Traditional insurance relies on loss assessment and claims adjustment processes after an event occurs, often causing delays in payout. Parametric insurance provides predetermined payouts based on objective parameters or triggers, such as weather data or seismic activity, enabling faster and more transparent compensation. This shift reduces administrative costs and mitigates disputes over claim validation, enhancing efficiency in risk management.
Table of Comparison
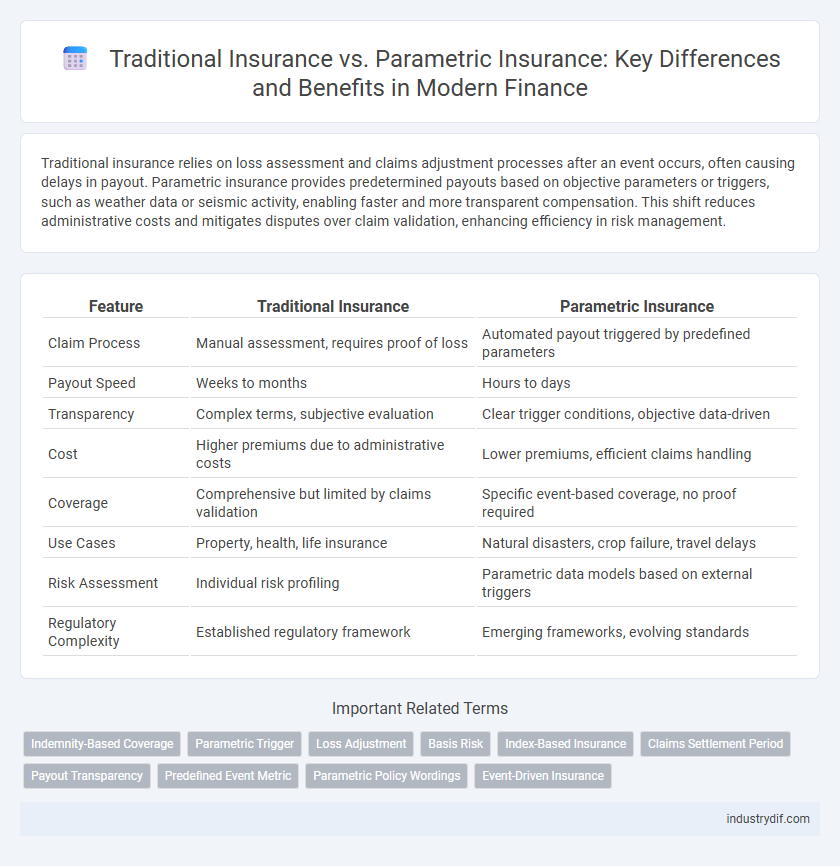
| Feature | Traditional Insurance | Parametric Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Claim Process | Manual assessment, requires proof of loss | Automated payout triggered by predefined parameters |
| Payout Speed | Weeks to months | Hours to days |
| Transparency | Complex terms, subjective evaluation | Clear trigger conditions, objective data-driven |
| Cost | Higher premiums due to administrative costs | Lower premiums, efficient claims handling |
| Coverage | Comprehensive but limited by claims validation | Specific event-based coverage, no proof required |
| Use Cases | Property, health, life insurance | Natural disasters, crop failure, travel delays |
| Risk Assessment | Individual risk profiling | Parametric data models based on external triggers |
| Regulatory Complexity | Established regulatory framework | Emerging frameworks, evolving standards |
Overview of Traditional Insurance
Traditional insurance involves indemnifying policyholders after verifying and assessing losses from insured events, relying heavily on claims adjustment processes and loss documentation. Policies typically cover a wide range of risks with payouts based on actual damages and contractual terms, leading to longer claim settlement times. Premiums are calculated through risk pooling, underwriting assessments, and actuarial models to balance coverage and financial stability.
Fundamentals of Parametric Insurance
Parametric insurance is based on predefined parameters or triggers, such as weather conditions or seismic activity, that activate automatic payouts without assessing actual losses. Unlike traditional insurance, which requires claims adjustment and thorough investigations, parametric insurance offers faster compensation and reduced administrative costs by relying on objective data from trusted sources. This fundamental difference enhances transparency, expedites disaster relief funding, and minimizes dispute risks in financial risk management.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Parametric Insurance
Traditional insurance involves indemnity-based claims where payouts depend on loss assessments, requiring lengthy claims processing and documentation. Parametric insurance offers predetermined payouts triggered by specific measurable parameters, such as weather data or seismic activity, enabling faster settlements and reduced administrative costs. The key difference lies in the claim mechanism: traditional insurance reimburses actual loss, while parametric insurance pays based on predefined event triggers, enhancing efficiency and transparency in coverage.
Claims Process: Indemnity vs. Trigger-Based Payments
Traditional insurance relies on indemnity-based claims where payouts are determined by assessed losses after detailed claims adjustment and verification, often causing delays and paperwork. Parametric insurance uses trigger-based payments that release funds automatically when predefined parameters, such as weather data or seismic activity thresholds, are met, ensuring faster and more transparent claims settlement. This model minimizes the need for loss assessments and reduces administrative costs, providing immediate liquidity to policyholders.
Risk Assessment and Pricing Models
Traditional insurance relies on thorough risk assessment through historical loss data and individual claim evaluations to determine pricing models based on probability and severity of specific events. Parametric insurance employs predefined triggers and objective parameters, such as weather indices or seismic measurements, to automate payouts, reducing the need for complex loss adjustments and enabling faster claim settlements. Pricing models in parametric insurance use statistical analysis of event probabilities, improving risk transfer efficiency by minimizing moral hazard and basis risk compared to traditional underwriting processes.
