize access and reduce costs, while investment banks provide established market credibility, regulatory compliance, and centralized risk management for large-scale capital raising.
On-chain Syndication
On-chain syndication in decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to enable transparent, automated syndicated loans and equity deals without intermediaries, reducing costs and improving efficiency compared to traditional investment banking syndication. Investment banking relies on centralized processes and regulatory frameworks to coordinate complex multi-party financing, while DeFi protocols use smart contracts to execute and verify transactions in real-time on public ledgers, enhancing liquidity and democratizing access to capital markets.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) in decentralized finance (DeFi) utilize smart contracts to enable continuous, permissionless asset trading without traditional intermediaries, contrasting sharply with investment banking's reliance on centralized order books and manual market-making processes. AMMs enhance liquidity and reduce transaction costs by algorithmically determining asset prices based on supply and demand within liquidity pools, disrupting conventional investment banking models that depend on client relationships and regulatory oversight.
Primary Issuance Platforms (DeFi)
Primary issuance platforms in decentralized finance (DeFi) enable asset tokenization and direct capital raising on blockchain networks, reducing reliance on traditional intermediaries associated with investment banking. These platforms leverage smart contracts to automate issuance processes, enhance transparency, and increase liquidity access compared to conventional underwriting methods.
Decentralized Underwriting
Decentralized underwriting in finance leverages blockchain technology to distribute risk assessment and capital allocation across a network of participants, enhancing transparency and reducing reliance on centralized intermediaries. Unlike traditional investment banking, which centralizes underwriting processes through financial institutions, decentralized underwriting democratizes access to financial services and fosters more inclusive, efficient market participation.
Institutional Yield Farming
Institutional yield farming in decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages smart contracts to optimize returns through liquidity provision and staking, offering higher transparency and efficiency compared to traditional investment banking methods. Unlike conventional finance, DeFi platforms enable institutional investors to access automated, algorithm-driven yield strategies without intermediaries, significantly reducing costs and operational risks.
Interoperable Liquidity Pools
Interoperable liquidity pools in decentralized finance enable seamless asset transfers across multiple blockchain networks, enhancing capital efficiency and reducing fragmentation compared to traditional investment banking's siloed liquidity frameworks. Integration of cross-chain protocols facilitates broader market access and real-time liquidity aggregation, challenging the centralized control and slower settlement processes characteristic of conventional financial institutions.
Investment Banking DAO
Investment Banking DAOs leverage blockchain technology to democratize access to capital markets, enabling decentralized governance and transparent decision-making processes traditionally controlled by centralized investment banks. These organizations combine the regulatory expertise of investment banking with the efficiency and inclusivity of decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, facilitating tokenized asset management and peer-to-peer investment opportunities.
Smart Contract Audited Deal Flows
Smart contract audited deal flows in decentralized finance (DeFi) enhance transparency and reduce counterparty risk compared to traditional investment banking processes reliant on intermediaries and manual compliance checks. These automated audits enable real-time validation of transactions, fostering trust and efficiency in decentralized markets while minimizing fraud and operational errors.
Cross-Chain M&A Execution
Cross-chain M&A execution in decentralized finance leverages blockchain interoperability to enable secure, transparent asset transfers and seamless deal settlements across multiple chains, reducing intermediaries and settlement times compared to traditional investment banking processes. Investment banking relies on centralized structures with extensive regulatory compliance and manual coordination, whereas decentralized finance utilizes smart contracts and automated protocols to streamline complex cross-border mergers and acquisitions efficiently.
Investment Banking vs Decentralized Finance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com