Futures markets enable participants to buy and sell contracts based on the future delivery of assets, providing a mechanism for hedging risks and discovering prices anchored in supply and demand dynamics. Prediction markets aggregate diverse viewpoints by allowing traders to speculate on the outcome of events, offering probabilistic insights that can outperform traditional forecasting methods. Both markets enhance decision-making processes, yet futures primarily target financial and commodity risk management, while prediction markets focus on tapping collective intelligence to predict event probabilities.
Table of Comparison
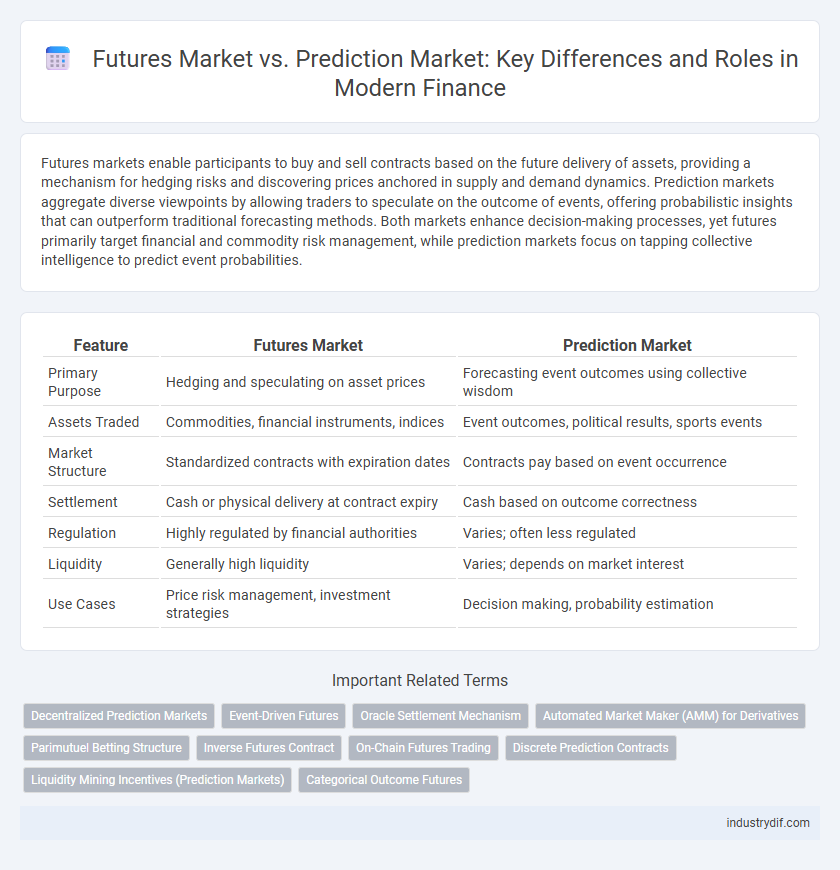
| Feature | Futures Market | Prediction Market |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Hedging and speculating on asset prices | Forecasting event outcomes using collective wisdom |
| Assets Traded | Commodities, financial instruments, indices | Event outcomes, political results, sports events |
| Market Structure | Standardized contracts with expiration dates | Contracts pay based on event occurrence |
| Settlement | Cash or physical delivery at contract expiry | Cash based on outcome correctness |
| Regulation | Highly regulated by financial authorities | Varies; often less regulated |
| Liquidity | Generally high liquidity | Varies; depends on market interest |
| Use Cases | Price risk management, investment strategies | Decision making, probability estimation |
Introduction to Futures Markets
Futures markets facilitate standardized contracts to buy or sell assets at predetermined prices on specific future dates, enabling investors to hedge risks or speculate on price movements. These markets play a crucial role in price discovery and liquidity for commodities, currencies, and financial instruments. Unlike prediction markets, which aggregate public opinion to forecast event outcomes, futures markets are driven by supply-demand dynamics and involve direct financial obligations.
