Fintech leverages advanced technology to improve traditional financial services by enhancing accessibility, efficiency, and user experience, often operating within regulated frameworks. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) removes intermediaries by utilizing blockchain technology and smart contracts to create open, permissionless financial systems that promote transparency and autonomy. Both models aim to revolutionize finance, but Fintech maintains centralized control while DeFi pushes for decentralized governance and democratized access.
Table of Comparison
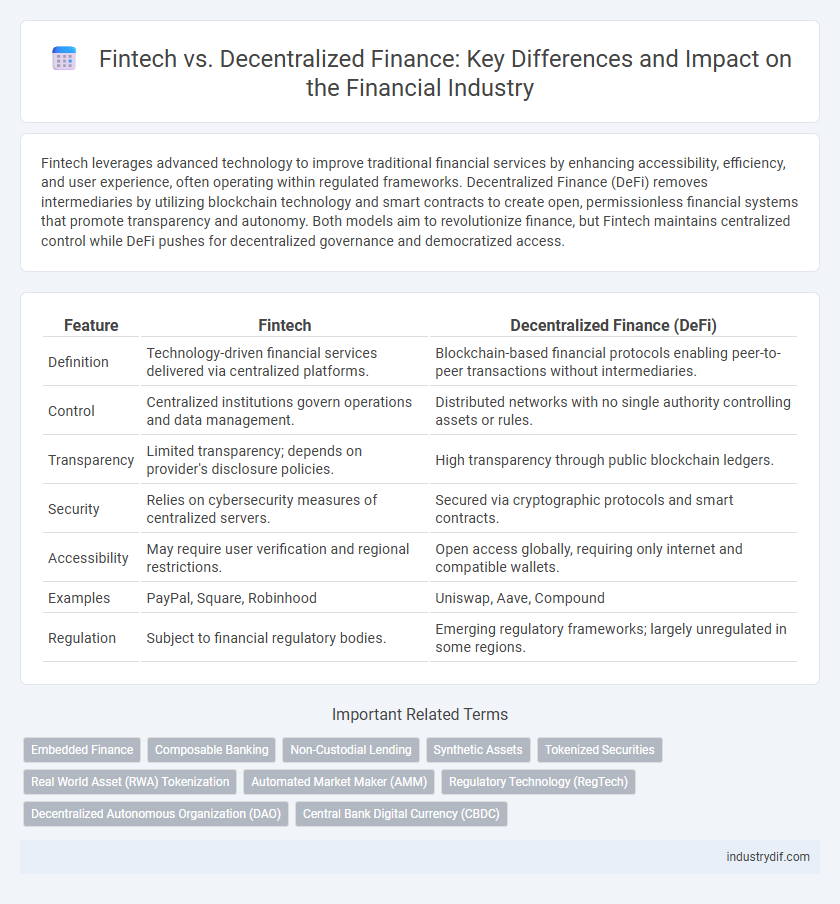
| Feature | Fintech | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technology-driven financial services delivered via centralized platforms. | Blockchain-based financial protocols enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. |
| Control | Centralized institutions govern operations and data management. | Distributed networks with no single authority controlling assets or rules. |
| Transparency | Limited transparency; depends on provider's disclosure policies. | High transparency through public blockchain ledgers. |
| Security | Relies on cybersecurity measures of centralized servers. | Secured via cryptographic protocols and smart contracts. |
| Accessibility | May require user verification and regional restrictions. | Open access globally, requiring only internet and compatible wallets. |
| Examples | PayPal, Square, Robinhood | Uniswap, Aave, Compound |
| Regulation | Subject to financial regulatory bodies. | Emerging regulatory frameworks; largely unregulated in some regions. |
Understanding Fintech: Evolution and Core Principles
Fintech represents the integration of technology within traditional financial services to enhance efficiency, accessibility, and user experience, driven by innovations such as digital payments, robo-advisors, and blockchain applications. Its evolution from basic automation to advanced algorithms and mobile banking platforms reflects the industry's adaptability in meeting consumer demands and regulatory requirements. Key principles include customer-centric design, security, scalability, and interoperability, which collectively shape modern financial ecosystems and influence emerging trends like Decentralized Finance (DeFi).
