Syndicated loans involve multiple financial institutions pooling resources to provide a large loan, offering shared risk and traditional credit evaluations. Decentralized finance (DeFi) lending utilizes blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer loans without intermediaries, increasing accessibility and transparency. While syndicated loans offer structured underwriting and legal protections, DeFi lending emphasizes speed, lower costs, and programmable smart contracts.
Table of Comparison
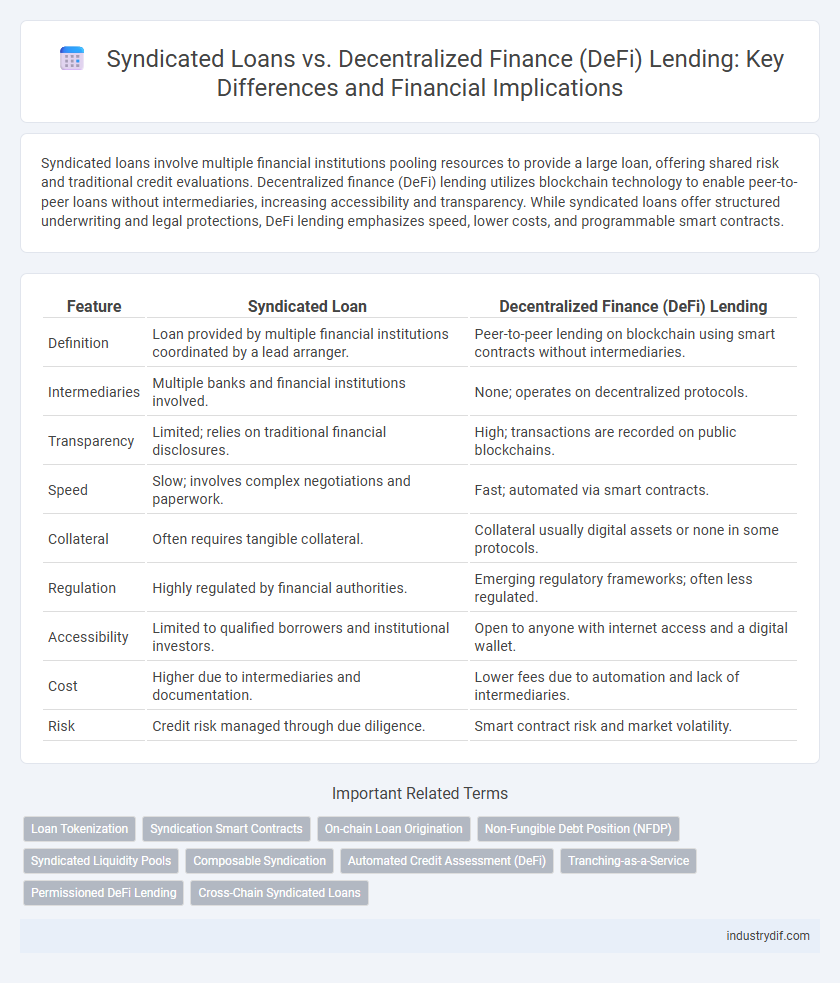
| Feature | Syndicated Loan | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loan provided by multiple financial institutions coordinated by a lead arranger. | Peer-to-peer lending on blockchain using smart contracts without intermediaries. |
| Intermediaries | Multiple banks and financial institutions involved. | None; operates on decentralized protocols. |
| Transparency | Limited; relies on traditional financial disclosures. | High; transactions are recorded on public blockchains. |
| Speed | Slow; involves complex negotiations and paperwork. | Fast; automated via smart contracts. |
| Collateral | Often requires tangible collateral. | Collateral usually digital assets or none in some protocols. |
| Regulation | Highly regulated by financial authorities. | Emerging regulatory frameworks; often less regulated. |
| Accessibility | Limited to qualified borrowers and institutional investors. | Open to anyone with internet access and a digital wallet. |
| Cost | Higher due to intermediaries and documentation. | Lower fees due to automation and lack of intermediaries. |
| Risk | Credit risk managed through due diligence. | Smart contract risk and market volatility. |
Overview of Syndicated Loans in Traditional Finance
Syndicated loans involve multiple lenders pooling resources to provide a large loan to a single borrower, typically facilitated by investment banks or financial institutions. These loans enable risk sharing and access to substantial capital for corporate clients, often used for mergers, acquisitions, or large projects. Traditional syndicated loan structures rely on established credit agreements, centralized underwriting, and legal frameworks to ensure lender protection and borrower compliance.
