Payment gateways facilitate online transactions by securely transmitting payment data between customers, merchants, and financial institutions, offering flexibility across multiple platforms and payment methods. Embedded payments integrate payment processing directly within an application or website, streamlining the checkout experience and reducing friction for users. Businesses seeking seamless user engagement and increased conversion rates often prefer embedded payments, while those prioritizing broad compatibility and control may choose traditional payment gateways.
Table of Comparison
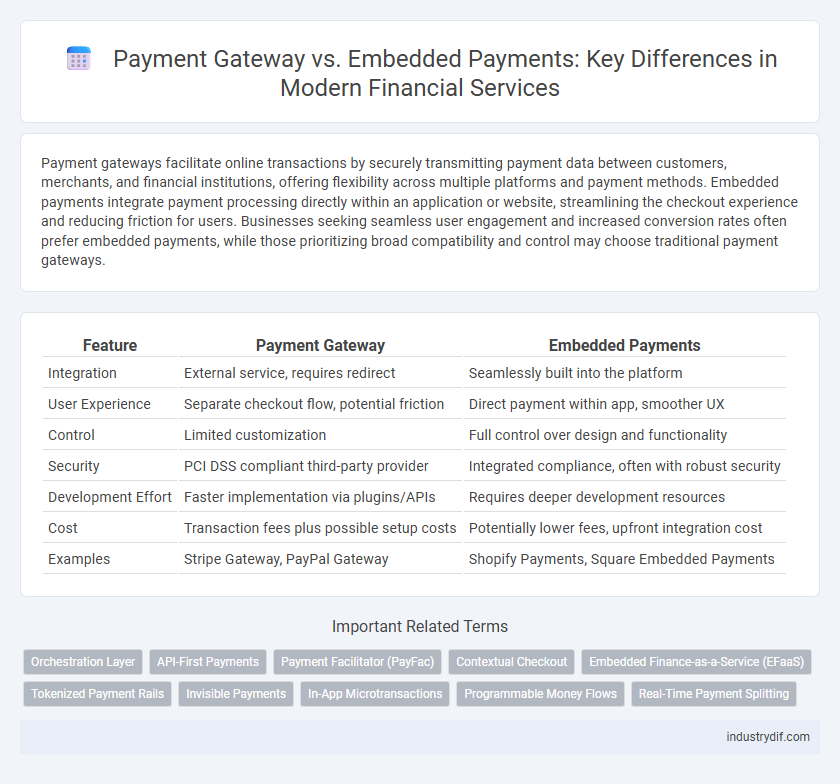
| Feature | Payment Gateway | Embedded Payments |
|---|---|---|
| Integration | External service, requires redirect | Seamlessly built into the platform |
| User Experience | Separate checkout flow, potential friction | Direct payment within app, smoother UX |
| Control | Limited customization | Full control over design and functionality |
| Security | PCI DSS compliant third-party provider | Integrated compliance, often with robust security |
| Development Effort | Faster implementation via plugins/APIs | Requires deeper development resources |
| Cost | Transaction fees plus possible setup costs | Potentially lower fees, upfront integration cost |
| Examples | Stripe Gateway, PayPal Gateway | Shopify Payments, Square Embedded Payments |
Introduction to Payment Gateway and Embedded Payments
A Payment Gateway serves as a secure online interface that authorizes and processes payments between customers, merchants, and financial institutions, ensuring encrypted transmission of payment data. Embedded Payments integrate payment processing directly within an app or platform, allowing users to complete transactions without redirecting to external sites, enhancing the user experience and streamlining checkout flows. Both systems leverage APIs and compliance standards like PCI DSS to safeguard transaction integrity and protect sensitive payment information.
Key Differences Between Payment Gateways and Embedded Payments
Payment gateways serve as intermediaries that securely process online transactions by redirecting customers to external payment pages, ensuring compliance with PCI DSS standards. Embedded payments integrate payment functionality directly within a merchant's app or website, providing a seamless checkout experience without redirecting users. Key differences include user experience, integration complexity, and control over payment data, with embedded payments offering more customization and smoother UX, while payment gateways prioritize ease of setup and security.
How Payment Gateways Work
Payment gateways act as digital intermediaries that securely authorize and process online transactions by encrypting sensitive payment information and transmitting it between customers, merchants, and banks. They facilitate transaction approval by verifying payment details, checking fraud alerts, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards such as PCI DSS. The gateway then communicates with the merchant's acquiring bank to complete the transaction, enabling seamless payment settlements and real-time transaction tracking.
Understanding Embedded Payments Solutions
Embedded payments solutions integrate payment processing directly within a platform, allowing seamless transactions without redirecting users to external gateways. These solutions enhance user experience by reducing payment friction, improving conversion rates, and providing real-time transaction data. By embedding payment capabilities, businesses can streamline workflows, support multiple payment methods, and maintain better control over transaction security and compliance.
Advantages of Payment Gateways
Payment gateways offer robust security features such as PCI-DSS compliance and advanced fraud detection, ensuring safe online transactions. They provide seamless integration with multiple payment methods and global currencies, enabling businesses to expand their market reach efficiently. High scalability and reliable transaction processing speed make payment gateways ideal for handling large volumes of payments with minimal downtime.
