Bank loans typically offer structured repayment plans with fixed interest rates and rely on creditworthiness assessments by financial institutions. Peer-to-peer lending connects borrowers directly with individual investors, often providing more flexible terms and potentially lower rates but with higher risk variability. Choosing between the two depends on factors like loan amount, approval speed, and tolerance for interest fluctuations.
Table of Comparison
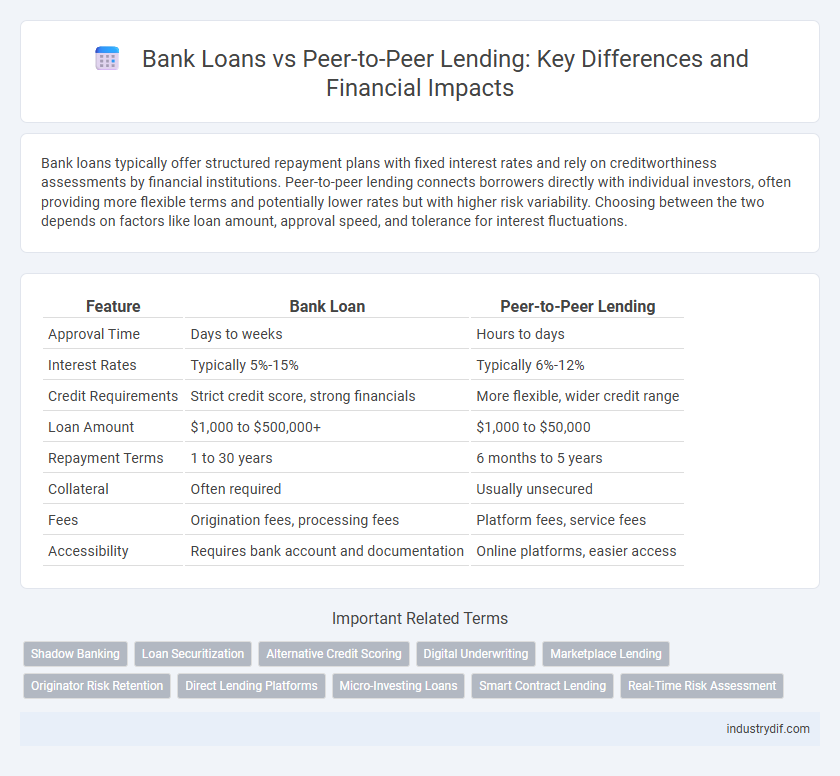
| Feature | Bank Loan | Peer-to-Peer Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Approval Time | Days to weeks | Hours to days |
| Interest Rates | Typically 5%-15% | Typically 6%-12% |
| Credit Requirements | Strict credit score, strong financials | More flexible, wider credit range |
| Loan Amount | $1,000 to $500,000+ | $1,000 to $50,000 |
| Repayment Terms | 1 to 30 years | 6 months to 5 years |
| Collateral | Often required | Usually unsecured |
| Fees | Origination fees, processing fees | Platform fees, service fees |
| Accessibility | Requires bank account and documentation | Online platforms, easier access |
Overview of Bank Loans and Peer-to-Peer Lending
Bank loans are traditional financing options offered by financial institutions, characterized by fixed interest rates, regulated lending criteria, and longer approval processes. Peer-to-peer lending connects borrowers directly with individual investors through online platforms, often offering competitive rates and faster access to funds. Both methods serve distinct borrower needs, with bank loans emphasizing security and scale, while peer-to-peer lending highlights flexibility and innovation.
Application Process: Bank Loans vs P2P Lending
The application process for bank loans typically involves extensive documentation, credit checks, and lengthy approval times due to stringent underwriting standards from traditional financial institutions. Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms offer a streamlined online application, faster approval, and less rigid credit requirements by directly connecting borrowers with individual investors. Borrowers seeking quicker access to funds and flexible criteria often prefer P2P lending, while those needing larger loan amounts usually opt for bank loans despite the more complex process.
Eligibility Criteria Comparison
Bank loan eligibility typically requires a strong credit score, stable income, and a detailed financial history, emphasizing traditional assessments by financial institutions. Peer-to-peer lending platforms often have more flexible criteria, considering alternative data points such as social behavior and transaction history, which can benefit borrowers with limited credit profiles. Both options weigh debt-to-income ratios, but peer-to-peer lending may offer quicker approval and less stringent requirements, attracting borrowers who face challenges with conventional banks.
Interest Rates and Fees Analysis
Bank loans typically feature fixed or variable interest rates set by financial institutions, often resulting in higher overall costs due to origination fees, processing charges, and penalties for early repayment. Peer-to-peer lending platforms offer competitive interest rates influenced by borrower credit profiles and market demand, frequently accompanied by lower administrative fees and transparent cost structures. Comparing average APRs reveals that P2P loans can be more affordable for prime borrowers, while bank loans provide stability and regulatory protections despite potentially higher fees.
Speed and Convenience of Funding
Bank loans generally involve longer approval processes due to stringent credit checks and documentation requirements, often taking weeks to disburse funds. Peer-to-peer lending platforms leverage digital technology to expedite approvals, frequently providing funding within days by matching borrowers with individual investors quickly. The convenience of online applications and less bureaucratic hurdles makes peer-to-peer lending a faster alternative for accessing capital compared to traditional banking institutions.
