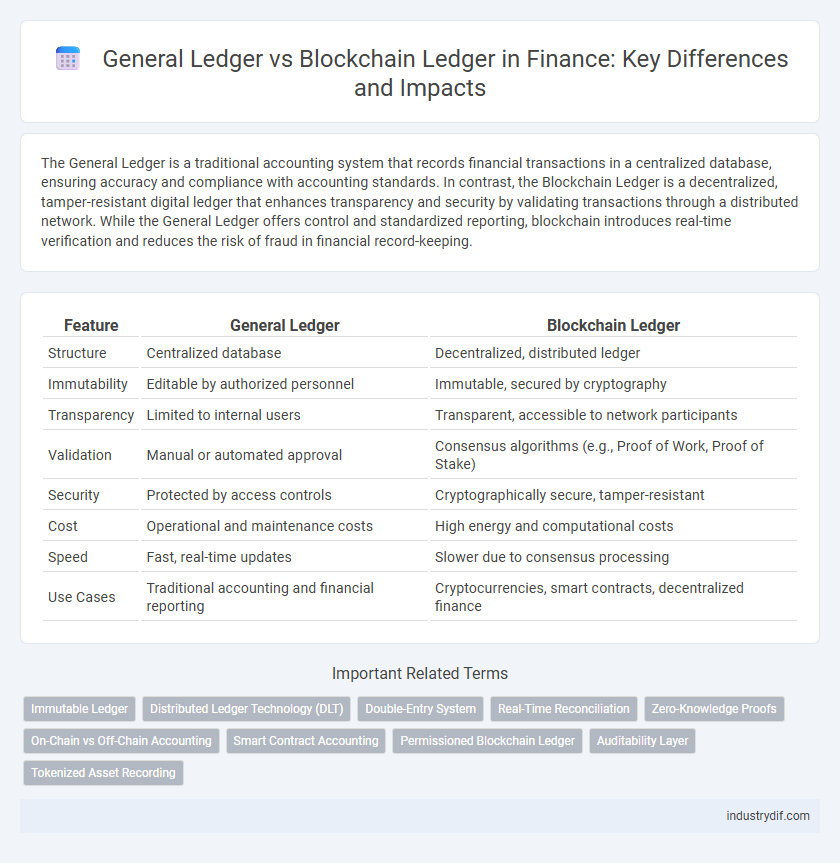
The General Ledger is a traditional accounting system that records financial transactions in a centralized database, ensuring accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. In contrast, the Blockchain Ledger is a decentralized, tamper-resistant digital ledger that enhances transparency and security by validating transactions through a distributed network. While the General Ledger offers control and standardized reporting, blockchain introduces real-time verification and reduces the risk of fraud in financial record-keeping.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | General Ledger | Blockchain Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Centralized database | Decentralized, distributed ledger |
| Immutability | Editable by authorized personnel | Immutable, secured by cryptography |
| Transparency | Limited to internal users | Transparent, accessible to network participants |
| Validation | Manual or automated approval | Consensus algorithms (e.g., Proof of Work, Proof of Stake) |
| Security | Protected by access controls | Cryptographically secure, tamper-resistant |
| Cost | Operational and maintenance costs | High energy and computational costs |
| Speed | Fast, real-time updates | Slower due to consensus processing |
| Use Cases | Traditional accounting and financial reporting | Cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, decentralized finance |
Definition of General Ledger
The General Ledger is a core accounting record that systematically organizes all financial transactions of a business, serving as the foundation for financial statements and reporting. It consolidates entries from various sub-ledgers, including accounts payable and receivable, ensuring accuracy and compliance with accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS. Unlike blockchain ledger technology, the General Ledger operates in a centralized and controlled environment, primarily managed by internal accounting departments for auditing and reconciliation purposes.
Definition of Blockchain Ledger
A blockchain ledger is a decentralized and immutable digital record that chronologically logs transactional data across a distributed network, enhancing transparency and security. It leverages cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms to ensure data integrity and prevent tampering or unauthorized alterations. Unlike a traditional general ledger, the blockchain ledger operates without a central authority, enabling real-time, trustless verification of financial transactions.
Key Components of General Ledger
The General Ledger consists of key components including accounts, journal entries, and trial balances, which collectively ensure accurate recording and classification of financial transactions. It serves as the central repository for all accounting data, enabling detailed financial reporting and audit trails. Unlike blockchain ledgers, the General Ledger relies on centralized control and periodic reconciliation to maintain accuracy and integrity.
Key Components of Blockchain Ledger
Blockchain ledger consists of decentralized, distributed databases that record transactions across multiple nodes, ensuring transparency and immutability. Key components include cryptographic hashing for data integrity, consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake to validate entries, and smart contracts that automate and enforce business rules. Unlike traditional general ledgers, blockchain ledgers provide enhanced security, real-time auditing capabilities, and resistance to data tampering.
Data Recording and Structure
General Ledger systems utilize a centralized database to record financial transactions in a structured, double-entry format ensuring consistency and accuracy across accounts. Blockchain ledgers distribute data across a decentralized network, using cryptographic hashing and an immutable chain of blocks to enhance transparency and security in transaction recording. While traditional ledgers offer streamlined reconciliation processes, blockchain ledgers provide tamper-resistant records that reduce the risk of fraud in financial data management.
