Agent-based distribution relies on knowledgeable insurance agents to provide personalized service, tailor policies, and build customer trust through direct interaction. Embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly into non-insurance platforms like e-commerce or travel, offering convenience and real-time protection without needing a separate purchase process. Choosing between these models depends on the target audience's preference for personalized advice versus instant, integrated solutions.
Table of Comparison
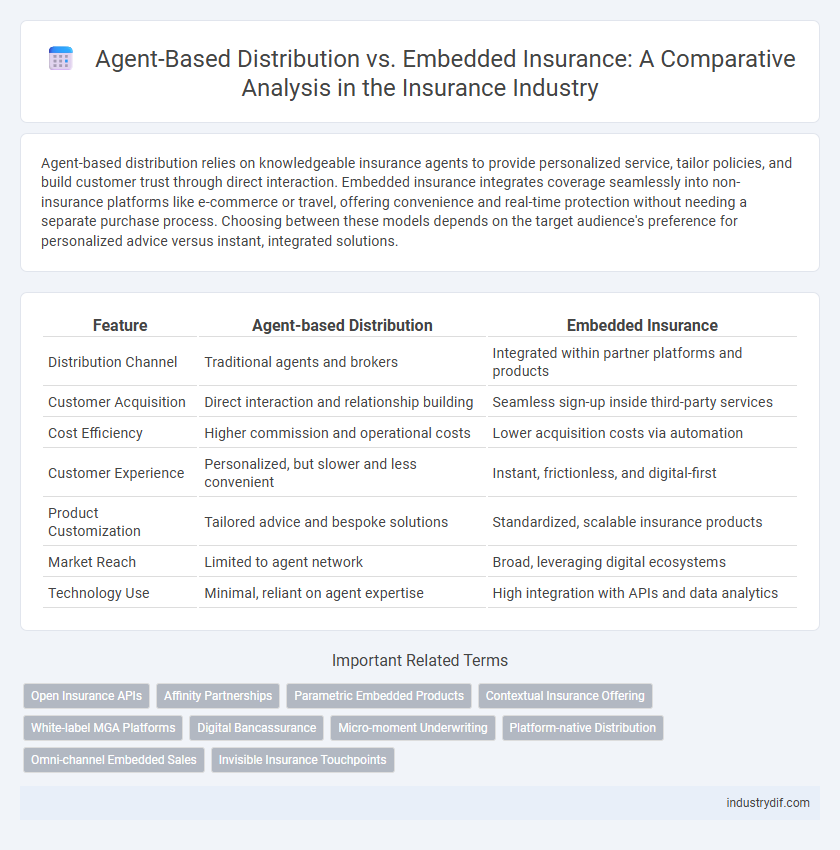
| Feature | Agent-based Distribution | Embedded Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Distribution Channel | Traditional agents and brokers | Integrated within partner platforms and products |
| Customer Acquisition | Direct interaction and relationship building | Seamless sign-up inside third-party services |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher commission and operational costs | Lower acquisition costs via automation |
| Customer Experience | Personalized, but slower and less convenient | Instant, frictionless, and digital-first |
| Product Customization | Tailored advice and bespoke solutions | Standardized, scalable insurance products |
| Market Reach | Limited to agent network | Broad, leveraging digital ecosystems |
| Technology Use | Minimal, reliant on agent expertise | High integration with APIs and data analytics |
Understanding Agent-Based Distribution in Insurance
Agent-based distribution in insurance relies on a network of licensed agents who actively engage customers to provide personalized policy advice and facilitate sales, offering tailored coverage options based on individual needs. This channel leverages agents' expertise and local market knowledge to build trust and foster long-term client relationships, often resulting in higher customer retention rates. Unlike embedded insurance, agent-based distribution emphasizes direct interaction and customized solutions, making it a critical strategy for complex insurance products requiring detailed explanation.
What Is Embedded Insurance?
Embedded insurance integrates coverage directly into the purchase of a product or service, eliminating the need for a separate buying process. This approach leverages digital platforms to offer seamless protection that enhances customer convenience and increases insurance accessibility. Unlike traditional agent-based distribution, embedded insurance reduces friction by embedding policies within transactions such as flight bookings or electronics sales.
Key Differences Between Agent-Based and Embedded Insurance
Agent-based distribution hinges on traditional insurance agents who actively sell policies through personal interactions, relying heavily on commissions and direct customer engagement. Embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly into the purchase of products or services, often via digital platforms, enhancing convenience and reducing sales friction. Key differences include the sales channel--human agents versus automated platforms--customer experience, and the degree of integration within non-insurance purchases.
