Bond trading involves buying and selling traditional debt securities to capitalize on price fluctuations and interest rate changes. Green bond investing specifically targets bonds issued to fund environmentally sustainable projects, combining financial returns with positive environmental impact. Investors considering these options should weigh the potential for steady income in bond trading against the ethical appeal and long-term growth prospects of green bonds.
Table of Comparison
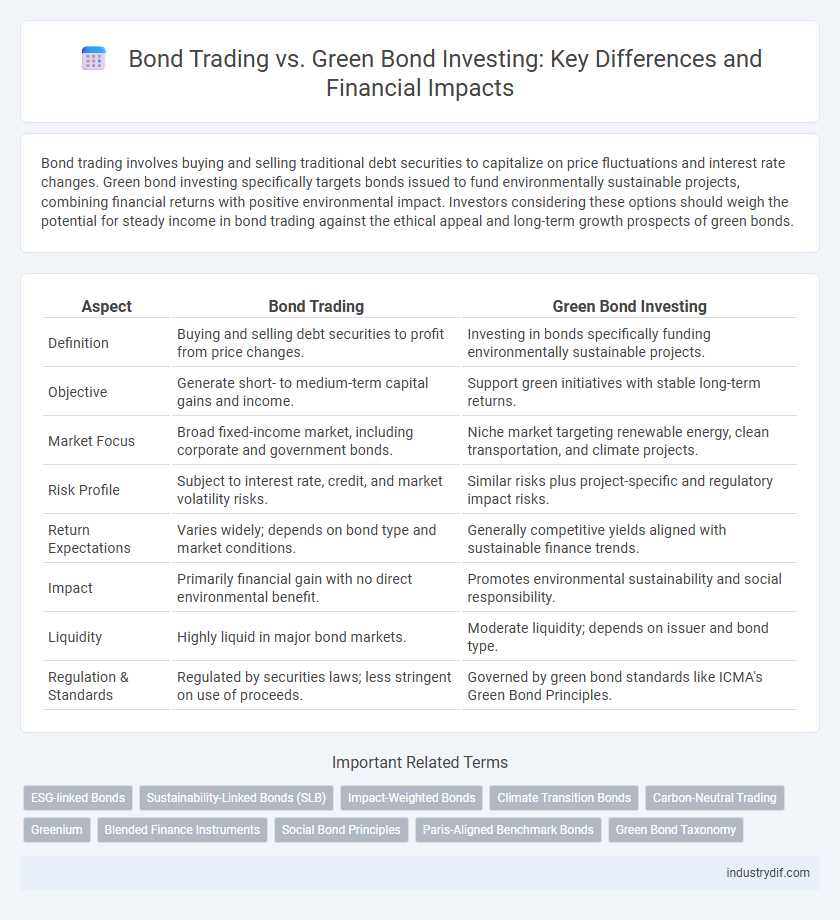
| Aspect | Bond Trading | Green Bond Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying and selling debt securities to profit from price changes. | Investing in bonds specifically funding environmentally sustainable projects. |
| Objective | Generate short- to medium-term capital gains and income. | Support green initiatives with stable long-term returns. |
| Market Focus | Broad fixed-income market, including corporate and government bonds. | Niche market targeting renewable energy, clean transportation, and climate projects. |
| Risk Profile | Subject to interest rate, credit, and market volatility risks. | Similar risks plus project-specific and regulatory impact risks. |
| Return Expectations | Varies widely; depends on bond type and market conditions. | Generally competitive yields aligned with sustainable finance trends. |
| Impact | Primarily financial gain with no direct environmental benefit. | Promotes environmental sustainability and social responsibility. |
| Liquidity | Highly liquid in major bond markets. | Moderate liquidity; depends on issuer and bond type. |
| Regulation & Standards | Regulated by securities laws; less stringent on use of proceeds. | Governed by green bond standards like ICMA's Green Bond Principles. |
Introduction to Bond Trading and Green Bond Investing
Bond trading involves buying and selling debt securities issued by corporations or governments to raise capital, with prices influenced by interest rates, credit ratings, and market demand. Green bond investing specifically targets bonds issued to fund environmentally sustainable projects, appealing to investors seeking both financial returns and positive environmental impact. Understanding these distinct market segments enables investors to diversify portfolios while aligning investments with sustainability goals.