Credit Score Requirements
Bank loans typically require a higher credit score, often above 650, to qualify for favorable interest rates and loan terms. Peer-to-peer lending platforms accept a wider range of credit scores, sometimes as low as 580, offering access to credit for borrowers with less-than-perfect credit histories. This flexibility in credit requirements makes peer-to-peer lending an attractive alternative for those unable to meet traditional bank loan thresholds.
Loan Amounts and Repayment Terms
Bank loans typically offer higher loan amounts ranging from $5,000 to $500,000 with structured repayment terms spanning 1 to 30 years, suited for larger financial needs. Peer-to-peer lending usually provides smaller loan amounts between $1,000 and $50,000 with flexible repayment periods often ranging from 6 months to 5 years, appealing to borrowers seeking quick access to funds. Repayment terms in bank loans include fixed or variable interest rates and strict schedules, while P2P lending may offer more personalized terms based on creditworthiness and platform policies.
Risks Associated with Each Option
Bank loans pose risks such as strict qualification criteria, potential collateral loss, and fixed repayment schedules that can strain borrowers during financial instability. Peer-to-peer lending carries risks including higher interest rates, less regulatory oversight, and increased default rates compared to traditional banks. Both options require careful assessment of personal financial situations and risk tolerance before committing.
Regulatory Framework and Protections
Bank loans are governed by strict regulatory frameworks established by central banks and financial authorities, which impose rigorous requirements on lenders to protect borrowers, including mandatory disclosures and dispute resolution mechanisms. Peer-to-peer lending platforms operate under evolving regulations that vary widely by jurisdiction, often offering fewer borrower protections and less stringent oversight, which can increase risk but also foster innovation and competitive interest rates. Borrowers choosing between these options should carefully assess the regulatory environment and available protections to ensure financial security and transparency.
Suitability for Different Borrower Profiles
Bank loans typically suit borrowers with strong credit histories and stable income due to stringent qualification criteria and lower interest rates. Peer-to-peer lending offers an alternative for individuals with limited creditworthiness or small businesses seeking quicker approval and flexible terms. Understanding borrowing needs, credit status, and repayment capacity helps determine the optimal financing option between traditional banks and P2P platforms.
Related Important Terms
Shadow Banking
Shadow banking, comprising peer-to-peer lending platforms, operates outside traditional bank loan frameworks by offering credit without direct regulatory oversight, increasing systemic risk in finance. Unlike conventional bank loans, shadow banking activities leverage non-bank intermediaries to channel funds, often resulting in higher interest rates and less transparent credit assessment processes.
Loan Securitization
Loan securitization transforms bank loans into tradable securities, enhancing liquidity and risk distribution within traditional banking, while peer-to-peer lending platforms typically offer unsecured loans, limiting opportunities for securitization. The structured pooling of bank loans facilitates credit risk transfer to investors through asset-backed securities, contrasting with the direct lending model of P2P platforms that relies on borrower-lender matching without intermediary risk redistribution.
Alternative Credit Scoring
Alternative credit scoring in peer-to-peer lending leverages non-traditional data sources such as social media activity, utility payments, and online behavior patterns to assess borrower risk more dynamically than conventional bank loan evaluations, which primarily rely on credit reports and income verification. This innovative approach enables broader access to credit for individuals with limited credit history while potentially reducing default rates through more personalized risk assessment models.
Digital Underwriting
Digital underwriting in bank loans relies on traditional credit scoring models and extensive financial documentation, ensuring stringent risk assessment and regulatory compliance. Peer-to-peer lending platforms leverage advanced algorithms and alternative data sources for faster, more flexible credit evaluations, enhancing borrower accessibility and streamlining loan approval processes.
Marketplace Lending
Marketplace lending in peer-to-peer lending platforms offers faster loan approval and competitive interest rates compared to traditional bank loans by connecting borrowers directly with investors. This decentralized model reduces banking overhead, enhances transparency, and often provides access to credit for borrowers with non-traditional credit profiles.
Originator Risk Retention
Bank loan originators typically retain a significant portion of the loan risk, aligning their incentives with the borrower's creditworthiness and reducing default rates. In peer-to-peer lending, originator risk retention varies widely, often resulting in higher risk exposure for investors due to less stringent underwriting standards.
Direct Lending Platforms
Direct lending platforms in peer-to-peer lending offer borrowers faster access to funds by connecting them directly with individual investors, often resulting in lower interest rates compared to traditional bank loans. These platforms leverage advanced algorithms to assess credit risk, enhancing loan approval efficiency and transparency through digital interfaces.
Micro-Investing Loans
Bank loans typically offer structured repayment plans and regulatory protection but often require higher minimum amounts and strict credit checks, whereas peer-to-peer lending platforms enable micro-investing loans with lower entry barriers and more flexible terms, attracting individual investors seeking diversification. Micro-investing loans through P2P lending democratize access to credit by connecting small-scale borrowers with investors, optimizing capital flow in underserved markets.
Smart Contract Lending
Smart contract lending in peer-to-peer platforms eliminates traditional bank intermediaries by automating loan agreements and repayments through blockchain technology, ensuring transparency and reducing processing time. Unlike conventional bank loans with fixed interest rates and credit checks, smart contract lending offers dynamic pricing based on real-time data and lower fees, enhancing accessibility and efficiency in finance.
Real-Time Risk Assessment
Real-time risk assessment in bank loans relies on traditional credit scoring models and historical financial data, whereas peer-to-peer lending platforms utilize advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze borrower behavior and alternative data sources instantly. This enables P2P lenders to dynamically adjust interest rates and lending decisions, often resulting in faster approvals and personalized loan terms compared to conventional banking processes.
Bank Loan vs Peer-to-Peer Lending Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com