Hedge funds employ diverse investment strategies, including discretionary and quantitative approaches, to maximize returns while managing risk across various asset classes. Quantitative trading relies heavily on mathematical models and algorithms to identify and exploit market inefficiencies with high-speed execution and data-driven decision making. While hedge funds may integrate quantitative trading techniques, the primary distinction lies in the broader strategic flexibility and active management employed by hedge funds compared to the systematic and model-based approach of quantitative traders.
Table of Comparison
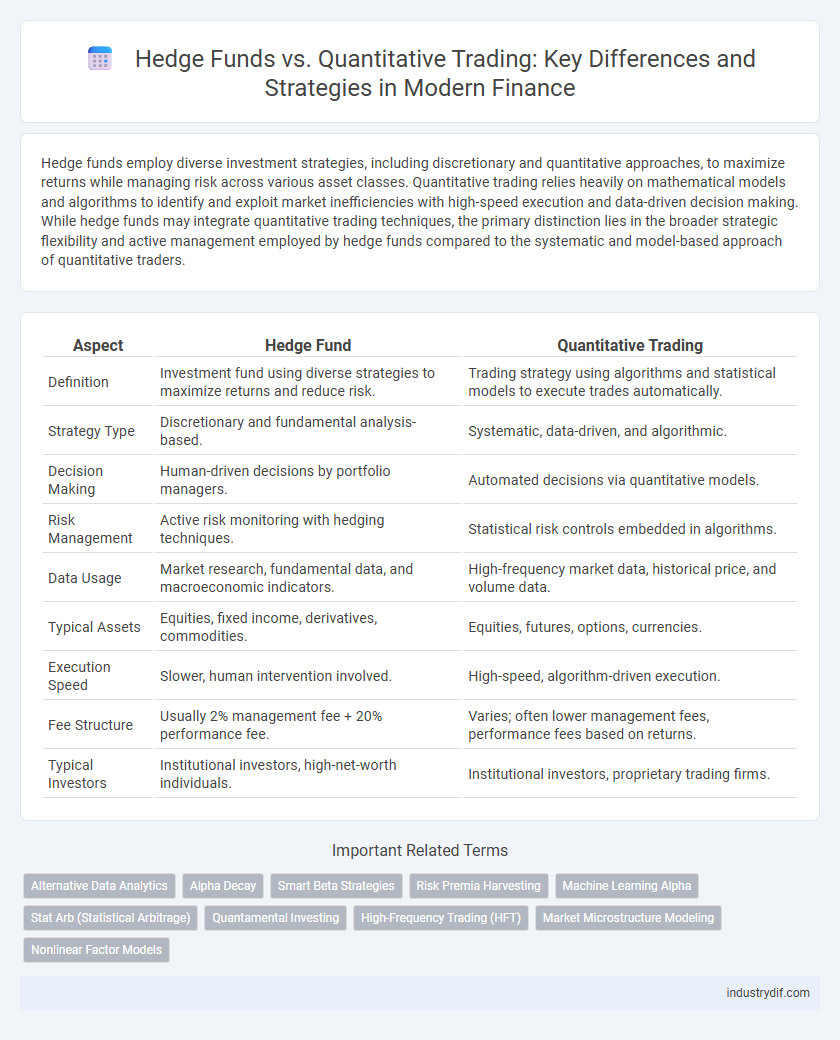
| Aspect | Hedge Fund | Quantitative Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment fund using diverse strategies to maximize returns and reduce risk. | Trading strategy using algorithms and statistical models to execute trades automatically. |
| Strategy Type | Discretionary and fundamental analysis-based. | Systematic, data-driven, and algorithmic. |
| Decision Making | Human-driven decisions by portfolio managers. | Automated decisions via quantitative models. |
| Risk Management | Active risk monitoring with hedging techniques. | Statistical risk controls embedded in algorithms. |
| Data Usage | Market research, fundamental data, and macroeconomic indicators. | High-frequency market data, historical price, and volume data. |
| Typical Assets | Equities, fixed income, derivatives, commodities. | Equities, futures, options, currencies. |
| Execution Speed | Slower, human intervention involved. | High-speed, algorithm-driven execution. |
| Fee Structure | Usually 2% management fee + 20% performance fee. | Varies; often lower management fees, performance fees based on returns. |
| Typical Investors | Institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals. | Institutional investors, proprietary trading firms. |
Introduction to Hedge Funds and Quantitative Trading
Hedge funds are pooled investment vehicles managed by professionals utilizing diverse strategies like long-short equity, arbitrage, and global macro to achieve alpha and manage risk. Quantitative trading employs algorithmic models and statistical techniques to analyze vast datasets and execute trades systematically, often emphasizing speed and precision. Both approaches leverage advanced financial theories and technology, but hedge funds blend discretionary decision-making with quantitative tools, while quantitative trading relies primarily on automated algorithms.