Understanding Traditional Bond Trading
Traditional bond trading involves buying and selling debt securities issued by governments or corporations to raise capital, with traders aiming to profit from interest payments and price fluctuations. These bonds are typically categorized by maturity, credit quality, and yield, influencing investor decisions based on risk tolerance and investment objectives. Understanding the mechanics of bond pricing, including factors such as coupon rates and market interest rates, is essential for evaluating returns and managing portfolio risk in conventional bond markets.
What Are Green Bonds? Definition and Objectives
Green bonds are fixed-income securities specifically designed to fund projects with positive environmental or climate benefits, such as renewable energy, clean transportation, and sustainable agriculture. Their primary objective is to attract capital towards sustainable development initiatives while offering investors financial returns comparable to traditional bonds. These bonds adhere to strict transparency and reporting standards to ensure the proceeds are used exclusively for environmentally beneficial projects.
Market Dynamics: Conventional Bonds vs Green Bonds
Market dynamics in bond trading reveal conventional bonds dominate with higher liquidity, broader investor base, and established pricing mechanisms, whereas green bonds, driven by sustainability goals, attract niche investors focusing on environmental impact. Conventional bonds benefit from extensive historical data and regulatory frameworks, enabling efficient price discovery and risk assessment, while green bonds face evolving standards and certification challenges influencing market confidence. The growing demand for green bonds highlights a shift toward integrating ESG criteria in portfolio management, gradually closing the liquidity gap with traditional bond markets.
Liquidity and Risk Profiles in Bond Trading
Bond trading typically offers higher liquidity with active secondary markets allowing quick entry and exit, whereas green bond investing may experience lower liquidity due to niche demand and specialized project financing. Risk profiles in bond trading vary widely based on issuer credit ratings, market volatility, and interest rate fluctuations, while green bonds generally carry environmental project risks alongside standard credit and interest rate risks. Investors prioritizing liquidity often favor traditional bond trading, whereas those focused on sustainability might accept lower liquidity for the environmental benefits of green bond investments.
Environmental Impact and ESG Considerations in Green Bond Investing
Green bond investing prioritizes environmental impact by channeling capital towards projects that promote renewable energy, pollution reduction, and climate resilience, aligning with stringent ESG criteria. Unlike conventional bond trading, which mainly targets financial returns, green bonds incorporate comprehensive environmental, social, and governance assessments to measure sustainability outcomes. This integration of ESG considerations enhances transparency and accountability, attracting socially responsible investors committed to sustainable development goals.
Return on Investment: Financial Performance Comparison
Bond trading typically offers higher liquidity and short-term gains through market price fluctuations, while green bond investing emphasizes stable, long-term returns aligned with sustainable projects and environmental impact. Financial performance comparison shows conventional bonds often provide stronger immediate returns, but green bonds attract investors prioritizing steady income with growing demand in ESG-compliant portfolios. Yield spreads, credit ratings, and maturity dates are key metrics influencing the ROI difference between traditional bond trading and green bond investing strategies.
Regulatory Landscape for Bonds and Green Bonds
The regulatory landscape for bond trading is governed by established securities laws and market regulations designed to ensure transparency, market integrity, and investor protection. Green bond investing faces additional regulatory scrutiny through environmental criteria and disclosure requirements imposed by frameworks such as the EU Green Bond Standard and the Climate Bonds Initiative, promoting sustainable finance. These regulations influence issuance standards, reporting obligations, and eligibility criteria, shaping investor confidence and market growth in both traditional and green bond markets.
Investor Profiles: Who Trades Bonds vs Who Buys Green Bonds
Traditional bond traders often include institutional investors, such as pension funds and hedge funds, focused on fixed income returns and market liquidity. Green bond investors typically consist of socially responsible investors, impact funds, and environmentally conscious retail investors prioritizing sustainable finance and positive environmental outcomes. Demographic trends indicate younger investors and ESG-focused portfolios are increasingly driving demand in the green bond sector.
