Fixed income investments provide predictable returns through interest payments from traditional bonds, offering stability and reduced risk. Tokenized bonds leverage blockchain technology to enable fractional ownership, increased liquidity, and faster settlement times, broadening access for smaller investors. While fixed income remains favored for reliability, tokenized bonds are transforming market accessibility and operational efficiency in the financial sector.
Table of Comparison
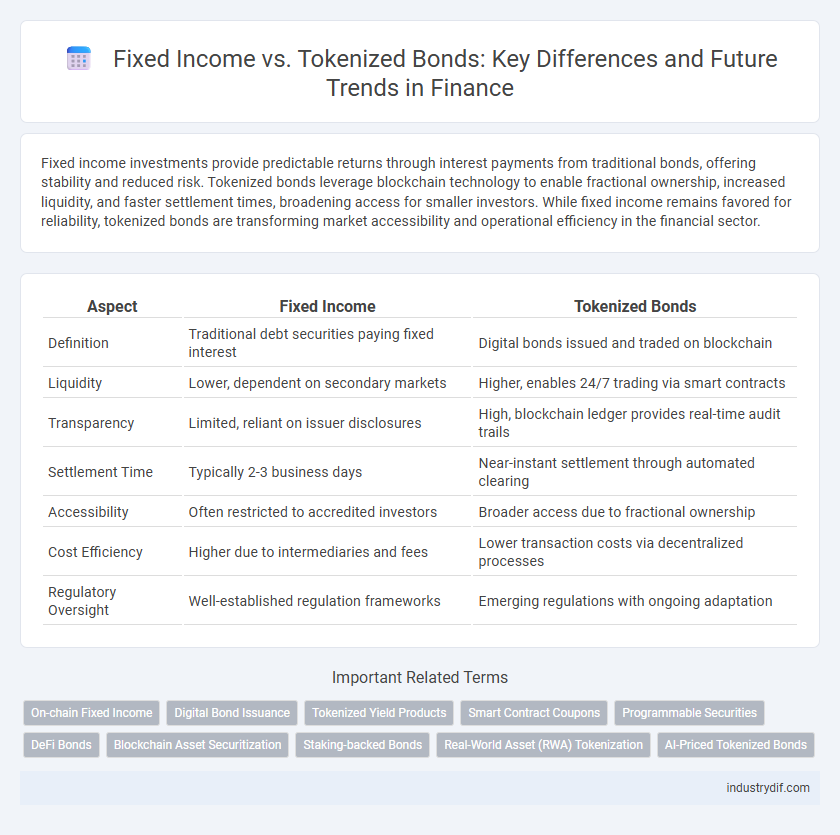
| Aspect | Fixed Income | Tokenized Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional debt securities paying fixed interest | Digital bonds issued and traded on blockchain |
| Liquidity | Lower, dependent on secondary markets | Higher, enables 24/7 trading via smart contracts |
| Transparency | Limited, reliant on issuer disclosures | High, blockchain ledger provides real-time audit trails |
| Settlement Time | Typically 2-3 business days | Near-instant settlement through automated clearing |
| Accessibility | Often restricted to accredited investors | Broader access due to fractional ownership |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher due to intermediaries and fees | Lower transaction costs via decentralized processes |
| Regulatory Oversight | Well-established regulation frameworks | Emerging regulations with ongoing adaptation |
Understanding Fixed Income Securities
Fixed income securities are debt instruments that provide investors with regular interest payments and the return of principal at maturity, including traditional bonds issued by governments or corporations. Tokenized bonds represent these traditional fixed income assets on a blockchain, enhancing transparency, liquidity, and accessibility through digital ownership. Understanding fixed income securities involves recognizing their role in portfolio diversification, fixed interest returns, and risk profiles compared to emerging tokenized alternatives.
Introduction to Tokenized Bonds
Tokenized bonds represent a digital transformation of traditional fixed income securities by leveraging blockchain technology to enable fractional ownership, enhanced liquidity, and faster settlement times. Unlike conventional bonds, tokenized bonds reduce intermediaries and operational costs through smart contracts, facilitating seamless transfers and increased accessibility for a broader range of investors. This innovation in fixed income markets supports improved transparency, real-time tracking, and programmable features that align with emerging decentralized finance trends.
Key Differences Between Fixed Income and Tokenized Bonds
Fixed income securities consist of traditional debt instruments like government and corporate bonds that offer regular interest payments and principal repayment at maturity, while tokenized bonds represent these assets on a blockchain, enabling faster settlement and enhanced transparency. Fixed income typically involves centralized intermediaries and slower transaction processes, whereas tokenized bonds leverage smart contracts for automated compliance and 24/7 trading on digital platforms. The liquidity of tokenized bonds can improve due to fractional ownership, contrasting with fixed income's often limited secondary market accessibility.
Advantages of Traditional Fixed Income Instruments
Traditional fixed income instruments provide established regulatory oversight and investor protections, ensuring lower counterparty risk and enhanced market transparency. They offer predictable cash flows with fixed interest payments, making them suitable for conservative investors seeking stable income. Additionally, the deep liquidity and well-developed secondary markets facilitate easier pricing and portfolio diversification compared to emerging tokenized bonds.
Benefits of Tokenized Bonds in Modern Finance
Tokenized bonds offer enhanced liquidity by enabling fractional ownership and 24/7 trading on blockchain platforms, reducing entry barriers for retail investors. They provide increased transparency and efficiency through smart contracts that automate coupon payments and settlements, cutting down operational costs and settlement times. Regulatory compliance is streamlined via programmable features, which allow real-time monitoring and auditability, fostering greater trust in the fixed income market.