Transparency and Security Features
General Ledger systems provide a centralized record-keeping method with controlled access, which can limit transparency but ensures data consistency through defined audit trails. Blockchain Ledger offers decentralized and immutable transaction records, enhancing transparency by enabling all participants to verify entries independently. Its cryptographic security features prevent tampering and fraud, delivering superior data integrity compared to conventional general ledgers.
Auditability and Compliance
The General Ledger provides a traditional centralized record system essential for regulatory compliance and straightforward audit trails through controlled access and transaction logs. Blockchain Ledger offers enhanced auditability by creating immutable, time-stamped records distributed across a decentralized network, reducing risks of tampering and fraud. Both systems support financial transparency, but blockchain's cryptographic validation significantly strengthens compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
Real-Time Access and Reconciliation
General Ledger systems provide structured financial record-keeping but often involve delayed reconciliation due to batch processing and periodic updates. Blockchain Ledger offers real-time access with decentralized, immutable records, enabling continuous, automated reconciliation across distributed participants. This instantaneous transparency reduces errors and enhances auditability, transforming financial operations with greater efficiency.
Cost and Implementation Challenges
General Ledger systems typically involve lower upfront costs but incur ongoing expenses related to manual reconciliation and centralized maintenance. Blockchain Ledger implementation demands higher initial investment due to infrastructure setup, integration complexity, and specialized expertise, yet offers reduced transactional costs through automation and enhanced transparency. Organizations face challenges such as scalability issues and regulatory compliance when deploying blockchain technology compared to traditional ledger systems.
Future Trends in Ledger Technology
Future trends in ledger technology indicate a growing convergence between traditional General Ledgers and Blockchain Ledgers, driven by advancements in distributed ledger technology (DLT) and real-time data processing. Blockchain's inherent transparency, immutability, and decentralized validation mechanisms offer enhanced security and auditability compared to conventional General Ledgers, making them increasingly attractive for complex financial ecosystems. Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning within these ledgers is expected to improve fraud detection, automate reconciliation processes, and optimize financial reporting accuracy.
Related Important Terms
Immutable Ledger
A General Ledger records financial transactions in accounting systems with possibilities for alteration or error correction, whereas a Blockchain Ledger ensures immutability by securely encrypting and timestamping each transaction across a decentralized network. This immutability characteristic of blockchain enhances financial transparency and auditability by preventing unauthorized data changes and providing a permanent, tamper-proof record.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
General Ledger remains the traditional centralized accounting system that records financial transactions within an organization, while Blockchain Ledger leverages Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) to offer decentralized, immutable, and transparent transaction records across multiple nodes. DLT enhances security, reduces reconciliation errors, and enables real-time auditing, providing a transformative alternative to conventional General Ledger systems in finance.
Double-Entry System
The General Ledger employs a traditional double-entry bookkeeping system, ensuring every financial transaction affects at least two accounts to maintain balanced records. In contrast, a Blockchain Ledger records transactions across a decentralized network with cryptographic verification, providing immutable and transparent entries but not inherently utilizing the double-entry accounting framework.
Real-Time Reconciliation
General Ledger systems traditionally rely on batch processing for reconciliation, often causing delays in transaction verification, whereas Blockchain Ledger offers real-time, decentralized transaction validation through cryptographic consensus mechanisms. This enables instantaneous, transparent reconciliation across distributed nodes, significantly reducing errors and enhancing auditability in financial reporting.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Zero-Knowledge Proofs enhance Blockchain Ledgers by enabling transaction verification without revealing sensitive financial data, providing superior privacy compared to traditional General Ledgers. This cryptographic technique ensures secure, transparent audit trails while maintaining confidentiality crucial for regulatory compliance in finance.
On-Chain vs Off-Chain Accounting
General Ledger systems maintain off-chain accounting records centralized within organizational databases, enabling controlled access and reconciliation processes. Blockchain ledgers provide on-chain accounting with decentralized, immutable transaction records that enhance transparency and reduce the risk of data tampering.
Smart Contract Accounting
General Ledger systems provide a centralized record of financial transactions, while Blockchain Ledgers offer decentralized and immutable transaction histories enabling enhanced transparency and security. Smart Contract Accounting automates financial processes by executing predefined contract terms on Blockchain Ledgers, reducing errors and ensuring real-time compliance.
Permissioned Blockchain Ledger
A permissioned blockchain ledger enhances traditional general ledger systems by providing decentralized, tamper-resistant transaction records with controlled access for authorized participants, ensuring transparency and auditability in financial operations. Its cryptographic security and consensus mechanisms reduce fraud risk and streamline reconciliation processes, making it ideal for regulated financial environments.
Auditability Layer
The General Ledger maintains a centralized record of financial transactions, relying on periodic audits and reconciliations to ensure accuracy and compliance. Blockchain Ledger enhances auditability by providing an immutable, decentralized ledger with transparent, cryptographically secured transactions, enabling real-time verification and reducing fraud risks.
Tokenized Asset Recording
General Ledger systems centralize financial records with traditional double-entry bookkeeping, while Blockchain Ledger offers decentralized, immutable tokenized asset recording that enhances transparency and security. Tokenized assets on blockchain enable real-time tracking, simplified audit trails, and improved liquidity through programmable smart contracts.
General Ledger vs Blockchain Ledger Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com