Fundamentals of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Lending
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) lending operates on blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, which contrasts with traditional syndicated loans that involve multiple financial institutions sharing risk and capital. DeFi lending relies on smart contracts to automate loan issuance, repayment, and collateral management, enhancing transparency and reducing operational costs. The fundamental mechanisms include over-collateralization, decentralized oracles for price feeds, and non-custodial asset control, providing users with increased liquidity and global access to credit markets.
Key Differences: Syndicated Loans vs DeFi Lending
Syndicated loans involve multiple financial institutions pooling funds to provide large-scale credit, typically facilitated through traditional banks with centralized control and stringent regulatory oversight. DeFi lending operates on blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, using smart contracts for automated loan agreements and collateral management. Key differences include transparency, where DeFi offers open access and real-time data on loan conditions, contrasting with the private, institution-driven nature of syndicated loans, and differences in liquidity and accessibility, as DeFi platforms allow broader participation from global users.
Structure and Participants in Syndicated Lending
Syndicated loans involve a structured group of financial institutions pooling resources to provide a large loan to a single borrower, typically organized by lead arrangers or agents who coordinate terms and repayments. Participants include banks, institutional investors, and sometimes hedge funds, each holding a portion of the loan, sharing both risk and returns based on their participation agreements. This centralized structure contrasts sharply with decentralized finance lending, where smart contracts and blockchain technology eliminate intermediaries and enable peer-to-peer borrowing.
Smart Contracts and Protocols in DeFi Lending
Syndicated loans involve a group of lenders pooling resources to provide large-scale financing, with terms managed through traditional legal contracts and centralized intermediaries. In contrast, decentralized finance (DeFi) lending utilizes blockchain-based smart contracts and protocols, enabling automated, transparent, and trustless loan issuance without intermediaries. Smart contracts in DeFi execute loan agreements, interest accrual, and repayments programmatically, enhancing efficiency and reducing counterparty risk compared to syndicated loan structures.
Risk Management in Syndicated Loans vs DeFi Platforms
Syndicated loans involve risk management strategies such as thorough credit assessments, covenants, and shared due diligence among multiple financial institutions, reducing individual lender exposure. In contrast, decentralized finance (DeFi) lending platforms rely on automated smart contracts and over-collateralization, which mitigate counterparty risk but expose users to protocol vulnerabilities and market volatility. The transparency and regulatory oversight in syndicated loans provide more predictable risk controls compared to the evolving and often unregulated DeFi ecosystems.
Transparency and Regulatory Considerations
Syndicated loans offer structured transparency through standardized documentation and regulatory oversight by financial authorities, ensuring clear terms for all participants. Decentralized finance (DeFi) lending operates on blockchain protocols, providing real-time transaction visibility yet presents challenges in regulatory compliance due to the lack of centralized control. Regulatory frameworks for syndicated loans are well-established, while DeFi lending faces evolving regulatory scrutiny aimed at mitigating risks related to fraud, money laundering, and investor protection.
Cost Efficiency and Accessibility
Syndicated loans typically involve higher costs due to underwriting fees, legal expenses, and intermediary charges, limiting cost efficiency compared to decentralized finance (DeFi) lending platforms that operate with minimal intermediaries. DeFi lending enhances accessibility by enabling borrowers worldwide to access funds through blockchain technology without stringent credit checks or centralized approval processes. The transparent, automated nature of DeFi protocols reduces operational costs and broadens participation, making financing more efficient and inclusive.
Use Cases: Corporate Applications vs DeFi Lending Solutions
Syndicated loans are predominantly utilized by large corporations and institutional borrowers to secure substantial financing by pooling resources from multiple lenders, facilitating structured debt for capital-intensive projects and mergers. Decentralized finance (DeFi) lending solutions cater to a broader range of users, including retail investors, by enabling peer-to-peer lending through smart contracts on blockchain networks, providing increased accessibility and transparency. Corporate applications prioritize risk management and regulatory compliance, whereas DeFi emphasizes efficiency, borderless transactions, and reduced reliance on intermediaries.
