A traditional ledger is a centralized record-keeping system maintained by a single entity, often used in banking and accounting to track financial transactions. Distributed ledger technology (DLT) decentralizes this process by allowing multiple participants to access and verify the same transaction records simultaneously, enhancing transparency and security. Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger that organizes data into immutable blocks, providing a robust framework for real-time auditing and fraud prevention in financial services.
Table of Comparison
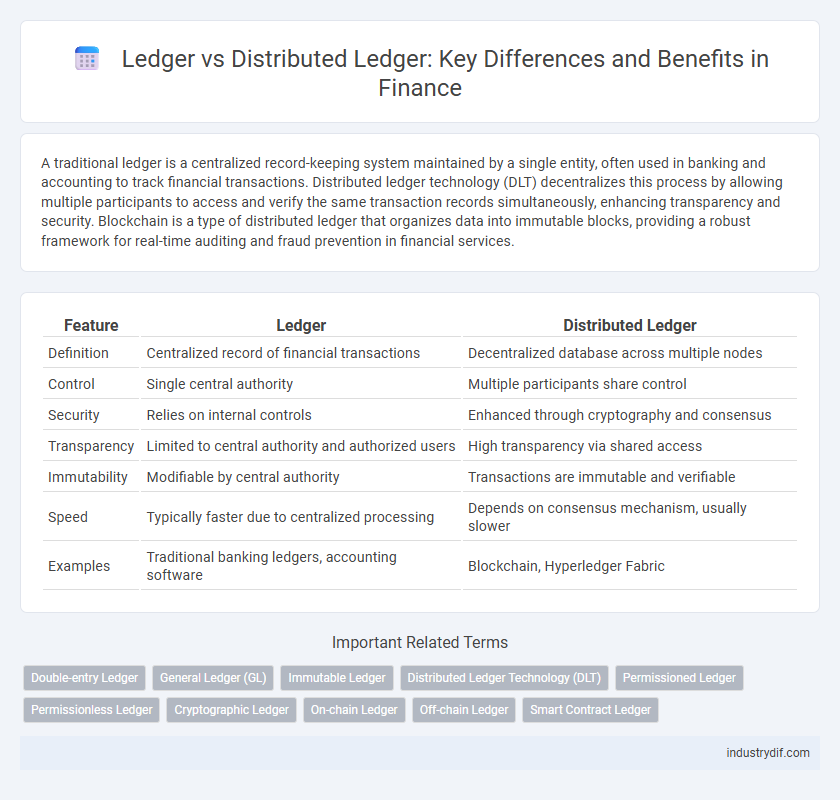
| Feature | Ledger | Distributed Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized record of financial transactions | Decentralized database across multiple nodes |
| Control | Single central authority | Multiple participants share control |
| Security | Relies on internal controls | Enhanced through cryptography and consensus |
| Transparency | Limited to central authority and authorized users | High transparency via shared access |
| Immutability | Modifiable by central authority | Transactions are immutable and verifiable |
| Speed | Typically faster due to centralized processing | Depends on consensus mechanism, usually slower |
| Examples | Traditional banking ledgers, accounting software | Blockchain, Hyperledger Fabric |
Understanding Traditional Ledgers in Finance
Traditional ledgers in finance function as centralized records where all transaction data is stored and maintained by a single authority, such as a bank or financial institution. These ledgers rely on trust in the central entity to ensure accuracy, security, and integrity of financial data. While efficient for internal auditing and compliance, traditional ledgers pose risks like single points of failure and limited transparency across multiple parties.
What is a Distributed Ledger?
A distributed ledger is a decentralized database where transaction records are maintained across multiple locations or participants, ensuring transparency and security without a central authority. Unlike a traditional ledger, which is managed by a single organization, a distributed ledger uses consensus mechanisms to validate and synchronize data across all nodes in the network. This technology underpins blockchain systems, enabling real-time, tamper-resistant financial record-keeping and reducing the risk of fraud.
Key Differences Between Ledger and Distributed Ledger
A traditional ledger is a centralized database that records financial transactions accessible by a single authority, whereas a distributed ledger is decentralized, with transaction data replicated across multiple nodes ensuring transparency and immutability. Key differences include data control, where ledgers rely on central oversight, while distributed ledgers employ consensus mechanisms to verify entries. Security and fault tolerance are enhanced in distributed ledgers through cryptographic protocols and redundancy, reducing the risk of data manipulation or system failure.
The Role of Centralization in Financial Ledgers
Centralized ledgers, maintained by a single authority such as a bank or financial institution, ensure streamlined control and accountability in transaction record-keeping. Distributed ledgers, like blockchain technology, decentralize data storage across multiple nodes, enhancing transparency and reducing the risk of single points of failure or fraud. The contrast in centralization profoundly impacts trust models, security protocols, and regulatory compliance within financial systems.
How Distributed Ledgers Enable Decentralization
Distributed ledgers transform traditional finance by enabling decentralization through a network of multiple participants that collectively maintain and verify transaction records, eliminating the need for a central authority. This decentralized approach enhances transparency, security, and resilience against fraud or system failures by distributing data across nodes worldwide. The technology underpinning distributed ledgers, such as blockchain, ensures immutability and trust through cryptographic validation and consensus mechanisms, empowering peer-to-peer financial interactions.
