Traditional lending involves financial institutions providing loans with strict credit requirements, often resulting in longer approval times and higher interest rates. Peer-to-peer lending connects borrowers directly with individual investors through online platforms, offering more flexible terms and faster access to funds. This alternative financing method can lower borrowing costs and expand credit availability for individuals who might not qualify for conventional bank loans.
Table of Comparison
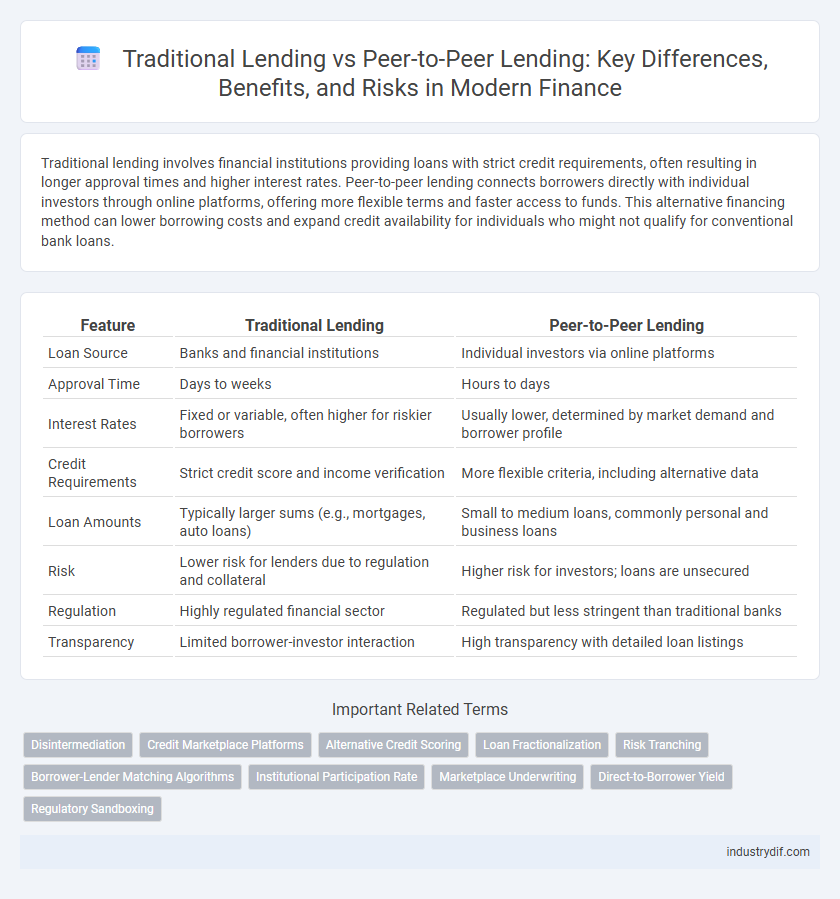
| Feature | Traditional Lending | Peer-to-Peer Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Source | Banks and financial institutions | Individual investors via online platforms |
| Approval Time | Days to weeks | Hours to days |
| Interest Rates | Fixed or variable, often higher for riskier borrowers | Usually lower, determined by market demand and borrower profile |
| Credit Requirements | Strict credit score and income verification | More flexible criteria, including alternative data |
| Loan Amounts | Typically larger sums (e.g., mortgages, auto loans) | Small to medium loans, commonly personal and business loans |
| Risk | Lower risk for lenders due to regulation and collateral | Higher risk for investors; loans are unsecured |
| Regulation | Highly regulated financial sector | Regulated but less stringent than traditional banks |
| Transparency | Limited borrower-investor interaction | High transparency with detailed loan listings |
Overview of Traditional Lending vs Peer-to-Peer Lending
Traditional lending involves financial institutions like banks providing loans backed by credit assessments, collateral, and regulatory oversight, resulting in structured repayment schedules and interest rates. Peer-to-peer lending connects borrowers directly with individual investors through online platforms, often offering more flexible terms and competitive rates due to reduced intermediary costs. Both models present distinct risk profiles and accessibility options, influencing borrower eligibility and investor returns.