Core Differences Between Hedge Funds and Quantitative Trading
Hedge funds employ diverse investment strategies, including fundamental analysis and discretionary decision-making, to achieve high returns, often combining multiple asset classes and risk factors. Quantitative trading relies on algorithmic models and statistical methods to execute high-frequency trades based on historical data and market patterns, emphasizing automation and systematic risk management. The core difference lies in hedge funds' flexible, human-driven approach versus quantitative trading's data-driven, model-based execution.
Investment Strategies in Hedge Funds
Hedge funds employ diverse investment strategies including long/short equity, global macro, and event-driven approaches to maximize returns while managing risk. These strategies often combine fundamental analysis with qualitative factors to exploit market inefficiencies and achieve absolute returns. In contrast, quantitative trading relies heavily on algorithmic models and statistical methods to identify trading opportunities based on historical data and market signals.
Quantitative Trading: Techniques and Models
Quantitative trading employs mathematical models, statistical analysis, and algorithmic strategies to identify and exploit market inefficiencies, often processing vast datasets at high speeds. Techniques such as machine learning, factor models, and high-frequency trading algorithms enable traders to optimize asset selection and risk management dynamically. These data-driven models enhance precision in signal generation, differentiating quantitative trading from traditional hedge fund discretionary approaches.
Risk Management Approaches: Hedge Funds vs Quantitative Trading
Hedge funds employ diversified risk management techniques including portfolio diversification, stop-loss orders, and dynamic hedging to mitigate market volatility and drawdowns. Quantitative trading relies heavily on algorithmic models and statistical methods such as value at risk (VaR), stress testing, and real-time risk analytics to optimize trade execution and minimize exposure. Both strategies integrate advanced risk controls, but quantitative trading emphasizes automation and predictive analytics to adjust risk in rapidly changing markets.
Technology and Data Utilization in Finance
Hedge funds leverage advanced technology platforms and alternative data sources to identify investment opportunities and manage risks, often blending discretionary strategies with algorithmic insights. Quantitative trading, driven by sophisticated mathematical models and high-frequency data analysis, relies heavily on big data processing and machine learning to execute automated trades at scale. Both approaches increasingly harness cloud computing, AI, and real-time datasets to enhance predictive accuracy and optimize portfolio performance in competitive financial markets.
Performance Metrics and Evaluation Standards
Hedge fund performance metrics primarily include the Sharpe ratio, alpha generation, and drawdown analysis to measure risk-adjusted returns and active management effectiveness. Quantitative trading evaluation emphasizes statistical metrics such as the Sortino ratio, information ratio, and backtested strategy robustness to assess algorithmic performance under varying market conditions. Both approaches require rigorous analysis of volatility, liquidity impact, and execution efficiency to ensure sustainable long-term returns.
Regulatory Environment: Compliance Challenges
Hedge funds face complex regulatory environments with stringent compliance requirements from bodies like the SEC and CFTC, including reporting obligations and anti-money laundering rules. Quantitative trading firms navigate additional challenges related to algorithmic trading regulations, real-time monitoring, and transparency mandates to prevent market manipulation. Both sectors must invest heavily in compliance infrastructure to mitigate risks and avoid substantial penalties.
Career Pathways: Hedge Fund vs Quantitative Analyst
Career pathways in hedge funds often emphasize portfolio management, risk analysis, and strategic decision-making, requiring expertise in financial markets and strong analytical skills. Quantitative analyst roles focus on developing mathematical models and algorithmic strategies to optimize trading performance, necessitating advanced knowledge in statistics, computer science, and financial theory. Both career trajectories demand proficiency in programming languages like Python and R, but quantitative analysts typically engage more deeply in data science and machine learning applications to drive algorithmic trading innovations.