What Is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a blockchain-based financial system that operates without traditional intermediaries like banks, enabling peer-to-peer transactions through smart contracts on networks such as Ethereum. DeFi platforms facilitate services including lending, borrowing, trading, and asset management with enhanced transparency, security, and accessibility. Unlike conventional fintech, DeFi emphasizes open-source protocols and decentralized governance, reducing reliance on centralized authorities and increasing financial inclusion.
Key Differences Between Fintech and DeFi
Fintech integrates technology with traditional financial services to enhance user experience and operational efficiency through centralized platforms like mobile banking and payment apps. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) operates on blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer financial transactions without intermediaries, using smart contracts and cryptocurrencies. Key differences include regulatory oversight, with Fintech firms subject to established financial regulations, whereas DeFi platforms often function in a less regulated environment, emphasizing transparency and user control.
Technology Stack: Fintech vs DeFi
Fintech leverages traditional technology stacks including cloud computing, APIs, and centralized databases to deliver financial services efficiently through established regulatory frameworks. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) utilizes blockchain technology, smart contracts, and decentralized ledgers to enable peer-to-peer financial transactions without intermediaries. The core divergence lies in Fintech's reliance on centralized infrastructures versus DeFi's open-source, permissionless platforms built on Ethereum and other blockchain protocols.
Regulatory Landscape: Fintech vs DeFi
Fintech operates within established regulatory frameworks, ensuring compliance with financial authorities like the SEC and FCA, which provides consumer protection and market stability. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) challenges traditional regulations by operating on blockchain networks without central intermediaries, creating regulatory ambiguity and potential risks for investors. Regulatory bodies are increasingly exploring frameworks to address DeFi's transparency and security issues while balancing innovation with consumer safeguards.
Security Considerations in Fintech and DeFi
Fintech platforms typically implement robust security protocols such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and regulatory compliance to safeguard user data and transactions. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) relies on blockchain technology and smart contracts, which provide transparency and immutability but present risks like code vulnerabilities and lack of centralized oversight. Security in DeFi requires rigorous smart contract audits, decentralized governance, and user education to mitigate potential exploits and protect digital assets.
User Experience and Accessibility
Fintech platforms enhance user experience through intuitive interfaces, seamless integration with traditional banking systems, and personalized financial services powered by AI algorithms. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) offers unparalleled accessibility by eliminating intermediaries, enabling peer-to-peer transactions on blockchain networks, and supporting borderless finance with lower fees. While Fintech prioritizes ease of use within regulated environments, DeFi expands financial inclusion by providing open-source protocols accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
Innovation Drivers in Fintech and DeFi
Innovation drivers in Fintech include advanced data analytics, artificial intelligence, and seamless integration of digital payment systems that enhance user experience and operational efficiency. In contrast, Decentralized Finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology, smart contracts, and transparency to disrupt traditional financial intermediaries, fostering trustless and permissionless transactions. Both ecosystems propel financial inclusion and automation but differ in their technological frameworks and regulatory challenges.
Challenges and Risks Facing Fintech and DeFi
Fintech faces regulatory compliance challenges, data privacy concerns, and cybersecurity risks due to centralized data storage, while DeFi encounters smart contract vulnerabilities, liquidity risks, and lack of regulatory oversight that heightens exposure to fraud and market manipulation. Both Fintech and DeFi must address operational risks, but DeFi's dependence on blockchain technology introduces transparency and scalability issues unique to decentralized protocols. Risk mitigation strategies involve robust security frameworks, continuous regulatory adaptation, and enhanced user education to safeguard assets and maintain trust in digital financial ecosystems.
Future Outlook: Will Fintech and DeFi Converge?
