Trading floors enable real-time human interaction and decision-making, providing a tactile environment for executing complex trades and managing large volumes with immediate feedback. Electronic trading platforms offer automated, fast execution with advanced algorithms and lower transaction costs, enhancing market accessibility and efficiency across global markets. The choice between these approaches depends on the trader's need for speed, flexibility, and the complexity of trading strategies.
Table of Comparison
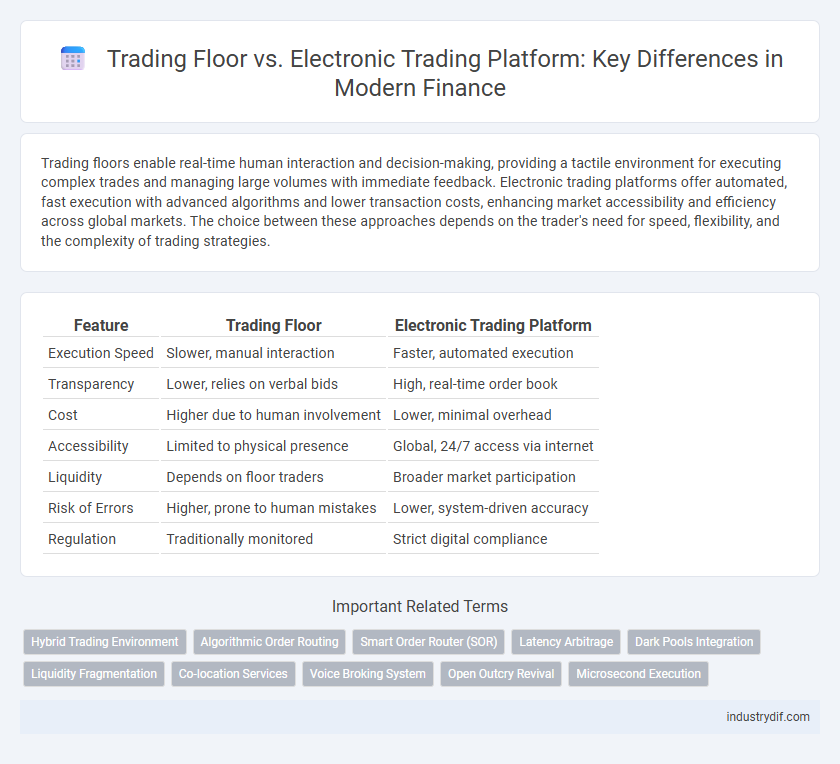
| Feature | Trading Floor | Electronic Trading Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Speed | Slower, manual interaction | Faster, automated execution |
| Transparency | Lower, relies on verbal bids | High, real-time order book |
| Cost | Higher due to human involvement | Lower, minimal overhead |
| Accessibility | Limited to physical presence | Global, 24/7 access via internet |
| Liquidity | Depends on floor traders | Broader market participation |
| Risk of Errors | Higher, prone to human mistakes | Lower, system-driven accuracy |
| Regulation | Traditionally monitored | Strict digital compliance |
Introduction to Trading Floors and Electronic Trading Platforms
Trading floors are physical locations where traders execute buy and sell orders for securities, commodities, or derivatives in real-time through direct interaction and verbal communication. Electronic trading platforms utilize advanced algorithms and digital networks to facilitate seamless, automated transactions with greater speed and efficiency, enabling access to global markets 24/7. Both systems play crucial roles in market liquidity, price discovery, and transparency but differ fundamentally in structure, technology, and operational dynamics.
Historical Evolution of Trading Methods in Finance
Trading floors dominated financial markets for centuries, relying on open outcry and physical presence to execute trades, which fostered real-time communication among brokers and traders. The advent of electronic trading platforms in the late 20th century revolutionized market efficiency by enabling automated, algorithm-driven transactions with reduced transaction costs and enhanced market liquidity. Historical shifts from manual pit trading to digital order books reflect broader technological advancements and regulatory changes shaping modern capital markets.
Key Features of Traditional Trading Floors
Traditional trading floors feature direct human interaction, enabling real-time decision-making and immediate negotiation between brokers and traders. The open outcry system facilitates voice and hand signal communication, promoting transparency and rapid price discovery. Physical presence on the trading floor also allows for enhanced relationship building and quick resolution of disputes.
Technological Advancements Driving Electronic Trading
Technological advancements such as high-speed internet, algorithmic trading, and artificial intelligence have revolutionized electronic trading platforms, enabling faster execution and greater market access compared to traditional trading floors. Electronic trading platforms utilize real-time data analytics and automated order matching systems that reduce human error and enhance liquidity. These innovations have shifted trading volumes away from physical trading floors towards digital environments, increasing efficiency and transparency in financial markets.
Speed and Efficiency: Floor Trading vs Electronic Platforms
Electronic trading platforms execute transactions in milliseconds through algorithmic precision, vastly outperforming traditional floor trading speed, which relies on human brokers and manual processes. The automation and direct market access of electronic systems boost efficiency by reducing latency, minimizing errors, and enabling simultaneous order execution across multiple markets. In contrast, floor trading's dependency on physical presence and verbal communication slows transaction times and limits scalability in fast-moving financial markets.
