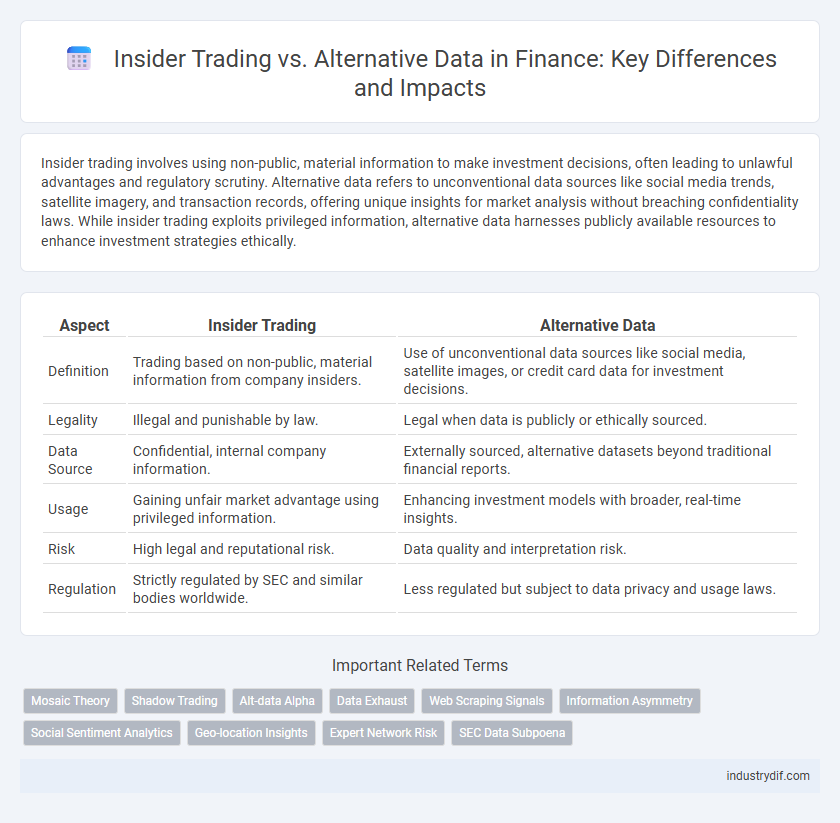
Insider trading involves using non-public, material information to make investment decisions, often leading to unlawful advantages and regulatory scrutiny. Alternative data refers to unconventional data sources like social media trends, satellite imagery, and transaction records, offering unique insights for market analysis without breaching confidentiality laws. While insider trading exploits privileged information, alternative data harnesses publicly available resources to enhance investment strategies ethically.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Insider Trading | Alternative Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading based on non-public, material information from company insiders. | Use of unconventional data sources like social media, satellite images, or credit card data for investment decisions. |
| Legality | Illegal and punishable by law. | Legal when data is publicly or ethically sourced. |
| Data Source | Confidential, internal company information. | Externally sourced, alternative datasets beyond traditional financial reports. |
| Usage | Gaining unfair market advantage using privileged information. | Enhancing investment models with broader, real-time insights. |
| Risk | High legal and reputational risk. | Data quality and interpretation risk. |
| Regulation | Strictly regulated by SEC and similar bodies worldwide. | Less regulated but subject to data privacy and usage laws. |
Introduction to Insider Trading in Finance
Insider trading involves buying or selling a company's stock based on non-public, material information, giving insiders an unfair advantage over other investors. Regulatory bodies like the SEC strictly monitor and enforce laws to prevent illegal insider trading, ensuring market integrity. Legal insider trading occurs when corporate insiders trade shares but report their transactions transparently to the public.
Defining Alternative Data in Financial Markets
Alternative data in financial markets refers to non-traditional data sources such as satellite imagery, social media sentiment, and credit card transactions that provide unique insights beyond standard financial reports. These data sets enable investors to identify market trends and company performance ahead of official disclosures. Unlike insider trading, which involves illicit use of confidential information, alternative data offers a legal and ethical avenue for gaining investment intelligence.
Legal Framework: Insider Trading Regulations
Insider trading regulations are governed by stringent securities laws such as the U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934, which prohibits trading based on material non-public information obtained from corporate insiders. Alternative data, while publicly sourced from social media, satellite imagery, or transaction records, must be analyzed carefully to avoid breaching insider trading laws by ensuring no confidential or non-public information is exploited. Regulatory bodies like the SEC actively monitor markets to enforce compliance, emphasizing clear distinctions between illegal insider trading and the legitimate use of alternative data in investment strategies.
Ethical Boundaries: Insider Trading vs Alternative Data
Insider trading involves using non-public, material information for financial gain, violating regulatory frameworks and ethical standards designed to ensure market fairness. Alternative data, sourced from public or anonymized datasets such as satellite imagery or social media trends, offers innovative investment insights while adhering to legal and ethical boundaries. Maintaining clear distinctions between these approaches is essential to uphold market integrity and avoid regulatory penalties.
Case Studies: Insider Trading Scandals
Insider trading scandals like the Enron and Martha Stewart cases highlight the detrimental impact of using non-public information for financial gain, exposing regulatory gaps and enforcement challenges. Alternative data, encompassing transaction records, satellite imagery, and social media analytics, offers a transparent and ethical means to generate investment insights without violating insider trading laws. Case studies demonstrate how firms leveraging alternative data can outperform traditional models while maintaining compliance and avoiding the legal risks associated with insider trading.
