Venture capital involves centralized investment funds managed by a group of partners who provide capital to startups in exchange for equity, relying heavily on expert due diligence and active portfolio management. Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds operate through blockchain-based smart contracts, enabling a community-driven investment approach where token holders collectively make decisions and govern the fund transparently. While venture capital emphasizes hierarchical control and selectivity, DAO funds prioritize decentralization, democratization of investment access, and automated execution of funding processes.
Table of Comparison
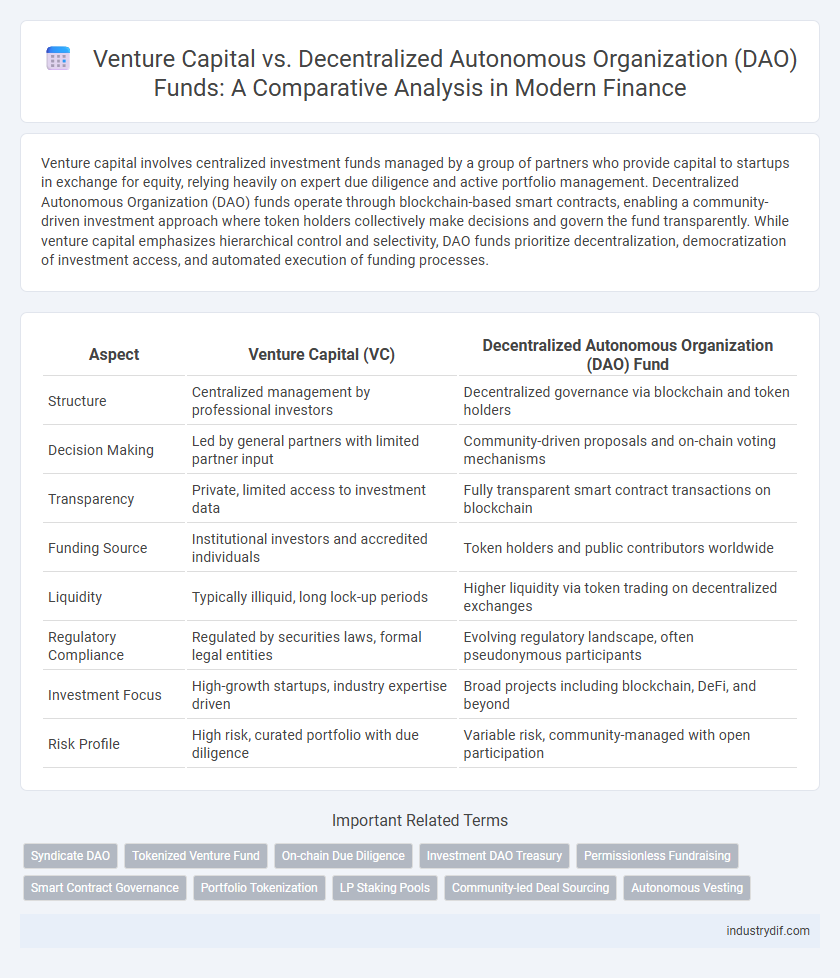
| Aspect | Venture Capital (VC) | Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Centralized management by professional investors | Decentralized governance via blockchain and token holders |
| Decision Making | Led by general partners with limited partner input | Community-driven proposals and on-chain voting mechanisms |
| Transparency | Private, limited access to investment data | Fully transparent smart contract transactions on blockchain |
| Funding Source | Institutional investors and accredited individuals | Token holders and public contributors worldwide |
| Liquidity | Typically illiquid, long lock-up periods | Higher liquidity via token trading on decentralized exchanges |
| Regulatory Compliance | Regulated by securities laws, formal legal entities | Evolving regulatory landscape, often pseudonymous participants |
| Investment Focus | High-growth startups, industry expertise driven | Broad projects including blockchain, DeFi, and beyond |
| Risk Profile | High risk, curated portfolio with due diligence | Variable risk, community-managed with open participation |
Introduction to Venture Capital and DAO Funds
Venture Capital (VC) involves private equity investments in early-stage companies with high growth potential, typically managed by specialized firms that provide funding in exchange for equity stakes. Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) Funds leverage blockchain technology to create community-driven investment pools, enabling token holders to collectively make funding decisions through smart contracts. Both VC and DAO Funds aim to support innovative startups, but VC relies on centralized management and expertise, whereas DAO Funds emphasize transparency and decentralized governance.