Fintech and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) are poised to increasingly intersect as innovations in blockchain technology enhance traditional financial services with greater transparency, security, and efficiency. The integration of smart contracts and decentralized applications within fintech platforms promises to revolutionize payments, lending, and asset management by reducing intermediaries and operational costs. Future outlooks indicate a convergence where hybrid financial ecosystems leverage both centralized regulatory frameworks and decentralized protocols to offer more inclusive and resilient financial solutions.
Related Important Terms
Embedded Finance
Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, streamlining customer experiences and expanding access beyond traditional fintech offerings. Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to offer peer-to-peer financial services without intermediaries, contrasting with embedded finance's seamless incorporation into everyday applications for enhanced convenience and scalability.
Composable Banking
Composable banking leverages modular financial services enabling fintech firms to integrate decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols seamlessly, enhancing flexibility and innovation in digital banking platforms. By combining traditional financial infrastructure with blockchain-enabled composability, composable banking revolutionizes product development speed, personalized user experiences, and secure asset management.
Non-Custodial Lending
Non-custodial lending in decentralized finance (DeFi) allows borrowers and lenders to interact directly through smart contracts on blockchain platforms, eliminating intermediaries characteristic of traditional fintech lending services. This peer-to-peer approach enhances transparency, reduces counterparty risk, and offers global accessibility compared to fintech's often centralized and regulated custodial lending systems.
Synthetic Assets
Synthetic assets in decentralized finance (DeFi) replicate real-world financial instruments using blockchain technology, offering increased transparency and accessibility compared to traditional fintech solutions which rely on centralized intermediaries. These synthetic assets leverage smart contracts to provide programmable, borderless exposure to equities, commodities, and derivatives without requiring ownership of the underlying asset.
Tokenized Securities
Tokenized securities in fintech offer enhanced liquidity and fractional ownership by representing traditional assets on blockchain platforms, enabling faster, more transparent transactions. Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages smart contracts to facilitate peer-to-peer trading of these tokenized securities, reducing intermediaries and operational costs while increasing market accessibility.
Real World Asset (RWA) Tokenization
Fintech innovations drive efficiency in traditional financial services by digitizing processes and improving user access, while Decentralized Finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Real World Asset (RWA) tokenization in DeFi bridges physical assets like real estate and commodities with digital tokens, enhancing liquidity, transparency, and fractional ownership in global markets.
Automated Market Maker (AMM)
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) revolutionize Decentralized Finance (DeFi) by enabling trustless, algorithm-driven liquidity provision without traditional intermediaries, contrasting with conventional Fintech platforms that rely on centralized order books and middlemen. AMMs use smart contracts to facilitate continuous token swaps, enhancing market efficiency and accessibility while reducing counterparty risk inherent in centralized Fintech models.
Regulatory Technology (RegTech)
Regulatory Technology (RegTech) enhances compliance efficiency in both Fintech and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) by leveraging AI-powered analytics and blockchain transparency to monitor transactions and flag irregularities in real time. While Fintech integrates RegTech within centralized frameworks for streamlined regulatory reporting, DeFi employs decentralized ledgers and smart contracts to automate compliance, posing unique challenges and opportunities in regulatory oversight.
Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO)
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) represent a core innovation within Decentralized Finance (DeFi), enabling transparent, automated governance through blockchain-based smart contracts without centralized intermediaries. Unlike traditional Fintech platforms that rely on centralized control and intermediaries for financial services, DAOs facilitate peer-to-peer decision-making and fund management, enhancing security, trust, and efficiency in financial ecosystems.
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) represents a state-backed digital asset that integrates traditional financial system stability with fintech innovations, offering improved payment efficiency, security, and reduced transaction costs. Unlike decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms operating on blockchain without central authority, CBDCs enable central banks to maintain monetary policy control while leveraging digital currency benefits for broader financial inclusion.
Fintech vs Decentralized Finance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com