Security Features of Distributed Ledgers vs. Traditional Ledgers
Distributed ledgers enhance security through decentralization, eliminating a single point of failure common in traditional ledgers. Cryptographic techniques such as hashing and digital signatures ensure transaction integrity and authentication across all nodes in the network. Consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance add robust protection against fraud, unauthorized changes, and data tampering.
Transparency and Immutability: A Comparative View
Traditional ledgers offer limited transparency and are prone to manipulation due to centralized control, whereas distributed ledgers enhance transparency by allowing multiple participants to access and verify transactions in real time. Immutability is stronger in distributed ledgers, as cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms prevent unauthorized alterations, ensuring data integrity. This comparative advantage makes distributed ledgers a preferred choice for secure and transparent financial record-keeping.
Efficiency and Scalability in Financial Record-Keeping
A traditional ledger centralizes financial transactions, which can limit scalability and slow processing speed due to bottlenecks in data verification. Distributed ledgers employ decentralized consensus mechanisms across multiple nodes, enhancing efficiency by enabling parallel transaction validation and faster settlement times. This scalability allows financial institutions to handle higher transaction volumes securely while reducing the risk of single points of failure.
Use Cases: Traditional Ledgers vs. Distributed Ledgers in Finance
Traditional ledgers in finance are widely used for centralized record-keeping in banks, accounting, and regulatory compliance, ensuring accuracy and auditability within a single trusted entity. Distributed ledgers excel in cross-border payments, trade finance, and clearing and settlement by enabling real-time, transparent transactions across multiple participants without intermediaries. The immutable and decentralized nature of distributed ledgers reduces fraud risk and operational costs, driving innovation in decentralized finance (DeFi) and digital asset management.
The Future of Ledgers in the Evolving Financial Industry
Distributed ledgers leverage blockchain technology to enhance transparency, security, and real-time reconciliation, transforming traditional ledger systems. The future of financial record-keeping lies in decentralized models that reduce fraud risks and operational costs while enabling seamless cross-border transactions. Integration of smart contracts within distributed ledgers is poised to automate complex financial processes, driving efficiency and innovation.
Related Important Terms
Double-entry Ledger
A double-entry ledger records financial transactions through equal debits and credits, ensuring accuracy and preventing errors in traditional accounting systems. Distributed ledgers expand on this by enabling decentralized, tamper-resistant record-keeping across multiple nodes, enhancing transparency and security in financial reconciliation.
General Ledger (GL)
The General Ledger (GL) serves as the primary accounting record for all financial transactions within an organization, maintaining a centralized and immutable ledger that summarizes assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses. Distributed ledgers, in contrast, use decentralized consensus mechanisms to enhance transparency and security across multiple participants, but the GL remains essential for standardized financial reporting and regulatory compliance.
Immutable Ledger
An immutable ledger ensures that once transactions are recorded, they cannot be altered or deleted, providing enhanced security and auditability compared to traditional ledgers. Distributed ledgers extend immutability by decentralizing data across multiple nodes, reducing the risk of centralized fraud and increasing transparency in financial systems.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) enables decentralized record-keeping across multiple nodes, enhancing transparency, security, and immutability compared to traditional centralized ledgers. By leveraging cryptographic algorithms and consensus mechanisms, DLT supports real-time transaction validation and reduces the risk of fraud in financial systems.
Permissioned Ledger
A permissioned ledger restricts access to known participants, enhancing security and control compared to traditional centralized ledgers by enabling selective transaction validation and data sharing. Unlike public distributed ledgers, permissioned ledgers provide efficient consensus mechanisms tailored for enterprise finance, reducing latency and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Permissionless Ledger
A permissionless ledger, often exemplified by blockchain technology in cryptocurrencies, allows anyone to participate in transaction validation without centralized control, enhancing transparency and decentralization compared to traditional ledgers. Distributed ledgers maintain synchronized copies of transaction records across nodes, but permissionless ledgers specifically enable open access and consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work or proof-of-stake to secure the network trustlessly.
Cryptographic Ledger
A cryptographic ledger uses advanced encryption techniques to secure and validate transactions, making it a foundational component of distributed ledger technology (DLT) which decentralizes data across multiple nodes for enhanced transparency and tamper resistance. Unlike traditional ledgers maintained by a single entity, distributed cryptographic ledgers enable trustless consensus mechanisms such as blockchain, improving security and auditability in financial systems.
On-chain Ledger
An on-chain ledger records all transaction data directly on the blockchain, ensuring immutable, transparent, and decentralized financial records without relying on a central authority. Unlike traditional centralized ledgers, distributed ledgers synchronize copies across multiple nodes, enhancing security and resilience in real-time financial operations.
Off-chain Ledger
Off-chain ledgers store transaction data outside the main blockchain, enabling faster processing and reduced network congestion compared to traditional distributed ledgers. These systems enhance scalability and privacy by handling sensitive financial records off the public ledger while still allowing periodic synchronization with the blockchain for security and transparency.
Smart Contract Ledger
A Smart Contract Ledger operates as a specialized distributed ledger that automates and enforces contractual agreements through self-executing code, enhancing transparency and reducing the need for intermediaries in financial transactions. Unlike traditional ledgers that merely record transaction histories, Smart Contract Ledgers enable programmable finance by securely executing complex, conditional operations across a decentralized network.
Ledger vs Distributed Ledger Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com