Insider trading involves trading securities based on non-public, material information, giving individuals an unfair advantage and often leading to legal penalties. Crowdsourced trading leverages collective public insights and data to inform investment decisions, promoting transparency and democratizing market participation. While insider trading breaches ethical and legal standards, crowdsourced trading encourages collaborative strategies within regulatory frameworks.
Table of Comparison
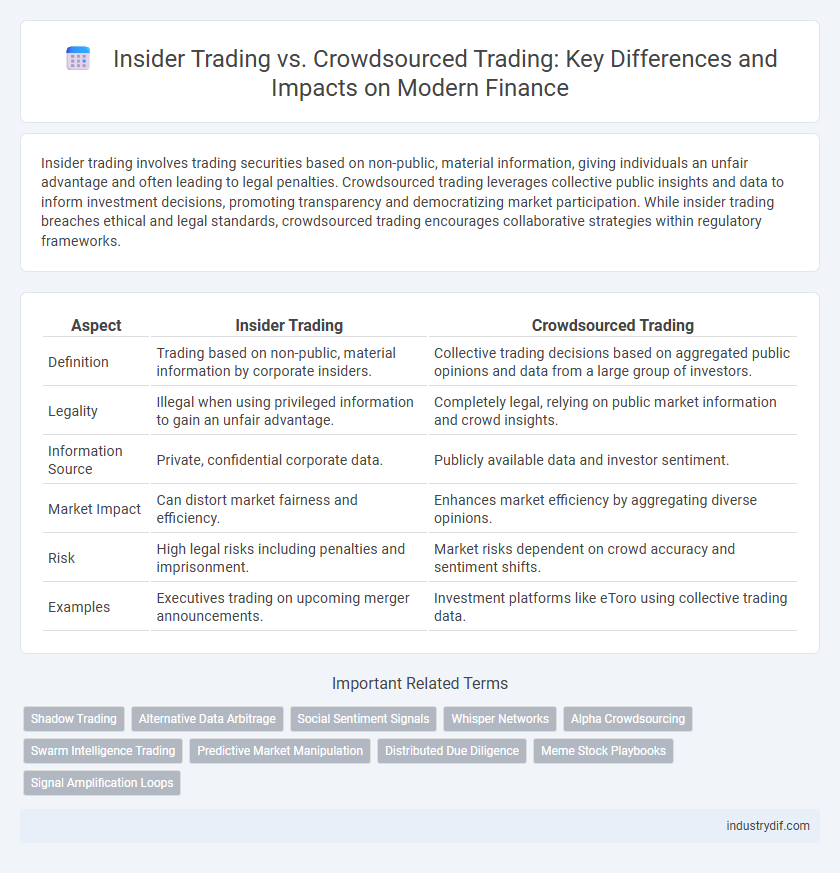
| Aspect | Insider Trading | Crowdsourced Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading based on non-public, material information by corporate insiders. | Collective trading decisions based on aggregated public opinions and data from a large group of investors. |
| Legality | Illegal when using privileged information to gain an unfair advantage. | Completely legal, relying on public market information and crowd insights. |
| Information Source | Private, confidential corporate data. | Publicly available data and investor sentiment. |
| Market Impact | Can distort market fairness and efficiency. | Enhances market efficiency by aggregating diverse opinions. |
| Risk | High legal risks including penalties and imprisonment. | Market risks dependent on crowd accuracy and sentiment shifts. |
| Examples | Executives trading on upcoming merger announcements. | Investment platforms like eToro using collective trading data. |
Definition of Insider Trading
Insider trading involves buying or selling a company's securities based on material, non-public information obtained by corporate insiders such as executives or employees. This illegal practice undermines market fairness and can lead to severe legal penalties. Crowdsourced trading, in contrast, relies on aggregated public information and collective investor insights without privileged access.
Definition of Crowdsourced Trading
Crowdsourced trading leverages the collective insights and decisions of a diverse group of investors to execute trades, enhancing market efficiency through distributed knowledge. Unlike insider trading, which involves illicit access to confidential information, crowdsourced trading capitalizes on publicly shared data and crowd wisdom to identify investment opportunities. This collaborative approach democratizes decision-making, often resulting in more balanced and transparent market outcomes.
Legal Framework Governing Insider Trading
The legal framework governing insider trading is anchored by regulations such as the U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934, which prohibits trading based on material non-public information to maintain market integrity. Enforcement agencies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) rigorously monitor and prosecute insider trading to safeguard investor confidence and ensure transparency. Crowdsourced trading operates within a legal context emphasizing public information sharing and collective market insights, distinctly separate from the prohibited use of confidential data in insider trading.
Regulatory Outlook on Crowdsourced Trading
Regulatory authorities are increasingly scrutinizing crowdsourced trading platforms to ensure compliance with securities laws and protect market integrity. Unlike insider trading, which involves illegal use of non-public information, crowdsourced trading relies on publicly shared insights but raises concerns about market manipulation and information asymmetry. Regulators may implement stricter disclosure requirements and monitoring mechanisms to address these risks while fostering transparency and investor protection.
Key Differences Between Insider and Crowdsourced Trading
Insider trading involves the buying or selling of securities based on non-public, material information held by corporate insiders, such as executives or employees, which is illegal and closely monitored by regulatory bodies like the SEC. Crowdsourced trading leverages the collective insights of a large group of retail investors who share information and strategies openly, relying on publicly available data and social platforms like Reddit or StockTwits. The key difference lies in the source and legality of information: insider trading uses confidential data with potential legal consequences, while crowdsourced trading depends on aggregated public opinion and is generally lawful.