Overview of Prediction Markets
Prediction markets aggregate diverse participant insights through trading contracts based on event outcomes, enabling real-time probabilistic forecasting of financial, political, or economic scenarios. Unlike futures markets, which primarily facilitate hedging and price discovery for commodities or financial instruments, prediction markets emphasize collective intelligence and information aggregation to anticipate uncertain future events. These markets improve decision-making by leveraging market-driven probabilities that reflect the collective sentiment and knowledge of traders.
Key Differences Between Futures and Prediction Markets
Futures markets involve standardized contracts to buy or sell assets at predetermined prices on future dates, primarily used for hedging risks and price discovery in commodities, currencies, and financial instruments. Prediction markets enable participants to trade contracts based on the outcome of specific events, aggregating collective intelligence to forecast events like elections, economic indicators, or product launches. Key differences include the underlying asset focus--tangible commodities versus event outcomes--and the purpose, where futures markets emphasize risk management and investment, while prediction markets serve as tools for information aggregation and probabilistic forecasting.
Historical Development of Both Markets
The futures market originated in the 19th century with agricultural commodity exchanges like the Chicago Board of Trade, evolving to manage price risk through standardized contracts. Prediction markets emerged more recently, around the early 2000s, leveraging collective intelligence to forecast outcomes in politics, economics, and other fields. Both markets have expanded with technological advancements, yet futures markets remain central to hedging in finance while prediction markets focus on information aggregation and decision-making.
Functional Mechanisms in Futures Trading
Futures trading operates through standardized contracts obligating the buyer to purchase or the seller to sell an asset at a predetermined price and date, ensuring price risk management and liquidity. Market participants use margin accounts and mark-to-market settlement to manage daily gains and losses, enhancing transparency and reducing default risk. Unlike prediction markets that aggregate event probabilities, futures markets primarily facilitate hedging and speculation based on underlying assets like commodities, currencies, and financial indices.
Prediction Market Structures and Operations
Prediction markets operate as decentralized platforms where participants trade contracts based on the outcome of future events, utilizing crowdsourced information to aggregate probabilities. These markets structure contracts to payout contingent on specific event results, fostering liquidity through a continuous double auction mechanism that enables real-time price discovery. Their operations rely heavily on diverse participant insights, enabling accurate forecasting by reflecting collective market sentiment and knowledge.
Use Cases and Applications in Finance
Futures markets enable investors to hedge against price volatility and secure asset prices for commodities, currencies, and financial instruments, providing essential tools for risk management and speculative trading. Prediction markets aggregate collective intelligence to forecast economic indicators, corporate earnings, and geopolitical events, assisting firms and policymakers in strategic decision-making and financial planning. Both markets drive market efficiency by offering transparent price signals, but futures focus on standardized contracts while prediction markets emphasize outcome betting on uncertain future events.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance
Futures markets operate under stringent regulatory frameworks such as the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) oversight in the U.S., ensuring transparency, standardized contracts, and protection against market manipulation. Prediction markets face varied regulatory scrutiny due to their nature of betting on event outcomes, often challenging traditional securities or gambling laws, which can limit their operation or classify them differently across jurisdictions. Compliance in futures markets requires adherence to margin requirements, reporting standards, and clearinghouse mandates, whereas prediction markets must navigate ambiguous legal environments focusing on risk disclosure and anti-fraud measures.
Risk Management Strategies
Futures markets enable risk management by locking in prices through standardized contracts, minimizing exposure to price volatility in commodities and financial instruments. Prediction markets aggregate diverse market participants' information to forecast event outcomes, indirectly assisting risk management by providing probabilistic insights. Combining futures market hedging with prediction market signals enhances strategic decision-making under uncertainty.