Future Trends in Hedge Funds and Quantitative Trading
Future trends in hedge funds emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance predictive analytics and risk management. Quantitative trading continues to evolve with increased use of alternative data sources and real-time processing capabilities to improve algorithmic strategies. Both sectors are expected to see more regulatory scrutiny and demand for transparency, driving innovation in compliance technologies.
Related Important Terms
Alternative Data Analytics
Hedge funds leverage alternative data analytics to gain unique market insights, enhancing traditional investment strategies with real-time, non-financial data such as social media trends, satellite imagery, and transaction records. Quantitative trading relies heavily on algorithmic models that integrate alternative data to identify patterns and execute high-frequency trades, optimizing returns through data-driven decision-making and machine learning techniques.
Alpha Decay
Alpha decay in hedge funds occurs as the unique advantages or market inefficiencies they exploit diminish over time, reducing their excess returns. Quantitative trading strategies often experience faster alpha decay due to widespread adoption and model crowding, leading to quicker erosion of predictive edge.
Smart Beta Strategies
Smart beta strategies blend passive investing with active risk management by systematically weighting assets based on factors like value, momentum, and volatility, offering an alternative to traditional hedge fund approaches. Unlike purely quantitative trading that relies heavily on algorithmic models and high-frequency data, smart beta emphasizes transparent, rule-based portfolio construction to capture factor premiums and enhance risk-adjusted returns.
Risk Premia Harvesting
Hedge funds utilize diverse strategies to capture risk premia by actively managing portfolios and exploiting market inefficiencies, while quantitative trading relies on algorithmic models and data-driven techniques to systematically harvest risk premia from asset price patterns. Both approaches aim to enhance returns through risk-adjusted performance but differ in their decision-making processes and execution methodologies.
Machine Learning Alpha
Hedge funds increasingly incorporate machine learning alpha strategies to enhance predictive accuracy and portfolio returns, leveraging vast datasets and complex algorithms for dynamic asset allocation. Quantitative trading firms prioritize real-time machine learning models to identify market inefficiencies and execute high-frequency trades, optimizing short-term alpha generation through automated signals.
Stat Arb (Statistical Arbitrage)
Hedge funds employing statistical arbitrage (Stat Arb) utilize complex algorithms and large datasets to exploit short-term mispricings in securities, combining quantitative models with discretionary decision-making. Quantitative trading in Stat Arb relies heavily on automated execution of statistically driven strategies, optimizing trade timing and risk management through advanced machine learning and high-frequency data analysis.
Quantamental Investing
Quantamental investing combines the systematic, data-driven models of quantitative trading with the discretionary insights of traditional hedge fund strategies to optimize portfolio performance. This hybrid approach leverages advanced algorithms and fundamental analysis to identify alpha opportunities while managing risk effectively.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
High-frequency trading (HFT) utilizes advanced algorithms and ultra-low latency technology to execute thousands of trades per second, maximizing profits through rapid market opportunities in quantitative trading strategies. Hedge funds may incorporate HFT within their broader investment portfolio, but quantitative trading focuses more narrowly on algorithm-driven, data-intensive techniques to optimize trade execution and manage risk.
Market Microstructure Modeling
Hedge funds leverage diverse strategies, including fundamental analysis and discretionary trading, while quantitative trading relies heavily on algorithmic models to exploit market inefficiencies, with market microstructure modeling playing a critical role in optimizing trade execution and minimizing transaction costs. Advanced microstructure models analyze order flow, bid-ask spreads, and liquidity dynamics, enabling both hedge funds and quantitative traders to enhance predictive accuracy and improve market timing.
Nonlinear Factor Models
Nonlinear factor models in hedge funds enable sophisticated risk assessment and alpha generation by capturing complex relationships and nonlinear dependencies missed by traditional linear models. Quantitative trading leverages these models through algorithmic strategies that dynamically adapt to market signals, enhancing predictive accuracy and optimizing portfolio performance under varied market conditions.
Hedge Fund vs Quantitative Trading Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com