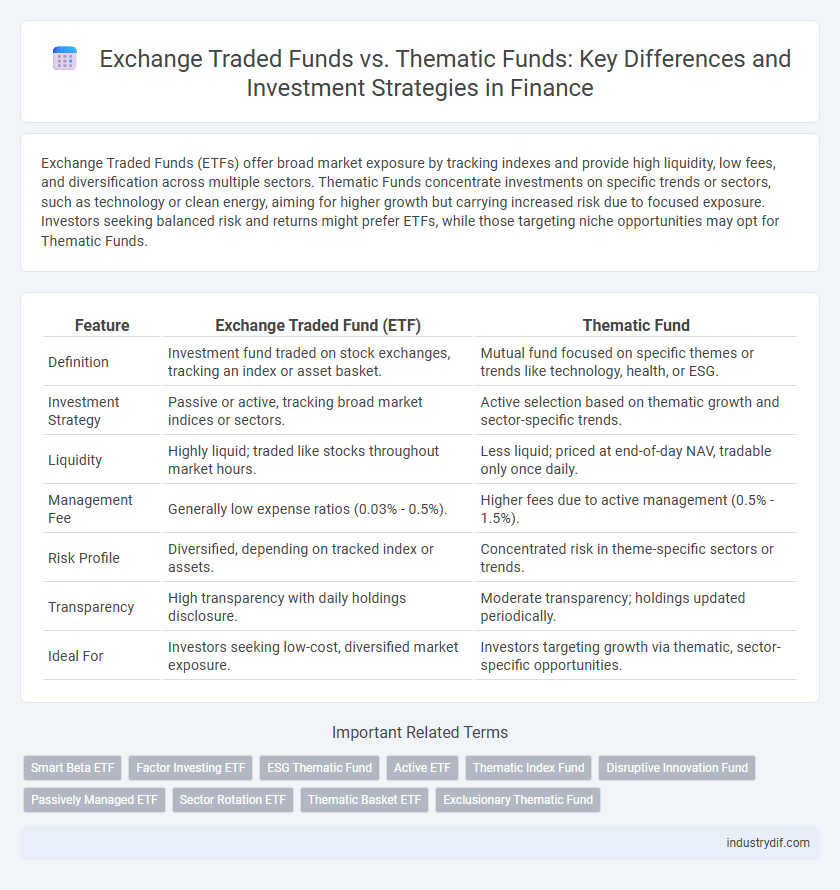
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) offer broad market exposure by tracking indexes and provide high liquidity, low fees, and diversification across multiple sectors. Thematic Funds concentrate investments on specific trends or sectors, such as technology or clean energy, aiming for higher growth but carrying increased risk due to focused exposure. Investors seeking balanced risk and returns might prefer ETFs, while those targeting niche opportunities may opt for Thematic Funds.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) | Thematic Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment fund traded on stock exchanges, tracking an index or asset basket. | Mutual fund focused on specific themes or trends like technology, health, or ESG. |
| Investment Strategy | Passive or active, tracking broad market indices or sectors. | Active selection based on thematic growth and sector-specific trends. |
| Liquidity | Highly liquid; traded like stocks throughout market hours. | Less liquid; priced at end-of-day NAV, tradable only once daily. |
| Management Fee | Generally low expense ratios (0.03% - 0.5%). | Higher fees due to active management (0.5% - 1.5%). |
| Risk Profile | Diversified, depending on tracked index or assets. | Concentrated risk in theme-specific sectors or trends. |
| Transparency | High transparency with daily holdings disclosure. | Moderate transparency; holdings updated periodically. |
| Ideal For | Investors seeking low-cost, diversified market exposure. | Investors targeting growth via thematic, sector-specific opportunities. |
Understanding Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs)
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) are investment funds traded on stock exchanges, offering diversified exposure to a broad range of assets such as stocks, bonds, or commodities. ETFs provide investors with liquidity, transparency, and lower expense ratios compared to traditional mutual funds, making them attractive for cost-conscious portfolios. Unlike thematic funds, which focus on specific sectors or trends, ETFs track indices or asset classes, delivering broad market exposure and risk diversification.
