Traditional banking relies on centralized institutions to manage and secure financial transactions, often resulting in higher fees and slower processes. Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer transactions, reducing intermediaries and increasing transparency. Enhanced accessibility and programmable smart contracts make DeFi an innovative alternative that challenges conventional banking models.
Table of Comparison
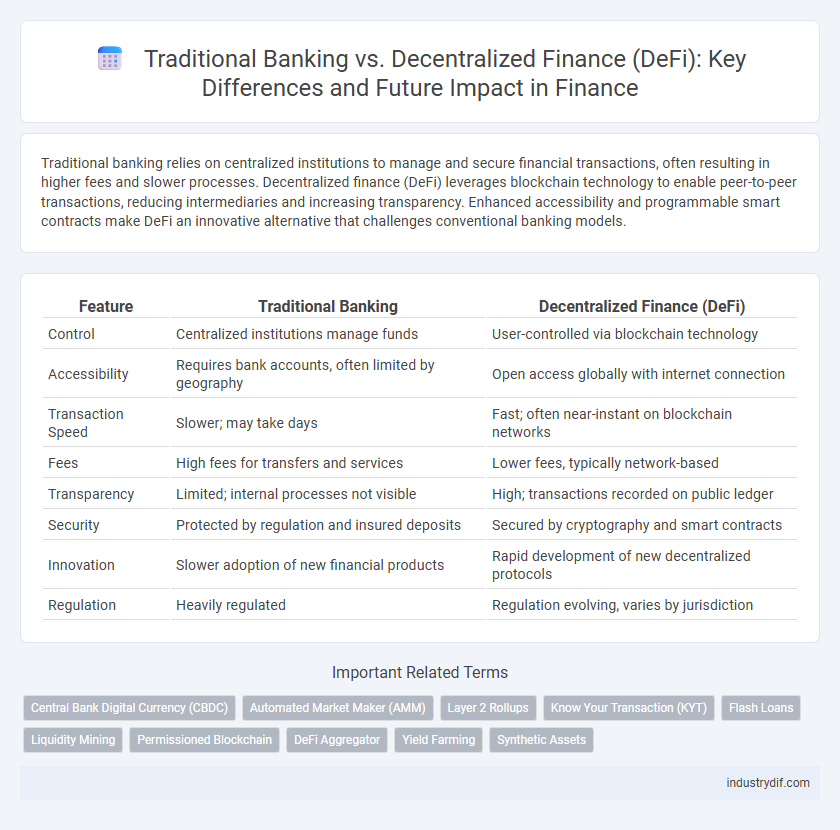
| Feature | Traditional Banking | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Centralized institutions manage funds | User-controlled via blockchain technology |
| Accessibility | Requires bank accounts, often limited by geography | Open access globally with internet connection |
| Transaction Speed | Slower; may take days | Fast; often near-instant on blockchain networks |
| Fees | High fees for transfers and services | Lower fees, typically network-based |
| Transparency | Limited; internal processes not visible | High; transactions recorded on public ledger |
| Security | Protected by regulation and insured deposits | Secured by cryptography and smart contracts |
| Innovation | Slower adoption of new financial products | Rapid development of new decentralized protocols |
| Regulation | Heavily regulated | Regulation evolving, varies by jurisdiction |
Overview of Traditional Banking
Traditional banking operates through centralized institutions such as commercial banks, credit unions, and savings banks that provide services including deposit accounts, loans, and payment processing under regulatory oversight. These banks rely on intermediaries and physical branches to facilitate transactions, maintaining trust through established reputations and government insurance schemes like the FDIC. Core features include interest-bearing savings accounts, fixed loan repayment schedules, and compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations.
Understanding Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) operates on blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer financial transactions without the need for traditional intermediaries like banks. Smart contracts automate processes such as lending, borrowing, and trading, increasing transparency and reducing costs. This financial ecosystem provides greater accessibility and control to users by eliminating centralized authority.
Core Differences Between Traditional Banking and DeFi
Traditional banking operates through centralized institutions that manage customer accounts, process transactions, and provide financial services under regulatory oversight, ensuring security but limited transparency. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer financial transactions without intermediaries, offering increased transparency, lower fees, and enhanced accessibility through smart contracts. Core differences include control mechanisms, with traditional banks holding custody of assets, while DeFi platforms give users full control over their funds and data.
Centralization vs Decentralization in Financial Systems
Traditional banking relies on centralized institutions that control and regulate financial transactions, maintaining authority over user accounts and data security. Decentralized finance (DeFi) operates on blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, thereby increasing transparency and reducing reliance on a single point of control. The shift from centralization to decentralization enhances financial inclusivity and resilience while challenging regulatory frameworks.
Security and Trust Mechanisms
Traditional banking employs centralized security protocols and regulatory oversight to safeguard assets and ensure trust through established financial institutions and government guarantees. Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology, cryptographic algorithms, and smart contracts to provide transparent, immutable transaction records and eliminate intermediaries, enhancing security but requiring users to trust code rather than institutions. While traditional systems rely on reputation and legal frameworks, DeFi's trust mechanisms depend on decentralized consensus, cryptographic validation, and open-source verification to mitigate fraud and increase resilience against single points of failure.
Regulatory Landscape: Banks vs DeFi
Traditional banking operates under strict regulatory frameworks enforced by government agencies such as the Federal Reserve and the Securities and Exchange Commission, ensuring consumer protection, anti-money laundering compliance, and financial stability. In contrast, decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms function on blockchain technology with minimal regulatory oversight, creating challenges for regulatory bodies attempting to enforce KYC/AML standards and protect investors. The evolving regulatory landscape presents a complex balance between fostering innovation in DeFi and maintaining the rigorous safeguards established in traditional banking systems.