Risks Associated with Tokenized and Traditional Bonds
Tokenized bonds offer enhanced liquidity and transparency through blockchain technology but carry risks such as smart contract vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainty, and cybersecurity threats. Traditional fixed income bonds face credit risk, interest rate fluctuations, and limited liquidity in secondary markets. Investors must assess these contrasting risk profiles to balance innovation benefits with established market stability.
Regulatory Landscape for Fixed Income vs. Tokenized Bonds
The regulatory landscape for fixed income securities is well-established, governed by stringent laws such as the Securities Act of 1933 and the Investment Company Act of 1940, ensuring investor protection and market stability. In contrast, tokenized bonds operate within a nascent regulatory framework, often facing uncertainty as jurisdictions develop guidelines for digital assets, including compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements. Regulatory bodies like the SEC and ESMA are increasingly focusing on creating compliant infrastructures for tokenized bonds to facilitate transparency while mitigating risks inherent to blockchain-based financial instruments.
Market Accessibility and Liquidity Comparisons
Fixed income securities typically offer broad market accessibility through established exchanges and institutional channels, but liquidity can be constrained by market hours and regulatory requirements. Tokenized bonds leverage blockchain technology to enhance market accessibility by enabling fractional ownership and 24/7 trading on decentralized platforms, significantly improving liquidity. The integration of smart contracts reduces settlement times and transactional friction compared to traditional fixed income instruments, fostering more dynamic market participation.
Technological Impact on Bond Issuance and Trading
Tokenized bonds leverage blockchain technology to enhance transparency, reduce issuance costs, and accelerate settlement times compared to traditional fixed income instruments. Smart contracts automate coupon payments and compliance checks, minimizing manual errors and operational risks. This technological innovation facilitates greater liquidity and accessibility, attracting a broader range of investors in the bond market.
The Future of Fixed Income Investments in a Tokenized World
Fixed income investments are rapidly evolving as tokenized bonds introduce enhanced liquidity, transparency, and accessibility to traditional debt markets. Tokenization enables fractional ownership and instant settlement through blockchain technology, reducing costs and expanding investor participation globally. This transformation positions the fixed income sector for increased innovation, efficiency, and diversification in future capital markets.
Related Important Terms
On-chain Fixed Income
On-chain fixed income leverages blockchain technology to offer increased transparency, faster settlement times, and enhanced liquidity compared to traditional fixed income instruments. Tokenized bonds facilitate fractional ownership and programmable features, enabling greater accessibility and efficiency in fixed income markets.
Digital Bond Issuance
Digital bond issuance through tokenized bonds enhances liquidity and transparency compared to traditional fixed income instruments by leveraging blockchain technology for secure, real-time settlement and fractional ownership. Tokenized bonds reduce issuance costs and enable faster access to global investors while maintaining fixed income characteristics such as predictable cash flows and credit risk exposure.
Tokenized Yield Products
Tokenized yield products leverage blockchain technology to enhance transparency, liquidity, and accessibility compared to traditional fixed income instruments. These digital assets enable fractional ownership, faster settlement, and programmable features, revolutionizing bond investment and portfolio diversification strategies.
Smart Contract Coupons
Fixed income securities traditionally deliver coupon payments through centralized issuers, while tokenized bonds leverage smart contracts to automate and ensure transparent coupon distributions directly on blockchain networks. Smart contract coupons enhance efficiency, reduce counterparty risk, and enable programmable payment schedules tailored to investor preferences.
Programmable Securities
Fixed income investments traditionally offer predictable cash flows through interest payments, while tokenized bonds leverage blockchain technology to enable programmable securities, allowing automated execution of contract terms such as coupon payments and compliance checks. Programmable securities enhance transparency, reduce settlement times, and enable fractional ownership, transforming fixed income markets by increasing liquidity and operational efficiency.
DeFi Bonds
Fixed income securities provide predictable cash flows through interest payments, while tokenized bonds leverage blockchain technology to enable fractional ownership, enhanced liquidity, and transparent settlement processes. DeFi bonds, as a subset of tokenized bonds, facilitate decentralized issuance and trading, reducing intermediaries and enabling programmable, automated yield distributions on blockchain platforms.
Blockchain Asset Securitization
Fixed income securities provide stable returns through traditional bond structures, while tokenized bonds leverage blockchain asset securitization to enhance transparency, liquidity, and fractional ownership. Blockchain technology facilitates secure, traceable transactions and reduces issuance costs, revolutionizing the fixed income market's accessibility and efficiency.
Staking-backed Bonds
Staking-backed bonds combine the stability of fixed income with blockchain-enhanced liquidity, offering investors a hybrid asset that secures returns through both coupon payments and staking rewards. This model leverages decentralized finance protocols to reduce default risk while enabling programmable, transparent dividend distribution compared to traditional fixed income securities.
Real-World Asset (RWA) Tokenization
Fixed income securities provide stable returns through interest payments, while tokenized bonds leverage blockchain technology to enhance liquidity and transparency in trading real-world assets (RWA). RWA tokenization transforms traditional bond markets by digitizing ownership, enabling fractional investments, and streamlining settlement processes for fixed income instruments.
AI-Priced Tokenized Bonds
AI-priced tokenized bonds leverage machine learning algorithms to dynamically assess market conditions and credit risk, offering enhanced pricing accuracy compared to traditional fixed income instruments. This innovation increases liquidity and transparency while reducing the inefficiencies and manual intervention typical in conventional bond markets.
Fixed Income vs Tokenized Bonds Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com