What Defines a Thematic Fund?
A thematic fund is defined by its investment strategy that targets specific trends or themes, such as technology innovation, clean energy, or demographic shifts, rather than traditional sectors or market capitalization. These funds focus on companies poised to benefit from long-term structural changes, offering exposure to niche markets with growth potential. Unlike general exchange-traded funds (ETFs), thematic funds emphasize concentrated portfolios aligned with evolving economic or social trends.
Key Differences: ETF vs Thematic Fund
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) offer broad market exposure and liquidity by tracking indexes with diversified holdings, while Thematic Funds concentrate investments on specific trends or sectors like technology or clean energy, leading to higher volatility and potential for targeted growth. ETFs generally have lower expense ratios and more transparent portfolios compared to Thematic Funds, which may charge premium fees due to specialized management and research. The primary key difference lies in investment strategy: ETFs prioritize market-wide diversification, whereas Thematic Funds emphasize thematic concentration aligned with evolving economic or societal trends.
Investment Strategies Compared: ETFs and Thematic Funds
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) employ diversified, passive investment strategies tracking broad market indices to minimize risk and provide steady returns. Thematic funds, by contrast, adopt active strategies targeting specific sectors or trends like technology, renewable energy, or demographics, aiming for higher growth through concentrated exposure. Investors seeking broad market exposure may prefer ETFs, while those aiming for specialized growth opportunities often choose thematic funds for targeted investment themes.
Portfolio Diversification: ETF vs Thematic Fund
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) typically offer broad portfolio diversification by tracking a wide range of indices or sectors, reducing individual asset risk through extensive market exposure. Thematic Funds concentrate investments on specific trends or sectors, increasing potential returns but also heightening exposure to sector-specific risks and reducing diversification. Investors seeking balanced risk management often prefer ETFs for their comprehensive market coverage, while those targeting growth in niche areas might opt for thematic funds despite their concentrated portfolios.
Risks and Return Profiles
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) typically offer diversified exposure and lower volatility, with returns closely tracking broad market indices, reducing company-specific risk. Thematic Funds concentrate investments in specific trends or sectors, leading to higher potential returns but increased risk due to sector concentration and market sensitivity. Investors should assess their risk tolerance and investment horizon when choosing between the stable, broad-market characteristics of ETFs and the focused, high-growth but volatile nature of Thematic Funds.
Cost Structure and Fees Analysis
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) typically feature lower expense ratios, averaging around 0.10% to 0.50%, due to their passive management and broad market exposure, making them cost-efficient for most investors. Thematic Funds often carry higher fees, ranging from 0.50% to over 1.00%, reflecting active management and specialized investment strategies targeting niche sectors or trends. Investors should carefully analyze management fees, transaction costs, and bid-ask spreads, as these directly impact net returns, with ETFs generally offering a more favorable cost structure compared to thematic alternatives.
Liquidity and Trading Flexibility
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) provide high liquidity due to their listing on major stock exchanges, enabling investors to trade shares throughout the trading day at market prices. In contrast, Thematic Funds, often structured as mutual funds or specialized ETFs, may experience lower liquidity and less frequent trading opportunities, limiting intraday price discovery. ETFs offer superior trading flexibility with real-time pricing and the ability to use advanced order types, whereas Thematic Funds generally lack these features, impacting portfolio adjustment speed and market responsiveness.
Suitability for Different Investors
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) offer broad market exposure, making them suitable for conservative investors seeking diversified, low-cost investment options with high liquidity. Thematic Funds target specific trends or sectors, appealing to investors with a higher risk tolerance who want to capitalize on emerging opportunities and growth potential. Risk appetite, investment horizon, and sector knowledge are critical factors in determining the appropriate choice between ETFs and Thematic Funds.
Future Outlook: ETFs and Thematic Funds in Modern Portfolios
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) continue to dominate modern portfolios with their liquidity, diversification, and low expense ratios, making them a preferred vehicle for broad market exposure and passive investment strategies. Thematic funds, focusing on specific trends like clean energy, technology innovation, or demographic shifts, offer targeted growth potential and appeal to investors seeking alignment with future-oriented sectors. As market demand evolves, the integration of ETFs with thematic strategies is expected to increase, enhancing portfolio customization and risk-adjusted returns in dynamic economic environments.