Cost Implications of Both Trading Systems
Trading floors involve significant overhead costs, including physical infrastructure, personnel salaries, and maintenance expenses, making them more costly to operate than electronic trading platforms. Electronic trading platforms reduce transaction costs through automation, faster execution, and lower commissions, enabling greater scalability and efficiency. Firms adopting electronic systems typically experience improved cost structures and tighter bid-ask spreads compared to traditional trading floor operations.
Market Accessibility and Global Reach Comparison
Trading floors provide direct access to markets through physical presence, facilitating real-time communication and immediate order execution, yet are limited by geographic location and trading hours. Electronic trading platforms offer 24/7 market accessibility with global reach, enabling traders worldwide to participate in multiple asset classes across diverse time zones. The scalability and advanced algorithmic tools of electronic platforms significantly enhance market liquidity and trading efficiency compared to traditional trading floors.
Security and Risk Management in Trading Environments
Trading floors offer direct oversight with physical presence, enabling immediate risk assessment and face-to-face communication to mitigate security threats and operational errors. Electronic trading platforms utilize advanced encryption, real-time monitoring, and algorithmic controls to enhance security and manage market risks dynamically across global networks. Both environments require robust compliance frameworks and comprehensive audit trails to ensure transparency and prevent fraud in high-frequency trading activities.
Impact on Market Liquidity and Transparency
Trading floors provide centralized venues where market makers and traders facilitate large volumes of transactions, enhancing market liquidity through direct interaction and immediate price discovery. Electronic trading platforms increase transparency by recording all orders and trades electronically, enabling broader market participation and real-time access to market data. The shift from trading floors to electronic platforms has generally improved price efficiency, reduced bid-ask spreads, and expanded liquidity pools, benefiting overall market integrity.
Future Trends: The Shift Toward Digital Trading
The future of finance is marked by a significant shift from traditional trading floors to electronic trading platforms, driven by advances in automation, big data analytics, and real-time market access. Electronic platforms provide increased transparency, lower transaction costs, and enhanced speed, reshaping liquidity and enabling traders to execute complex strategies globally. This digital transformation accelerates with the adoption of AI-powered algorithms and blockchain technologies, paving the way for more efficient and secure financial markets.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Trading Environment
A hybrid trading environment integrates the physical trading floor's direct interaction with the efficiency and speed of electronic trading platforms, enhancing liquidity and order execution. This synergy enables traders to utilize real-time data analytics while maintaining the benefits of human judgment and rapid decision-making in volatile markets.
Algorithmic Order Routing
Algorithmic order routing on electronic trading platforms utilizes advanced algorithms and real-time data to execute trades with optimal speed and efficiency, significantly reducing human error compared to traditional trading floors. These platforms provide greater market access, enhanced transparency, and improved liquidity by automatically directing orders to the best available venues across multiple exchanges.
Smart Order Router (SOR)
Smart Order Router (SOR) enhances trading efficiency by automatically directing orders to the best available prices across multiple trading venues, optimizing execution quality on both traditional trading floors and electronic trading platforms. Integrating SOR technology with electronic trading platforms reduces latency and improves market liquidity access compared to manual order routing on physical trading floors.
Latency Arbitrage
Latency arbitrage exploits time delays between trading floors and electronic trading platforms, allowing traders to capitalize on price discrepancies before slower systems update. High-frequency trading firms deploy advanced algorithms on electronic platforms to gain microsecond advantages, rendering traditional trading floors less competitive in latency-sensitive environments.
Dark Pools Integration
Dark pools integration enhances electronic trading platforms by providing institutional investors with access to large, non-displayed liquidity pools, reducing market impact and improving price execution. Trading floors, while traditional, lack the seamless dark pool connectivity and algorithmic efficiency that electronic platforms offer for optimized trade execution.
Liquidity Fragmentation
Liquidity fragmentation occurs when trading is split between traditional trading floors and electronic trading platforms, leading to dispersed order books and reduced price transparency. This dispersion can increase trading costs and complicate the execution of large orders, impacting market efficiency and overall liquidity.
Co-location Services
Co-location services enable traders to place their servers physically close to electronic trading platform data centers, significantly reducing latency and improving execution speed compared to traditional trading floors. This proximity advantage is crucial in high-frequency trading, where milliseconds impact profitability and market responsiveness.
Voice Broking System
Voice broking systems on a traditional trading floor enable direct human interaction for negotiating complex financial transactions, offering real-time market insights and personalized execution. In contrast, electronic trading platforms automate order processing and provide immediate access to liquidity pools, but may lack the nuanced judgment and relationship-driven advantages present in voice broking.
Open Outcry Revival
The open outcry system, once dominant on traditional trading floors, is experiencing a niche revival as traders seek enhanced price discovery and transparency in volatile markets. Electronic trading platforms continue to offer faster execution and greater accessibility, but the tactile interaction of open outcry fosters nuanced communication and strategic insight unavailable through digital interfaces.
Microsecond Execution
Trading floors rely on human brokers and traditional systems, causing latency that can extend beyond milliseconds, whereas electronic trading platforms leverage advanced algorithms and high-frequency trading technologies to achieve microsecond execution speeds. These platforms optimize order routing and market data processing, reducing slippage and maximizing trade efficiency crucial for arbitrage and market making strategies.
Trading Floor vs Electronic Trading Platform Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com