Future Trends and Innovations
Futures markets facilitate standardized contracts for assets delivering at specified dates, enabling risk management and price discovery based on underlying asset values. Prediction markets aggregate collective insights to forecast event outcomes, harnessing crowd wisdom for real-time probability assessment. Emerging innovations integrate blockchain technology and AI analytics, enhancing transparency, liquidity, and predictive accuracy across both futures and prediction markets.
Related Important Terms
Decentralized Prediction Markets
Decentralized prediction markets utilize blockchain technology to enable transparent, trustless forecasting of future events, contrasting with traditional futures markets that primarily focus on hedging and speculation through centralized exchanges. These decentralized platforms facilitate collective intelligence and real-time data aggregation by allowing participants to create and trade event-based contracts without intermediaries, enhancing market efficiency and price discovery in a secure environment.
Event-Driven Futures
Event-driven futures contracts in the futures market allow investors to hedge or speculate on the financial impact of specific events, such as earnings announcements or regulatory decisions, by locking in prices ahead of time. Prediction markets aggregate collective forecasts to price the probability of these events, offering real-time sentiment but lack the standardized trading and liquidity features of event-driven futures contracts.
Oracle Settlement Mechanism
The futures market relies on oracles to provide accurate and timely settlement prices based on verified market data, ensuring contract fulfillment and minimizing counterparty risk. Prediction markets use decentralized oracle mechanisms to aggregate diverse information sources, enhancing outcome accuracy and reducing manipulation in event-based contract settlements.
Automated Market Maker (AMM) for Derivatives
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) in futures markets facilitate decentralized trading of derivative contracts by utilizing liquidity pools and algorithmic pricing to ensure continuous market availability and price discovery. In contrast, prediction markets leverage AMMs to aggregate collective forecasts on future events, enabling probabilistic pricing without traditional order books or counterparties.
Parimutuel Betting Structure
The futures market relies on standardized contracts traded on regulated exchanges to hedge or speculate on price movements, whereas prediction markets utilize a parimutuel betting structure where all bets are pooled and odds reflect collective probability estimates. This parimutuel system aggregates individual wagers into a single liquidity pool, dynamically adjusting payouts based on total bets placed, enhancing market efficiency through crowd-sourced information.
Inverse Futures Contract
Inverse futures contracts in the futures market allow traders to hedge or speculate with payouts denominated in the base currency, often used in cryptocurrency trading to manage exposure without holding the underlying asset. Prediction markets differ by enabling participants to bet on the outcome of future events with contracts settled based on event results, providing real-time aggregated probabilities but without the leverage or margin features of inverse futures.
On-Chain Futures Trading
On-chain futures trading leverages blockchain technology to provide transparent, secure, and immutable contracts that enable market participants to hedge or speculate on asset price movements without intermediaries. Unlike prediction markets that aggregate subjective event outcomes, futures markets focus on standardized derivative contracts with settled delivery dates, offering enhanced liquidity and regulated price discovery mechanisms on decentralized platforms.
Discrete Prediction Contracts
Discrete prediction contracts in futures markets are standardized agreements that obligate the purchase or sale of an asset at a predetermined price on a specific date, providing clear price discovery and risk management tools. In contrast, prediction markets utilize discrete contracts to aggregate crowd-sourced probabilities on future events, offering probabilistic forecasts rather than fixed financial transactions.
Liquidity Mining Incentives (Prediction Markets)
Liquidity mining incentives in prediction markets drive enhanced user participation by rewarding token holders who provide liquidity, thereby increasing market efficiency and price discovery compared to futures markets. These incentives foster deeper liquidity pools and reduce bid-ask spreads, enabling more accurate forecasting and robust decentralized finance ecosystems.
Categorical Outcome Futures
Categorical outcome futures in the futures market provide standardized contracts based on specific, discrete event outcomes, facilitating hedging and speculation with clear payoff structures. Prediction markets offer similar categorical outcome contracts but emphasize collective forecasting through aggregated market sentiments, often resulting in more efficient and accurate probability-based price discovery.
Futures Market vs Prediction Market Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com