Future Trends: Evolution of Bond Trading and Green Bond Markets
The future of bond trading is increasingly shaped by digital platforms and artificial intelligence, enhancing liquidity and pricing efficiency. Green bond markets are set to expand rapidly, driven by rising environmental regulations and investor demand for sustainable assets. Integration of ESG criteria into traditional bond trading will reshape portfolio strategies and catalyze capital flows towards climate-conscious investments.
Related Important Terms
ESG-linked Bonds
ESG-linked bonds, including green bonds, integrate environmental, social, and governance criteria into traditional bond trading, attracting investors prioritizing sustainable impact alongside financial returns. The growing market for green bond investing offers diversification opportunities with lower carbon footprints and supports projects addressing climate change, contrasting with conventional bond trading focused primarily on credit risk and yield.
Sustainability-Linked Bonds (SLB)
Sustainability-Linked Bonds (SLBs) enhance traditional bond trading by aligning financial returns with measurable environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals, offering dynamic incentives for issuers to improve sustainability performance. Unlike standard green bonds that fund specific eco-friendly projects, SLBs link coupon rates to sustainability KPIs, driving broader corporate responsibility and innovation in finance.
Impact-Weighted Bonds
Impact-weighted bonds integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics into traditional bond trading, enabling investors to quantify the positive outcomes of green projects alongside financial returns. This approach contrasts with conventional bond trading by prioritizing measurable sustainability impacts, thus attracting capital toward initiatives that drive tangible environmental benefits while maintaining market-driven risk and yield profiles.
Climate Transition Bonds
Climate transition bonds uniquely finance projects that reduce carbon emissions, providing targeted investment opportunities within bond trading markets aimed at supporting environmental sustainability. Unlike traditional bonds, these fixed-income securities not only offer financial returns but also advance corporate and governmental commitments to climate goals by directing capital toward decarbonization efforts.
Carbon-Neutral Trading
Bond trading involves buying and selling traditional debt securities to generate returns, while green bond investing specifically targets environmentally sustainable projects aimed at reducing carbon emissions. Carbon-neutral trading in green bonds supports financing renewable energy, energy efficiency, and other eco-friendly initiatives, promoting sustainable investment strategies aligned with global climate goals.
Greenium
Greenium represents the premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds compared to conventional bonds due to their environmental benefits and positive social impact. This price differential highlights the growing demand for sustainable finance products within bond trading, influencing yield spreads and investment strategies in fixed income markets.
Blended Finance Instruments
Blended finance instruments combine public and private capital to enhance bond trading liquidity while supporting sustainable investments like green bonds, thereby reducing risk for investors and amplifying environmental impact. These hybrid financial tools enable efficient allocation of funds by leveraging concessional finance with market-rate investments to drive scalable financing for climate-friendly projects.
Social Bond Principles
Social Bond Principles guide the issuance and investment of bonds aimed at financing projects with positive social outcomes, emphasizing transparency, impact reporting, and use of proceeds. Bond trading involves buying and selling various bonds for profit, while green bond investing specifically supports environmentally sustainable projects aligned with these principles.
Paris-Aligned Benchmark Bonds
Paris-Aligned Benchmark Bonds are fixed-income securities designed to meet the climate targets outlined in the Paris Agreement, offering investors opportunities to support sustainable projects while achieving competitive returns. Compared to traditional bond trading, investing in these green bonds aligns portfolio strategies with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, enhancing both financial performance and long-term ecological impact.
Green Bond Taxonomy
Green bond investing targets projects with environmental benefits, classified under the Climate Bonds Initiative taxonomy, which includes renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable land use. Bond trading involves buying and selling various fixed-income securities, but green bonds are distinguished by their compliance with green bond principles that promote transparency and impact reporting in environmental finance.
Bond Trading vs Green Bond Investing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com