Lending Models Compared: Bank Loans and P2P Platforms
Traditional bank loans rely on centralized financial institutions that assess creditworthiness through extensive documentation and underwriting processes, often resulting in higher interest rates and longer approval times. Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms connect borrowers directly with individual investors, utilizing algorithmic credit evaluations to offer more competitive rates and faster funding. This decentralized approach reduces operational costs and expands access to capital for borrowers who may not qualify for conventional bank loans.
Credit Assessment and Risk Management Approaches
Traditional lending relies on extensive credit scoring models, collateral evaluation, and regulatory compliance to assess borrower creditworthiness and manage risk, often using FICO scores and income verification as key criteria. Peer-to-peer lending platforms implement alternative credit assessment methods, including social data analytics, machine learning algorithms, and real-time borrower behavior tracking to diversify risk evaluation. Risk management in P2P lending also involves portfolio diversification by lenders and automated loan grading systems to mitigate default rates compared to conventional banking practices.
Interest Rate Structures: Fixed vs Marketplace Dynamics
Traditional lending typically features fixed interest rates determined by financial institutions, providing predictable repayment schedules and risk assessment models based on credit scores. Peer-to-peer lending employs marketplace dynamics where interest rates fluctuate according to borrower risk profiles and investor competition, often resulting in variable rates that can be more favorable for high-credit borrowers. This decentralized approach leverages real-time data and investor demand, creating diverse interest rate structures tailored to individual loan risk and market conditions.
Loan Origination and Approval Speed
Traditional lending involves a lengthy loan origination process due to extensive credit checks, paperwork, and regulatory compliance, often taking weeks for approval. Peer-to-peer lending platforms leverage advanced algorithms and digital verification to expedite loan approval, frequently reducing turnaround time to days or even hours. The streamlined, technology-driven model of peer-to-peer lending significantly enhances borrower access to faster funding compared to conventional financial institutions.
Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance Standards
Traditional lending operates under stringent regulatory frameworks established by federal and state agencies, including the Federal Reserve and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, ensuring comprehensive compliance with banking laws and consumer protection standards. Peer-to-peer lending platforms are subject to securities regulations and must comply with the Securities and Exchange Commission's rules, which focus on transparency, investor protection, and fraud prevention, but often face less rigorous oversight compared to traditional banks. The variance in compliance standards impacts risk management, borrower eligibility verification, and reporting requirements, making regulatory adherence a critical factor in choosing lending models.
Borrower Accessibility and Qualification Criteria
Traditional lending often requires borrowers to meet stringent qualification criteria, including high credit scores, collateral, and extensive documentation, which can limit accessibility for many individuals and small businesses. Peer-to-peer lending platforms use alternative credit assessments and flexible approval processes, increasing accessibility for borrowers with diverse financial backgrounds. This model leverages technology to evaluate risk more dynamically, enabling quicker access to capital without the rigid constraints of traditional banking institutions.
Investor Participation and Returns
Investor participation in traditional lending typically involves financial institutions or banks offering loans with regulated interest rates and risk management protocols. Peer-to-peer lending platforms enable individual investors to directly fund borrowers, often resulting in higher returns due to lower overhead costs and increased risk exposure. Returns in peer-to-peer lending tend to vary widely based on borrower creditworthiness and platform fees, while traditional lending usually offers more stable but lower yields.
Default Rates and Loan Recovery Mechanisms
Traditional lending typically experiences lower default rates due to stringent credit assessments and established collateral requirements, enhancing loan recovery mechanisms through legal enforcement and structured repayment plans. Peer-to-peer lending often faces higher default risks because of limited credit checks and unsecured loans, relying on platform-facilitated collections as the primary recovery strategy. Effective loan recovery in peer-to-peer networks depends on borrower reputation scoring and automated reminders, differing significantly from conventional banking recovery processes.