Related Important Terms
Smart Beta ETF
Smart Beta ETFs leverage factor-based strategies to optimize returns by systematically targeting risk factors such as value, momentum, and low volatility, differing from traditional thematic funds that focus on sector or trend-based exposure. This approach offers more transparent, rules-based exposure and often improved risk-adjusted performance compared to thematic funds, which may carry higher thematic concentration risk and less consistent return profiles.
Factor Investing ETF
Factor Investing ETFs emphasize exposure to specific investment factors such as value, momentum, or quality, providing targeted returns through systematic strategies, whereas Thematic Funds concentrate on broader market trends or sectors like technology or clean energy, capturing growth driven by macro trends. Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) offer liquidity and transparency, making Factor Investing ETFs a preferred choice for investors seeking disciplined, factor-based risk-return profiles compared to the more speculative focus of Thematic Funds.
ESG Thematic Fund
ESG Thematic Funds prioritize investments in companies with strong environmental, social, and governance practices, offering targeted exposure to sustainable and responsible business themes. Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) provide diversified, low-cost access to ESG strategies but may lack the specialized focus and active management found in ESG Thematic Funds, which concentrate on specific sectors or themes driving long-term sustainable growth.
Active ETF
Active ETFs combine the liquidity and transparency of traditional Exchange Traded Funds with the dynamic management style of Thematic Funds, targeting specific sectors or trends for enhanced growth potential. Unlike passive ETFs, Active ETFs adjust holdings based on market conditions and thematic insights, offering investors a proactive approach to portfolio diversification and risk management.
Thematic Index Fund
Thematic index funds focus on investing in specific sectors or trends such as renewable energy, technology innovation, or biotechnology, offering targeted exposure aligned with emerging market themes. Unlike broad exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track wide market indices, thematic funds concentrate on defined themes, enabling investors to capitalize on long-term growth opportunities tied to transformative economic shifts.
Disruptive Innovation Fund
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) provide diversified exposure to broad market indices with high liquidity and lower expense ratios, while Thematic Funds concentrate on specific trends or sectors, such as the Disruptive Innovation Fund, which targets companies driving transformative technologies like AI, blockchain, and renewable energy. Investors seeking focused growth in cutting-edge industries may prefer Disruptive Innovation Thematic Funds for their targeted approach, despite potentially higher volatility compared to traditional ETFs.
Passively Managed ETF
Passively managed Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) track broad market indexes and offer lower fees with diversified exposure, whereas thematic funds concentrate on specific sectors or trends, often employing active management and higher risk. ETFs emphasize cost-efficiency and liquidity, making them attractive for long-term investors seeking stable market replication without the volatility of focused thematic strategies.
Sector Rotation ETF
Sector Rotation ETFs strategically allocate assets across various industry sectors based on economic cycle analysis to capitalize on market trends, offering more dynamic exposure compared to traditional Thematic Funds that focus narrowly on specific themes or industries. These ETFs enable investors to enhance diversification and potential returns by systematically shifting investments among sectors poised for growth in different economic phases.
Thematic Basket ETF
Thematic Basket ETFs strategically combine diverse assets centered on specific investment themes such as technology innovation, clean energy, or healthcare advancements, offering focused exposure with lower fees compared to actively managed thematic funds. These ETFs provide investors with a transparent, liquid, and cost-effective way to capitalize on macro trends while maintaining diversification within the chosen theme.
Exclusionary Thematic Fund
Exclusionary thematic funds focus on investing in specific themes while deliberately avoiding sectors or companies that conflict with their ethical, environmental, or social criteria, contrasting with broad exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track general market indexes. These funds leverage thematic investment strategies combined with exclusionary screens to align portfolios with values-driven objectives, enhancing targeted exposure without compromising on ESG considerations.
Exchange Traded Fund vs Thematic Fund Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com