The trading floor offers transparency and real-time price discovery through open market access, enabling traders to execute orders with visible bids and offers. In contrast, dark pools provide private, off-exchange venues where large institutional investors can trade blocks of shares anonymously to minimize market impact and reduce price slippage. Choosing between a trading floor and dark pool involves balancing the needs for liquidity, speed, and confidentiality in executing trades.
Table of Comparison
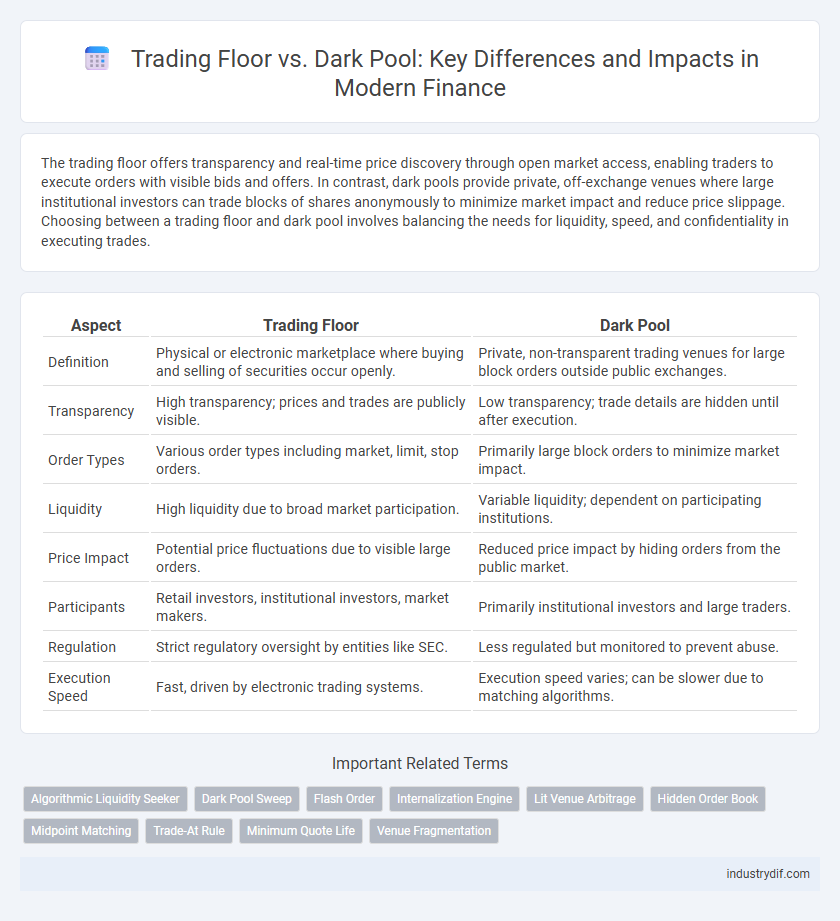
| Aspect | Trading Floor | Dark Pool |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical or electronic marketplace where buying and selling of securities occur openly. | Private, non-transparent trading venues for large block orders outside public exchanges. |
| Transparency | High transparency; prices and trades are publicly visible. | Low transparency; trade details are hidden until after execution. |
| Order Types | Various order types including market, limit, stop orders. | Primarily large block orders to minimize market impact. |
| Liquidity | High liquidity due to broad market participation. | Variable liquidity; dependent on participating institutions. |
| Price Impact | Potential price fluctuations due to visible large orders. | Reduced price impact by hiding orders from the public market. |
| Participants | Retail investors, institutional investors, market makers. | Primarily institutional investors and large traders. |
| Regulation | Strict regulatory oversight by entities like SEC. | Less regulated but monitored to prevent abuse. |
| Execution Speed | Fast, driven by electronic trading systems. | Execution speed varies; can be slower due to matching algorithms. |
Overview of Trading Floors and Dark Pools
Trading floors are centralized physical locations where brokers and traders execute buy and sell orders in real-time, offering transparency and immediate price discovery through open outcry or electronic systems. Dark pools are private, non-transparent trading venues allowing large institutional investors to execute sizable trades anonymously, minimizing market impact and reducing information leakage. While trading floors facilitate public market interactions with visible order flow, dark pools prioritize confidentiality and reduced volatility during large block trades.
Key Differences Between Trading Floors and Dark Pools
Trading floors are centralized venues where buyers and sellers execute trades transparently with real-time price discovery, typically involving brokers and market makers. Dark pools are private, off-exchange platforms allowing institutional investors to trade large blocks of shares anonymously, minimizing market impact and price exposure. The primary difference lies in transparency and execution environment: trading floors offer visible, regulated market prices, while dark pools ensure confidentiality and reduced information leakage.
How Trading Floors Operate
Trading floors operate as centralized venues where traders engage in the buying and selling of financial instruments through real-time open outcry and electronic systems, facilitating immediate price discovery and liquidity. These physical or virtual spaces enable market participants to execute trades with transparency and regulatory oversight, contrasting sharply with dark pools, which are private exchanges lacking pre-trade transparency. The trading floor's structure supports price formation by aggregating supply and demand data visible to all participants, enhancing market efficiency and investor confidence.
The Structure of Dark Pools
Dark pools are private, non-exchange trading venues designed to facilitate large block trades without exposing intentions to the public market, reducing market impact and price slippage. Unlike the transparent and centralized trading floors where buy and sell orders are publicly displayed, dark pools operate with limited transparency and trade execution information is only disclosed post-trade. These alternative trading systems use complex algorithms and matching engines to anonymously match buyers and sellers, attracting institutional investors seeking confidentiality and minimal market disruption.