Future Trends in Lending: Digital Transformation and Fintech Impact
Traditional lending is increasingly integrating digital technologies to streamline loan approval processes and enhance risk assessment accuracy using big data and AI algorithms. Peer-to-peer lending platforms leverage blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi) to offer transparent, faster, and lower-cost lending solutions, disrupting conventional banking models. The fintech impact accelerates this transformation by fostering personalized lending experiences and expanding access to credit for underbanked populations worldwide.
Related Important Terms
Disintermediation
Disintermediation in finance reduces reliance on traditional lending institutions by enabling peer-to-peer lending platforms to directly connect borrowers and investors, lowering costs and increasing access to capital. Traditional lending involves banks acting as intermediaries, which often results in higher fees and longer approval processes compared to the streamlined, technology-driven peer-to-peer model.
Credit Marketplace Platforms
Credit marketplace platforms connect borrowers with multiple traditional lenders, offering competitive loan options based on creditworthiness and risk profiles. Peer-to-peer lending platforms facilitate direct loans between individuals, leveraging technology to reduce costs and provide faster access to funds, often resulting in more flexible credit terms.
Alternative Credit Scoring
Alternative credit scoring in peer-to-peer lending leverages non-traditional data such as social media activity, transaction histories, and utility payments to assess borrower creditworthiness, enhancing access for individuals with limited credit history. Traditional lending relies heavily on credit scores from established bureaus, often excluding those without extensive credit records and limiting financial inclusion.
Loan Fractionalization
Loan fractionalization in traditional lending often involves bundling loans into securities sold to institutional investors, limiting access for individual participants. Peer-to-peer lending platforms enable fractional investment by allowing multiple individuals to fund portions of a single loan, increasing diversification and reducing risk for lenders.
Risk Tranching
Traditional lending involves banks assuming full credit risk by underwriting loans with collateral and stringent credit assessments, whereas peer-to-peer lending platforms employ risk tranching to distribute credit risk among multiple investor tiers, enhancing portfolio diversification and potentially increasing returns. This segmentation allows higher-risk tranches to attract investors with higher risk tolerance while protecting senior tranches, thereby optimizing risk-adjusted capital allocation.
Borrower-Lender Matching Algorithms
Traditional lending relies on credit scores and manual underwriting processes to match borrowers with lenders, often resulting in slower approval times and limited flexibility. Peer-to-peer lending platforms utilize advanced borrower-lender matching algorithms that analyze behavioral data, risk profiles, and social indicators to optimize loan offers and improve funding efficiency.
Institutional Participation Rate
Traditional lending involves financial institutions such as banks and credit unions with an institutional participation rate close to 100%, driving most loan approvals and capital allocation. Peer-to-peer lending platforms feature a significantly lower institutional participation rate, relying primarily on individual investors to fund loans, which diversifies risk but limits large-scale capital inflows.
Marketplace Underwriting
Traditional lending relies on banks' internal credit assessment teams using standardized criteria for underwriting, while peer-to-peer lending platforms utilize marketplace underwriting that leverages data analytics, borrower behavior patterns, and alternative credit scoring models to assess risk. Marketplace underwriting enhances loan accessibility, often offering faster decisions and tailored risk evaluation compared to conventional bank loans.
Direct-to-Borrower Yield
Traditional lending relies on financial institutions as intermediaries, often resulting in lower direct-to-borrower yields due to operational costs and profit margins. Peer-to-peer lending platforms eliminate intermediaries, enabling borrowers to access funds at potentially lower interest rates while investors benefit from higher direct returns on their capital.
Regulatory Sandboxing
Regulatory sandboxing allows traditional lending institutions to test new financial products and technologies within a controlled environment under regulatory supervision, reducing compliance risks and fostering innovation. Peer-to-peer lending platforms benefit from sandbox frameworks by gaining clearer guidelines and operational flexibility, accelerating market entry while ensuring investor protection.
Traditional lending vs Peer-to-peer lending Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com