The Role of Alternative Data in Investment Decisions
Alternative data plays a crucial role in investment decisions by providing unique insights that are not available through traditional financial statements or insider information. Hedge funds and asset managers leverage alternative data sources such as satellite imagery, social media sentiment, and transaction data to gain a competitive edge and predict market movements more accurately. This enables more informed and timely investment strategies, reducing reliance on potentially illegal insider trading practices.
Data Sources: Insider Information Versus Alternative Data
Insider trading relies on non-public, material information obtained directly from company insiders such as executives or employees, offering a highly sensitive data source that can significantly influence stock prices. In contrast, alternative data encompasses a diverse range of publicly available or third-party data sets, including social media sentiment, satellite imagery, and transaction records, providing broader market insights without breaching confidentiality agreements. Investors increasingly integrate alternative data with traditional insider information to enhance predictive accuracy and gain a competitive edge in financial decision-making.
Compliance Challenges Facing Investors
Insider trading regulations impose strict compliance requirements to prevent the misuse of non-public, material information, posing significant challenges for investors navigating alternative data sources. Alternative data, such as satellite imagery or social media sentiment, often blurs the line between public and non-public information, increasing the risk of inadvertent regulatory breaches. Ensuring robust compliance frameworks and real-time monitoring systems is essential for investors to mitigate legal risks and maintain transparency in using alternative data for trading decisions.
Technology’s Impact on Detecting Insider Trading
Advanced machine learning algorithms and big data analytics significantly enhance the detection of insider trading by analyzing alternative data sources such as social media, transaction patterns, and communication metadata. Technology enables real-time monitoring of unusual trading activities and correlations with non-public information, improving regulatory enforcement and market transparency. Integrating alternative data with traditional insider trading surveillance systems reduces false positives and accelerates the identification of illicit market behavior.
Future Trends: Alternative Data and Market Surveillance
Alternative data sources such as satellite imagery, social media analytics, and transaction records are transforming market surveillance by providing real-time insights beyond traditional insider trading signals. Advanced machine learning algorithms enhance detection of anomalous trading patterns, enabling regulators to identify illicit activities more effectively. Future trends indicate a growing reliance on alternative data to create proactive, rather than reactive, enforcement mechanisms in financial markets.
Related Important Terms
Mosaic Theory
Mosaic Theory in finance leverages the aggregation of non-material, alternative data sources combined with public information to identify investment insights without breaching insider trading laws. This approach enables analysts to build a comprehensive investment thesis by synthesizing market signals from social media trends, satellite imagery, and web scraping data, thus avoiding the use of material non-public information.
Shadow Trading
Shadow trading involves the clandestine execution of trades based on non-public insider information, blurring lines between legal insider trading and illicit activities. Alternative data, sourced from unconventional channels like social media sentiment or satellite imagery, offers firms a legal edge while reducing reliance on risky shadow trading practices.
Alt-data Alpha
Insider trading exploits non-public, material information for market advantage, while alternative data leverages publicly available, unconventional datasets like satellite imagery, social media trends, and transaction records to generate predictive alpha signals. Alt-data alpha enhances investment strategies by uncovering hidden patterns and market sentiments inaccessible through traditional financial reports, driving superior returns and risk management.
Data Exhaust
Insider trading leverages non-public, material information from company insiders to gain an unfair market advantage, whereas alternative data utilizes vast, unstructured data sources like social media, satellite images, and data exhaust--traces of digital activity such as transaction logs, web browsing history, and sensor data--to identify market trends and investment opportunities. Data exhaust offers a rich, real-time reservoir of behavioral insights that, when properly analyzed, can complement traditional financial metrics and enhance predictive modeling in asset management and risk assessment.
Web Scraping Signals
Insider trading relies on non-public material information for market advantage, whereas alternative data from web scraping signals captures real-time, publicly available insights such as social media trends, news sentiment, and transactional data to predict stock movements. Leveraging machine learning algorithms to analyze web scraping signals enhances investment strategies by providing transparent, legally compliant data alternatives to traditional insider information.
Information Asymmetry
Insider trading exploits non-public, material information to gain unfair advantage, intensifying information asymmetry by privileging select market participants. Alternative data, derived from unconventional sources like social media, satellite imagery, and web traffic, aims to democratize insights, reducing information gaps and leveling the playing field in financial markets.
Social Sentiment Analytics
Insider trading involves using confidential, non-public information to gain an advantage in financial markets, whereas alternative data leverages publicly available sources such as social sentiment analytics to predict market trends. Social sentiment analytics analyze large volumes of social media and news data to gauge investor mood, providing a transparent and ethical approach for market forecasting compared to the illicit nature of insider trading.
Geo-location Insights
Insider trading involves exploiting non-public, material information, often leading to legal consequences, whereas alternative data such as geo-location insights provide real-time, anonymized movement patterns of consumers and assets, enabling investors to infer market trends and company performance without breaching regulations. Geo-location data enhances quantitative models by offering granular visibility into store traffic, supply chain dynamics, and economic activity, driving more informed and timely investment decisions.
Expert Network Risk
Expert networks facilitating insider trading risk exposing firms to significant regulatory penalties and reputational damage, as undisclosed material non-public information obtained through these channels can lead to market manipulation violations. Alternative data leveraged improperly increases vulnerability to compliance breaches, necessitating robust due diligence and monitoring protocols to mitigate insider trading risks effectively.
SEC Data Subpoena
Insider trading investigations increasingly leverage alternative data alongside traditional SEC data subpoenas to detect illicit market activities. The SEC's use of subpoenas targets both transactional records and unstructured alternative datasets, enhancing enforcement precision and uncovering hidden trading patterns.
Insider Trading vs Alternative Data Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com