Use Cases and Applications in Finance
Traditional insurance primarily covers losses based on actual damage assessed through claims adjustment, making it suitable for complex liability and property insurance in finance. Parametric insurance offers rapid payouts triggered by predefined events like natural disasters or market fluctuations, ideal for hedging risk in agriculture loans or catastrophe bonds. Financial institutions leverage parametric models to optimize risk management and improve liquidity during extreme events without the delays of conventional claim processing.
Advantages of Traditional Insurance Solutions
Traditional insurance solutions offer comprehensive coverage tailored to individual risks with detailed policy terms and conditions, providing policyholders with explicit financial protection against a wide range of perils. These solutions benefit from established claim processes and regulatory frameworks, ensuring reliability and dispute resolution support. Additionally, traditional insurance allows for customized premiums based on in-depth risk assessments, enabling more precise risk management for both insurers and insured parties.
Benefits of Parametric Insurance Products
Parametric insurance offers rapid claim settlements by triggering payouts based on predefined parameters, such as weather data or seismic measurements, eliminating lengthy damage assessments. This product design enhances transparency and reduces operational costs, benefiting both insurers and policyholders with clear, objective criteria. It provides customized coverage for specific risks, improving risk management and financial resilience in volatile markets.
Industry Trends and Adoption Rates
Parametric insurance is gaining traction in the finance industry due to its rapid claim settlements and transparency compared to traditional indemnity-based insurance. Recent reports indicate that parametric insurance adoption rates have increased by over 25% annually, driven by advancements in data analytics and growing demand for tailored risk management solutions. Traditional insurance remains dominant but faces challenges in digital transformation and customer experience, fueling the shift towards parametric models in sectors like agriculture, disaster recovery, and climate risk management.
Future Outlook: Evolving Insurance Paradigms
Parametric insurance is rapidly gaining traction due to its efficiency, transparency, and quicker claim settlements, driven by advancements in data analytics and IoT integration. Traditional insurance models face increasing pressure to adapt as customers demand more flexible, tailored coverage that parametric solutions offer through predefined triggers and automated payouts. The future of insurance lies in hybrid approaches, combining the robustness of traditional underwriting with the agility and precision of parametric innovations to address emerging risks in climate change and digital ecosystems.
Related Important Terms
Indemnity-Based Coverage
Indemnity-based coverage in traditional insurance reimburses policyholders for actual losses after claim assessment, often involving lengthy adjustment processes. Parametric insurance simplifies payouts by triggering predefined payments based on measurable parameters, reducing claim settlement time and administrative costs.
Parametric Trigger
Parametric insurance utilizes a predefined parametric trigger, such as a specific earthquake magnitude or rainfall level, to automatically initiate payout without the need for damage assessment, enabling faster claims processing and reduced administrative costs. Unlike traditional insurance, where claims adjusters evaluate losses, parametric triggers rely on objective, quantifiable data from trusted sources, enhancing transparency and predictability in risk management.
Loss Adjustment
Traditional insurance relies on detailed loss adjustment processes involving claim verification and on-site assessments, often leading to prolonged settlement periods. Parametric insurance uses predefined triggers linked to objective parameters, enabling swift payouts without the need for extensive loss validation, thereby reducing administrative costs and accelerating recovery.
Basis Risk
Traditional insurance involves indemnity payments based on actual loss assessments, which can lead to claim disputes and delayed settlements due to complex evaluations. Parametric insurance reduces basis risk by triggering payouts through predefined parameters like earthquake magnitude or rainfall levels, ensuring faster, objective, and transparent compensation without the need for loss adjustment.
Index-Based Insurance
Traditional insurance relies on claims adjustment and indemnity payments based on documented losses, whereas parametric insurance, particularly index-based insurance, triggers payouts when predefined indices such as weather data or crop yields reach specified thresholds, enabling faster and more transparent compensation. Index-based insurance reduces moral hazard and adverse selection by eliminating loss verification, offering scalable solutions for sectors like agriculture and disaster management.
Claims Settlement Period
Traditional insurance claims settlement periods often extend from weeks to months due to detailed loss assessments and indemnity verification, impacting liquidity for policyholders. Parametric insurance dramatically accelerates claims settlement through predefined triggers and data-driven payouts, enabling settlements within days or even hours.
Payout Transparency
Parametric insurance offers clear payout transparency by triggering payments based on predefined parameters such as weather data or seismic activity, eliminating the need for claim adjustments. Traditional insurance relies on subjective damage assessments and lengthy claim processes, often causing delays and disputes over payout amounts.
Predefined Event Metric
Traditional insurance relies on claims assessments and indemnity payments after loss verification, whereas parametric insurance triggers payouts based on predefined event metrics such as earthquake magnitude or rainfall levels, enabling faster and more transparent settlements. Using objective parameters like wind speed or crop yield indexes reduces claim disputes and accelerates financial recovery for policyholders.
Parametric Policy Wordings
Parametric insurance policy wordings specify predefined triggers and payout amounts based on objective parameters such as weather data or seismic activity, eliminating the need for loss adjustment and enabling faster claims processing. Unlike traditional insurance, which relies on detailed damage assessments and indemnity clauses, parametric policies prioritize clarity and precision by outlining exact conditions that activate predefined compensation.
Event-Driven Insurance
Event-driven insurance, such as parametric insurance, offers rapid payouts based on predefined triggers like natural disasters, contrasting with traditional insurance that relies on loss assessments and claim adjustments. Parametric insurance enhances liquidity and reduces claim settlement time by utilizing objective event data, supporting faster recovery for businesses facing financial disruptions.
Traditional insurance vs Parametric insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com