Transparency: Trading Floor vs Dark Pool
Trading floors provide high transparency through real-time price discovery and public order books, enabling traders to see market depth and execution details. Dark pools operate with limited transparency, concealing order sizes and execution prices to protect large trades from market impact. This opacity in dark pools reduces visible liquidity but aims to minimize price slippage compared to the fully transparent trading floors.
Impact on Market Liquidity
Trading floors contribute significantly to market liquidity by enabling transparent, real-time matching of buy and sell orders through open outcry or electronic systems. Dark pools, with their private and anonymous trading environment, can reduce market impact and price volatility by allowing large trades to be executed discreetly but may also lead to fragmentation and reduced overall market transparency. The balance between trading floors and dark pools influences how liquidity is distributed across markets, affecting price discovery and execution quality.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance Issues
Trading floors operate under stringent regulatory frameworks like the SEC and FINRA, ensuring transparency and real-time reporting of transactions to prevent market manipulation. Dark pools, while offering anonymity, face increased regulatory scrutiny regarding fair pricing, pre-trade transparency, and potential conflicts of interest due to their non-public nature. Compliance challenges in dark pools include adherence to anti-fraud provisions and implementation of robust surveillance systems to detect illicit trading activities.
Advantages and Disadvantages for Investors
Trading floors offer investors transparency and immediate price discovery, enabling quick reactions to market developments; however, they expose traders to higher volatility and potential front-running risks. Dark pools provide large investors anonymity to execute sizable trades without impacting market prices significantly, reducing market impact costs but sacrificing transparency and potentially leading to less favorable execution prices. The choice between trading floors and dark pools depends on investor priorities regarding price certainty, order size, and the need for discretion.
Role in Price Discovery and Execution
The trading floor facilitates transparent price discovery by matching buy and sell orders in real-time, reflecting market sentiment and liquidity through visible order books. Dark pools, operating privately, execute large block trades anonymously to minimize market impact, but lack transparency, which can obscure true price formation. While trading floors enhance market efficiency and price accuracy, dark pools prioritize discreet execution, often at the cost of reduced price visibility.
Future Trends in Trade Execution Venues
Future trends in trade execution venues indicate a growing integration of advanced algorithmic trading and artificial intelligence on traditional trading floors to enhance liquidity and price discovery. Dark pools are expected to evolve with improved transparency protocols and blockchain technology to reduce information asymmetry and regulatory risks. The convergence of these innovations aims to balance market efficiency with trader anonymity, reshaping the landscape of equity and derivative trading.
Related Important Terms
Algorithmic Liquidity Seeker
Algorithmic liquidity seekers exploit trading floors to access visible order books, enabling real-time price discovery and robust market depth. In contrast, dark pools facilitate large block trades with minimal market impact by concealing order sizes, offering algorithmic traders stealth execution and reduced information leakage.
Dark Pool Sweep
Dark pool sweep refers to a trading strategy where large institutional investors execute large blocks of shares within dark pools to minimize market impact and avoid price slippage commonly found on the traditional trading floor. By leveraging dark pool sweeps, traders can discreetly access multiple liquidity venues simultaneously, ensuring anonymity and achieving better execution prices than public exchanges.
Flash Order
Flash orders on trading floors offer immediate, transparent execution visible to all participants, enhancing liquidity and price discovery, whereas dark pools execute orders privately, concealing trade intentions from the market to minimize market impact and reduce price slippage. The use of flash orders can expose strategies to high-frequency traders on lit exchanges, while dark pools provide an alternative venue designed to protect large institutional trades from predatory practices.
Internalization Engine
The internalization engine in trading floors facilitates the matching of buy and sell orders within the same brokerage, enhancing liquidity and price discovery without exposing orders to public markets, unlike dark pools which anonymously execute large block trades off-exchange to minimize market impact. Trading floors leverage internalization to reduce transaction costs and improve execution speed by internalizing order flow, whereas dark pools prioritize anonymity and size over immediate price transparency.
Lit Venue Arbitrage
Lit venue arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between transparent trading floors, where bid and ask orders are visible, and dark pools, private exchanges with hidden order books, enabling traders to capitalize on latency and information asymmetry. This strategy leverages the real-time public order flow in lit venues to predict and anticipate trades in dark pools, enhancing execution efficiency and reducing market impact.
Hidden Order Book
The trading floor operates with transparent order books, allowing market participants to view bids and offers, whereas dark pools utilize hidden order books to execute large block trades anonymously, minimizing market impact. This concealment of liquidity in dark pools provides institutional investors with strategic advantages in managing order execution and price discovery.
Midpoint Matching
Midpoint matching on trading floors provides transparent price discovery by allowing buyers and sellers to transact at the midpoint of the bid-ask spread, enhancing market efficiency. Dark pools offer midpoint matching in a private setting, reducing market impact and enabling large block trades without revealing order details to the public market.
Trade-At Rule
The Trade-At Rule mandates that trading venues like dark pools must match the best available public price on lit trading floors before executing orders, ensuring price transparency and market fairness. This regulation reduces the advantage of dark pools by limiting order executions at inferior prices, promoting liquidity and better price discovery on public exchanges.
Minimum Quote Life
Minimum quote life on a trading floor is typically fixed and transparent to maintain market stability and facilitate real-time price discovery, whereas in dark pools, quote life is often variable or undefined, allowing for discreet execution of large orders without immediate public exposure. This distinction impacts liquidity and price transparency, with trading floors offering continuous quotes that support active market participation and dark pools prioritizing anonymity and reduced market impact.
Venue Fragmentation
Venue fragmentation in finance significantly impacts liquidity and price discovery by dividing trading activity between transparent trading floors and opaque dark pools. This segmentation challenges market efficiency as visible order books on traditional trading floors contrast with limited information in dark pools, complicating traders' ability to assess market depth and execution quality.
Trading Floor vs Dark Pool Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com