Future Trends in Global Lending Markets
Syndicated loans remain a dominant instrument in global lending markets due to their capacity to pool large sums from multiple financial institutions, offering enhanced risk mitigation and structured credit facilities. Decentralized finance (DeFi) lending is rapidly emerging, driven by blockchain technology, smart contracts, and transparency, enabling peer-to-peer lending without intermediaries, which reduces costs and increases accessibility. Future trends indicate a convergence where traditional syndicated loan markets may integrate DeFi protocols to enhance efficiency, liquidity, and global reach in credit distribution.
Related Important Terms
Loan Tokenization
Loan tokenization in syndicated loans enhances liquidity and transparency by converting debt into tradable digital assets on blockchain platforms, streamlining participation for institutional investors. Decentralized finance (DeFi) lending utilizes smart contracts to facilitate peer-to-peer loans without intermediaries, offering greater access and efficiency but currently faces scalability and regulatory challenges compared to traditional syndicated loan structures.
Syndication Smart Contracts
Syndication smart contracts automate the distribution and management of syndicated loans by enhancing transparency, reducing administrative costs, and ensuring real-time compliance among multiple lenders. These contracts provide predefined conditional logic that streamlines loan servicing and risk-sharing, creating a more efficient alternative to traditional decentralized finance lending platforms.
On-chain Loan Origination
On-chain loan origination in decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to enable transparent, automated, and permissionless credit underwriting, contrasting with syndicated loans that rely on traditional intermediaries and extensive off-chain documentation. DeFi lending platforms utilize smart contracts to facilitate instant loan approval, secure collateral management, and real-time repayment tracking, enhancing efficiency and reducing counterparty risk compared to syndicated loan structures.
Non-Fungible Debt Position (NFDP)
Syndicated loans consolidate debt under a centralized structure managed by a syndicate of lenders, whereas decentralized finance (DeFi) lending leverages blockchain technology to create Non-Fungible Debt Positions (NFDPs), enabling unique, tradable debt instruments with enhanced transparency and liquidity. NFDPs tokenize individual loan agreements on decentralized platforms, allowing borrowers and lenders to customize and transfer debt obligations seamlessly without intermediaries.
Syndicated Liquidity Pools
Syndicated loan structures aggregate liquidity from multiple institutional lenders to distribute credit risk while providing large capital access, creating efficient syndicated liquidity pools in traditional finance. Unlike decentralized finance lending protocols, these pools rely on regulated entities and centralized oversight, ensuring borrower creditworthiness and structured repayment schedules.
Composable Syndication
Composable syndication in syndicated loans enables multiple lenders to pool resources and share risk efficiently through a structured, centralized agreement, enhancing credit access and capital allocation. In contrast, decentralized finance (DeFi) lending leverages blockchain technology to facilitate peer-to-peer, permissionless lending without intermediaries, offering transparency and composability but often with higher volatility and regulatory uncertainty.
Automated Credit Assessment (DeFi)
Automated credit assessment in decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology and smart contracts to evaluate borrower risk using real-time data and transparent algorithms, reducing reliance on traditional credit scores typical in syndicated loan processes. This automation enhances efficiency and inclusivity by enabling instant, permissionless loan approvals without intermediaries, contrasting with the slower, institution-driven credit evaluations in syndicated lending.
Tranching-as-a-Service
Syndicated loans traditionally distribute risk by segmenting debt into tranches sold to institutional investors, enabling tailored exposure levels and credit profiles within large-scale finance. Tranching-as-a-Service in decentralized finance automates this segmentation on blockchain platforms, enhancing transparency and accessibility while allowing retail investors to participate in varied risk-return setups.
Permissioned DeFi Lending
Permissioned DeFi lending platforms enable vetted participants to access decentralized loan markets with enhanced transparency and reduced counterparty risk, contrasting with syndicated loans that rely on traditional banks coordinating multiple lenders under centralized control. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, permissioned DeFi lending offers streamlined loan origination and automated enforcement of terms, increasing efficiency while maintaining regulatory compliance within controlled environments.
Cross-Chain Syndicated Loans
Cross-chain syndicated loans leverage blockchain interoperability to enable multiple lenders across different decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms to collaboratively fund large-scale loans, enhancing liquidity and reducing counterparty risk. This innovation integrates traditional syndicated loan structures with DeFi's transparency and automation, facilitating seamless cross-chain asset transfers and improving capital efficiency.
Syndicated Loan vs Decentralized Finance Lending Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com