Key Differences Between Venture Capital and DAO Funds
Venture capital (VC) funds are centralized investment vehicles managed by professional firms that pool capital to invest in startups with high growth potential, emphasizing thorough due diligence and active portfolio management. Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds operate on blockchain technology, enabling a distributed community to collectively govern investments through smart contracts and token-based voting, prioritizing transparency and democratic decision-making. The key differences lie in governance structure, decision-making processes, and regulatory oversight, with VC funds relying on traditional frameworks while DAO funds leverage decentralized protocols for funding and control alignment.
Structure and Governance Models
Venture capital funds operate with centralized management structures led by general partners who make investment decisions and manage portfolio companies, ensuring accountability and regulatory compliance. Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds utilize blockchain-based governance models, enabling token holders to participate in voting and decision-making processes transparently and without centralized control. This shift in governance allows DAOs to democratize investment strategies, reduce intermediaries, and increase community engagement through automated smart contracts.
Funding Processes and Decision-Making
Venture capital funding relies on centralized investment committees and rigorous due diligence to evaluate startups, enabling structured capital deployment through staged financing rounds. Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds utilize blockchain-based governance mechanisms where token holders vote on proposals, promoting transparency and community-driven decision-making without intermediaries. The DAO funding process accelerates resource allocation via smart contracts but may face challenges in aligning diverse stakeholder interests compared to traditional venture capital's expert-driven approach.
Investor Participation and Rights
Venture capital investors typically gain equity stakes and board representation, granting them significant influence over company decisions and exit strategies. In contrast, investors in Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds participate through token holdings that confer voting rights on proposals, enabling a more democratic and transparent governance model without centralized control. DAO participants experience fluid rights tied to smart contracts, offering real-time participation but potentially less predictable influence compared to traditional VC agreements.
Risk Management and Due Diligence
Venture capital funds implement rigorous due diligence processes, including financial audits and market analysis, to mitigate high investment risks through structured oversight and active portfolio management. Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds rely on blockchain transparency and community voting mechanisms for risk management, but face challenges due to limited regulatory scrutiny and potential governance vulnerabilities. Comparing both, venture capital offers established frameworks for risk assessment, while DAO funds present innovative, yet less predictable, decentralized risk mitigation strategies.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance
Venture capital funds operate under established regulatory frameworks such as the Investment Company Act of 1940 and require registration with the SEC, ensuring investor protection and compliance with anti-money laundering laws. Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds face an evolving regulatory landscape with limited clear guidelines, often encountering challenges related to securities laws, jurisdictional ambiguities, and compliance enforcement. Regulatory agencies are increasingly scrutinizing DAOs to address transparency, governance, and investor protection, creating a dynamic environment for decentralized fundraising mechanisms.
Transparency and Accountability
Venture capital firms operate with structured transparency through regulated reporting and fiduciary responsibilities, providing accountability via established governance frameworks. Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds leverage blockchain technology to enhance transparency by publicly recording transactions and decision-making processes on an immutable ledger. Accountability in DAO funds is community-driven, relying on token holder voting and smart contracts to enforce funding decisions without centralized intermediaries.
Case Studies and Notable Examples
Case studies reveal that traditional venture capital firms like Sequoia Capital and Andreessen Horowitz focus on equity stakes in startups, providing strategic guidance and structured exit paths, exemplified by investments in companies such as Airbnb and Coinbase. In contrast, Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds like The DAO and MetaCartel operate on blockchain governance, enabling token holders to vote on funding proposals with transparent, code-driven mechanisms, showcased by MetaCartel's support for community-driven Web3 projects. Notable examples highlight venture capital's influence in scaling disruptive technologies, while DAO funds emphasize community participation and decentralized decision-making in early-stage investments.