Benefits of Embedded Payments
Embedded payments streamline the customer experience by integrating payment processing directly within a platform, reducing transaction friction and increasing conversion rates. This seamless integration improves data security through centralized management and reduces reliance on third-party gateways, lowering operational costs. Businesses benefit from enhanced customization options, faster checkout times, and improved cash flow management, driving higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Security Considerations: Payment Gateways vs Embedded Payments
Payment gateways provide robust security frameworks, including PCI DSS compliance, tokenization, and fraud detection systems, ensuring secure transaction processing between customers and merchants. Embedded payments integrate payment processing directly within apps or websites, which can introduce vulnerabilities if not implemented with strict encryption and secure API protocols. Selecting payment solutions with end-to-end encryption and regular security audits is critical to mitigate risks such as data breaches and payment fraud.
Cost Comparison: Fees and Charges
Payment gateways typically involve multiple fees, including setup charges, transaction fees ranging from 2% to 3.5%, and monthly maintenance costs, which can increase overall expenses for merchants. Embedded payments often reduce costs by integrating directly into platforms, eliminating the need for third-party services and lowering transaction fees, sometimes to as low as 1.5%. Choosing embedded payments can enhance cost-efficiency by minimizing hidden charges and streamlining payment processing expenses.
Integration and User Experience
Payment gateways offer seamless integration with various e-commerce platforms, enabling secure transaction processing through external payment processors. Embedded payments optimize user experience by allowing customers to complete transactions directly within the merchant's app or website, reducing friction and increasing conversion rates. Choosing between a payment gateway and embedded payments depends on the desired balance between integration complexity and streamlined, in-app payment flow.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Selecting between a payment gateway and embedded payments depends on your business's transaction volume, customer experience goals, and technical resources. Payment gateways offer secure, straightforward transaction processing suitable for businesses with diverse payment needs, while embedded payments provide seamless integration directly within your app or website, enhancing user convenience and engagement. Evaluate factors such as integration complexity, cost, security compliance, and scalability to choose the payment solution that optimally supports your business growth.
Related Important Terms
Orchestration Layer
The orchestration layer in payment gateways centralizes transaction routing, fraud detection, and reconciliation across multiple payment processors, enhancing operational efficiency and scalability. Embedded payments integrate this orchestration layer directly within platforms, enabling seamless, context-aware transactions that improve user experience and reduce friction in the payment flow.
API-First Payments
API-first payment solutions enable seamless integration of payment gateways directly into digital platforms, enhancing customization and control over transaction flows. Embedded payments leverage these APIs to offer a unified user experience, reducing friction by allowing payments within the app environment without redirecting to external sites.
Payment Facilitator (PayFac)
Payment Facilitators (PayFacs) streamline transaction processing by integrating embedded payments directly into merchant platforms, reducing onboarding time compared to traditional payment gateways that require separate account setups. PayFacs enhance cash flow management and customer experience by enabling seamless, real-time payment acceptance within digital environments.
Contextual Checkout
Contextual checkout in embedded payments integrates the payment process directly within the merchant's platform, enhancing user experience by reducing friction and increasing conversion rates. Payment gateways route transactions through external platforms, often causing additional steps, whereas embedded payments streamline checkout by maintaining the transaction context and minimizing redirects.
Embedded Finance-as-a-Service (EFaaS)
Embedded Finance-as-a-Service (EFaaS) enables businesses to integrate payment processing directly into their platforms, offering seamless and customizable payment experiences without redirecting customers to external gateways. Unlike traditional payment gateways, EFaaS solutions provide comprehensive financial services, including lending, insurance, and compliance tools, enhancing user engagement and accelerating transaction workflows within a unified interface.
Tokenized Payment Rails
Tokenized payment rails enhance security and efficiency by replacing sensitive payment data with unique tokens, reducing fraud risks in both payment gateway and embedded payment systems. Embedded payments leverage tokenization to streamline user experience by integrating secure transactions directly within apps, while traditional payment gateways rely on tokenized data to protect cardholder information during third-party processing.
Invisible Payments
Invisible payments leverage embedded payment technology to process transactions seamlessly within apps or websites, enhancing user experience by eliminating the need for redirecting to external payment gateways. This integration boosts conversion rates and reduces friction while maintaining robust security and compliance standards.
In-App Microtransactions
In-app microtransactions benefit from embedded payments by enabling seamless, frictionless purchases without redirecting users to external payment gateways, thereby enhancing user experience and boosting conversion rates. Embedded payments integrate directly into apps, reducing latency and security risks common with third-party gateways while supporting diverse payment methods tailored for microtransaction economies.
Programmable Money Flows
Programmable money flows in payment gateways enable customizable transaction routing through APIs, enhancing control over payment processes and integration flexibility. Embedded payments streamline user experiences by integrating payment functionalities directly into platforms, facilitating automated programmable flows that reduce friction and increase conversion rates.
Real-Time Payment Splitting
Real-time payment splitting enables seamless transaction distribution among multiple parties instantly, enhancing liquidity and operational efficiency in both payment gateway and embedded payment systems. Embedded payments offer deeper integration within platforms, allowing automated, context-aware payment allocation without redirecting users to external interfaces.
Payment Gateway vs Embedded Payments Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com