Impact on Market Integrity
Insider trading undermines market integrity by exploiting non-public information for unfair profit, creating asymmetric advantages that erode investor confidence. Crowdsourced trading, driven by collective public sentiment and widely available data, fosters transparency and democratic participation but may increase volatility and herd behavior. Balancing regulation to deter illicit insider trading while encouraging responsible crowdsourced strategies is crucial for maintaining fair and efficient capital markets.
Risks and Consequences of Insider Trading
Insider trading involves trading based on non-public, material information, exposing individuals to severe legal risks including hefty fines, imprisonment, and reputational damage. Regulatory bodies like the SEC aggressively monitor and prosecute illegal insider trading to maintain market integrity and investor confidence. Unlike crowdsourced trading, which aggregates public sentiment, insider trading undermines market fairness and transparency, leading to significant economic and ethical consequences.
Potential Pitfalls of Crowdsourced Trading
Crowdsourced trading platforms aggregate diverse investor insights but face potential pitfalls such as herding behavior that can amplify market volatility and lead to irrational price movements. Lack of transparent accountability increases the risk of misinformation or coordinated manipulation, undermining market integrity. Unlike insider trading, which involves illegal use of non-public information, crowdsourced trading risks stem from collective biases and the challenge of filtering credible signals amid noise.
Case Studies: Notable Insider and Crowdsourced Trading Incidents
Notable insider trading cases such as the Martha Stewart scandal in 2001 and Raj Rajaratnam's Galleon Group insider trading ring highlight the severe legal repercussions and market manipulation risks posed by non-public information exploitation. In contrast, crowdsourced trading platforms like Robinhood have been pivotal in episodes such as the GameStop short squeeze in 2021, demonstrating how collective retail investor actions can create significant market volatility and challenge traditional Wall Street dynamics. These incidents collectively underscore the evolving regulatory and ethical landscape in financial markets influenced by both privileged information misuse and mass investor behavior.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Trading Strategies
Emerging technologies and data analytics are reshaping trading strategies by enhancing transparency and market efficiency, shifting the dynamic from traditional insider trading towards crowdsourced trading models. Artificial intelligence and blockchain integration enable real-time information sharing among diverse investors, democratizing market access and reducing reliance on privileged information. Future trends indicate a growing emphasis on collective intelligence platforms and decentralized exchanges, which are expected to redefine market behavior and regulatory frameworks in the finance industry.
Related Important Terms
Shadow Trading
Shadow trading involves investors mimicking the trades of insiders to capitalize on non-public information indirectly, leveraging collective data analytics and behavioral patterns. This contrasts with crowdsourced trading, where decisions emerge from aggregated user insights without relying on privileged information, highlighting ethical and legal distinctions in market participation.
Alternative Data Arbitrage
Insider trading exploits non-public, material information for market advantage, whereas crowdsourced trading leverages aggregated alternative data from diverse public sources to identify arbitrage opportunities. Alternative data arbitrage in crowdsourced trading utilizes patterns in real-time social sentiment, satellite imagery, and transactional data to outperform traditional insider signals, democratizing access to market insights.
Social Sentiment Signals
Insider trading leverages non-public, material information to gain an unfair market advantage, while crowdsourced trading utilizes aggregated social sentiment signals from platforms like Twitter and Reddit to identify trends and inform investment decisions. Social sentiment analysis processes vast amounts of user-generated data to predict stock movements, enhancing decision-making transparency and democratizing market insights compared to traditional insider trading methods.
Whisper Networks
Whisper networks facilitate crowdsourced trading by aggregating non-public market insights from a distributed group of investors, offering a decentralized alternative to traditional insider trading which relies on privileged information from corporate insiders. This approach leverages collective intelligence and real-time social data to predict market movements, potentially increasing transparency and reducing regulatory risks associated with illicit insider trading activities.
Alpha Crowdsourcing
Alpha Crowdsourcing leverages the collective intelligence of diverse retail investors to identify market inefficiencies and generate alpha, contrasting with insider trading that relies on non-public, material information for unfair advantage. By harnessing large-scale, real-time data from crowdsourced trades, Alpha Crowdsourcing promotes transparency and democratizes access to alpha signals, disrupting traditional finance models based on insider knowledge.
Swarm Intelligence Trading
Swarm intelligence trading leverages collective decision-making by aggregating insights from diverse market participants, contrasting with insider trading, which relies on privileged information for unfair advantage. Harnessing real-time data and crowd sentiment, swarm intelligence models optimize trade accuracy and mitigate risks by democratizing access to market signals.
Predictive Market Manipulation
Insider trading exploits non-public, material information to execute trades that anticipate market moves, often undermining market integrity and creating unfair advantages. Crowdsourced trading aggregates diverse, public investor insights, yet its predictive capabilities can be vulnerable to coordinated manipulations that artificially influence market trends and prices.
Distributed Due Diligence
Distributed due diligence leverages crowdsourced trading by aggregating diverse investor insights, enhancing transparency and reducing reliance on potentially biased insider information. This collective approach mitigates risks associated with insider trading, promoting more equitable market dynamics through democratized access to data and analysis.
Meme Stock Playbooks
Insider trading exploits non-public, material information for profit, often involving regulatory risks, whereas crowdsourced trading leverages collective retail investor sentiment and social media trends to drive meme stock playbooks. Meme stock strategies rely on viral online communities and platform-driven momentum, contrasting the secrecy and expertise central to insider trading.
Signal Amplification Loops
Insider trading leverages non-public, material information to create rapid signal amplification loops among select market participants, driving price movements before information becomes widely available. Crowdsourced trading relies on aggregating diverse public signals from a broad base, generating feedback loops that amplify collective market sentiment and influence trading volumes through social platforms.
Insider Trading vs Crowdsourced Trading Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com