Future Trends in Venture Capital and DAO Financing
Venture capital (VC) is increasingly integrating blockchain technology to enhance transparency and efficiency, while decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) are disrupting traditional funding models by enabling community-driven investment decisions. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach where VC firms leverage DAOs for decentralized governance, tokenized equity, and democratized access to startup funding. The evolving landscape highlights a shift towards more inclusive, technology-enabled financing mechanisms that combine VC's strategic expertise with DAO's decentralized innovation.
Related Important Terms
Syndicate DAO
Venture capital (VC) relies on centralized decision-making with limited partners and general partners managing pooled investments, while Syndicate DAO exemplifies a Decentralized Autonomous Organization Fund utilizing blockchain technology to enable transparent, community-driven investment syndicates. Syndicate DAO leverages smart contracts for automated governance and provides investors with direct access to deal flows and voting rights, enhancing efficiency and reducing intermediaries compared to traditional VC models.
Tokenized Venture Fund
Tokenized venture funds leverage blockchain technology to enable decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) to pool capital and invest in startups, enhancing transparency and liquidity compared to traditional venture capital firms. These DAOs use governance tokens to facilitate investor participation in decision-making and streamline fund management through smart contracts, offering a more democratic and accessible investment model.
On-chain Due Diligence
On-chain due diligence in venture capital leverages transparent blockchain data to verify transaction histories, token distributions, and smart contract audits, enhancing investment accuracy and risk assessment. Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds utilize decentralized governance and real-time on-chain analytics to democratize decision-making, increasing trust and reducing information asymmetry compared to traditional venture capital processes.
Investment DAO Treasury
Investment DAO treasuries leverage blockchain transparency and community governance to pool venture capital, enabling decentralized decision-making and lowering barriers for diverse investor participation. Unlike traditional venture capital firms, Investment DAOs automate fund management through smart contracts, enhancing liquidity and reducing operational costs.
Permissionless Fundraising
Venture capital relies on accredited investors and centralized decision-making, limiting access to fundraising opportunities, whereas decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) funds enable permissionless fundraising by allowing global participants to contribute and vote transparently through blockchain technology. DAO funds democratize capital allocation, reducing barriers to entry and fostering inclusive investment ecosystems beyond traditional venture capital constraints.
Smart Contract Governance
Venture capital typically relies on traditional governance structures with defined decision-making hierarchies, while Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds leverage smart contract governance to automate investment decisions and enhance transparency. Smart contracts enable DAOs to execute funding approvals and portfolio management through programmable rules encoded on blockchain networks, reducing human intervention and increasing efficiency.
Portfolio Tokenization
Venture capital firms traditionally invest in startups through equity stakes, while Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds utilize blockchain technology to tokenize portfolios, enabling fractional ownership and increased liquidity. Portfolio tokenization in DAOs fosters transparency, reduces entry barriers for investors, and streamlines asset management compared to conventional VC structures.
LP Staking Pools
Venture capital funds traditionally pool limited partners' (LP) capital for equity investments in startups, offering structured governance and regulatory oversight, whereas decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) funds enable LP staking pools where token holders collectively govern investment decisions through blockchain-based smart contracts, ensuring transparency and liquidity. LP staking pools in DAO funds reduce entry barriers and provide dynamic portfolio management via programmable protocols, contrasting with the fixed capital commitments and operational constraints typical in venture capital models.
Community-led Deal Sourcing
Venture Capital firms rely on structured networks and expert-driven processes for deal sourcing, whereas Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds leverage community-led mechanisms, harnessing collective intelligence and broad participation to identify promising startups. Community-led deal sourcing in DAOs increases transparency and democratizes investment opportunities, enabling diverse stakeholders to contribute insights and vote on funding decisions.
Autonomous Vesting
Venture capital traditionally relies on structured funding rounds with predetermined equity stakes, while Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) funds utilize autonomous vesting mechanisms enabled by smart contracts to ensure transparent, gradual release of tokens or funds based on predefined conditions. Autonomous vesting in DAO funds reduces reliance on centralized decision-making, enhancing investor confidence through programmable, immutable distribution schedules.
Venture Capital vs Decentralized Autonomous Organization Fund Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com