Accessibility and Financial Inclusion
Traditional banking often imposes barriers such as minimum balance requirements and limited branch access, restricting financial services for underbanked populations. Decentralized finance (DeFi) utilizes blockchain technology to provide permissionless access to financial products, enabling users globally to participate without intermediaries. This shift enhances financial inclusion by offering transparent, affordable, and accessible alternatives to conventional banking systems.
Transaction Speed and Cost Comparison
Traditional banking systems typically involve multiple intermediaries, resulting in slower transaction processing times that can range from several hours to days and incur higher fees due to overhead and regulatory costs. Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms leverage blockchain technology to enable near-instantaneous transactions, often settling within seconds or minutes, with significantly lower fees by eliminating intermediaries. This speed and cost efficiency make DeFi a compelling alternative for users seeking faster and cheaper financial services compared to traditional banks.
Risks and Challenges Facing Both Systems
Traditional banking faces significant risks including centralized control vulnerability, regulatory compliance burdens, and exposure to systemic financial crises. Decentralized finance (DeFi) introduces challenges such as smart contract vulnerabilities, lack of regulatory oversight, and potential liquidity shortages. Both systems encounter cybersecurity threats, but DeFi's anonymous and immutable transactions amplify the difficulty of fraud prevention and dispute resolution.
Future Outlook: Traditional Banking and DeFi Integration
Traditional banking institutions are increasingly exploring decentralized finance (DeFi) integration to enhance transparency, reduce transaction costs, and improve customer access to financial services. Blockchain technology adoption allows banks to streamline processes such as cross-border payments, lending, and asset management while maintaining regulatory compliance. The future outlook points to hybrid financial systems where DeFi protocols coexist with conventional banking infrastructures to create more efficient and inclusive financial ecosystems.
Related Important Terms
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) represents a pivotal innovation bridging traditional banking and decentralized finance, offering enhanced transaction transparency, reduced settlement times, and increased financial inclusion under central bank supervision. Unlike fully decentralized cryptocurrencies, CBDCs maintain government-backed stability while leveraging blockchain technology to streamline payments and enforce regulatory compliance.
Automated Market Maker (AMM)
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) in Decentralized Finance (DeFi) utilize smart contracts to facilitate instant, permissionless asset trading without relying on traditional order books found in conventional banking. This contrasts with Traditional Banking systems where liquidity is provided by centralized institutions, often resulting in slower transaction speeds and higher fees.
Layer 2 Rollups
Layer 2 rollups enhance decentralized finance by processing transactions off-chain while leveraging the security of Layer 1 blockchains, significantly reducing costs and increasing throughput compared to traditional banking systems. This scalability innovation addresses the latency and high fees inherent in conventional finance, enabling faster and more efficient peer-to-peer transactions without reliance on centralized intermediaries.
Know Your Transaction (KYT)
Traditional banking relies on Know Your Transaction (KYT) protocols that monitor and verify customer transactions through centralized databases to ensure compliance and prevent fraud, while decentralized finance (DeFi) employs blockchain analytics and smart contracts to achieve transparent, automated transaction tracking without intermediaries. Advanced KYT solutions in DeFi utilize real-time data aggregation and AI-driven risk assessment to enhance transaction transparency and regulatory adherence across distributed networks.
Flash Loans
Flash loans in decentralized finance (DeFi) offer instant, uncollateralized borrowing within a single blockchain transaction, providing unprecedented liquidity access compared to traditional banking, where loans require credit checks and collateral. The ability to execute complex arbitrage, refinancing, or collateral swapping strategies in seconds differentiates DeFi's flash loans from slower, permissioned banking processes.
Liquidity Mining
Liquidity mining in decentralized finance (DeFi) offers users the opportunity to earn rewards by providing liquidity on platforms without intermediaries, contrasting traditional banking where liquidity is centralized and controlled by financial institutions. This shift enables more transparent, permissionless access to capital markets, increasing efficiency and democratizing financial participation.
Permissioned Blockchain
Permissioned blockchains in decentralized finance (DeFi) offer enhanced security and controlled access compared to traditional banking systems, enabling institutions to maintain regulatory compliance while facilitating faster, transparent transactions. These blockchains restrict participation to verified entities, reducing risks and improving trust without sacrificing decentralization benefits.
DeFi Aggregator
DeFi aggregators optimize decentralized finance by pooling liquidity and offering users seamless access to multiple protocols, outperforming traditional banking's siloed services and limited transparency. These platforms reduce transaction costs and increase yield opportunities by automatically sourcing the best rates for lending, borrowing, and trading across various decentralized pools.
Yield Farming
Yield farming in decentralized finance (DeFi) offers significantly higher annual percentage yields (APYs) compared to traditional banking savings accounts, often ranging from 10% to over 100%, by leveraging liquidity pools and smart contracts. Traditional banks provide lower returns typically under 1% APY but offer more regulatory security and insured deposits through institutions like the FDIC.
Synthetic Assets
Synthetic assets in decentralized finance (DeFi) replicate traditional financial instruments like stocks, commodities, or fiat currencies using blockchain technology and smart contracts, enabling global, permissionless access without intermediaries. Unlike traditional banking, which relies on centralized entities for issuance and settlement, synthetic assets leverage decentralized oracles and collateralized protocols to provide transparent, programmable exposure to real-world asset prices.
Traditional Banking vs Decentralized Finance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com