Advantages of Agent-Based Distribution Channels
Agent-based distribution channels offer personalized customer interactions, enhancing trust and tailored insurance solutions through experienced agents. These channels enable comprehensive advice that addresses unique client needs, improving policy retention and customer satisfaction. Direct human engagement helps navigate complex insurance products, fostering long-term relationships and higher conversion rates compared to embedded insurance models.
Benefits of Embedded Insurance Models
Embedded insurance models streamline the customer journey by integrating coverage directly into product purchases, enhancing convenience and reducing friction. This seamless approach increases conversion rates and customer retention by offering tailored insurance solutions at the point of sale, driven by real-time data and user behavior. Insurers benefit from expanded distribution channels and lower acquisition costs compared to traditional agent-based models, improving overall profitability and market reach.
Customer Experience: Human Touch vs. Seamless Integration
Agent-based distribution offers personalized interactions and tailored advice, enhancing trust and customer satisfaction through direct human engagement. Embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly into digital platforms, providing quick, convenient access without disrupting the user journey. Customers seeking empathy and customized service prefer agent-based models, while tech-savvy users prioritize the efficiency and simplicity of embedded insurance solutions.
Technology’s Role in Insurance Distribution
Agent-based distribution leverages technology to enhance customer relationship management, streamline policy servicing, and optimize lead generation through CRM platforms and digital communication tools. Embedded insurance integrates insurance products directly within non-insurance platforms using APIs and digital wallets, enabling seamless purchase experiences and real-time underwriting. Advanced technologies such as AI, machine learning, and blockchain drive efficiency and personalization in both distribution models, reshaping the insurance landscape by improving risk assessment and customer engagement.
Regulatory Considerations for Both Models
Agent-based distribution requires compliance with licensing regulations specific to insurance intermediaries, including adherence to state and national insurance laws, consumer protection standards, and anti-money laundering requirements. Embedded insurance models face evolving regulatory scrutiny focusing on transparency, data privacy, and the integration of insurance products within non-insurance platforms, often demanding collaboration between insurers and third-party distributors to ensure compliance. Both models must navigate regulatory frameworks that impact product disclosure, claims handling, and consumer rights to maintain trust and legal integrity.
Growth Trends: Industry Shift Toward Embedded Insurance
The insurance industry is experiencing significant growth in embedded insurance, driven by seamless integration within digital platforms that enhances customer convenience and reduces friction. Agent-based distribution still holds value for personalized services but faces challenges in scalability and efficiency compared to embedded models. Market data indicates a rapid shift, with embedded insurance projected to capture a larger share of new policies due to its alignment with customer expectations and technological advancements.
Future Outlook: Coexistence or Disruption in Insurance Distribution
Agent-based distribution continues to leverage personalized customer relationships and expert advice, maintaining a strong presence in complex insurance segments. Embedded insurance, integrated seamlessly into digital platforms and ecosystems, is rapidly expanding due to ease of access and enhanced customer convenience. The future of insurance distribution hinges on a hybrid model where agent expertise complements embedded embedded insurance scalability, fostering coexistence rather than outright disruption.
Related Important Terms
Open Insurance APIs
Agent-based distribution relies on intermediaries who use Open Insurance APIs to access customer data and policy details, enhancing personalized service and real-time underwriting. Embedded insurance integrates these APIs directly into third-party platforms, enabling seamless policy issuance and claims processing within non-insurance environments, driving convenience and faster customer acquisition.
Affinity Partnerships
Agent-based distribution relies on trained insurance agents to actively sell policies, leveraging their expertise and personal connections to build trust and close sales. Embedded insurance integrates coverage directly into third-party products or services through affinity partnerships, streamlining customer access and enhancing value by bundling insurance with relevant purchases.
Parametric Embedded Products
Agent-based distribution relies on trained insurance agents to sell customized policies, ensuring personalized customer interaction and complex risk assessment. Parametric embedded insurance integrates automated, trigger-based coverage directly into platforms or devices, offering instantaneous payouts based on predefined parameters without traditional claims processing.
Contextual Insurance Offering
Agent-based distribution relies on personalized interactions between insurance agents and customers to tailor policies, enhancing trust and customization in coverage. Embedded insurance integrates protection seamlessly within product or service purchases, enabling real-time contextual insurance offerings that improve customer convenience and relevance.
White-label MGA Platforms
White-label MGA platforms enable insurers to leverage agent-based distribution by providing customizable solutions that streamline policy management and enhance agent performance. Embedded insurance integrates seamlessly within third-party platforms, but white-label MGA models prioritize agent control and brand identity, optimizing customer engagement and operational efficiency.
Digital Bancassurance
Agent-based distribution leverages licensed insurance agents to promote and sell policies, enabling personalized customer interactions and tailored coverage options that enhance trust and retention. Embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly within digital banking platforms, streamlining the purchase process and boosting convenience, which drives higher uptake rates and supports scalable growth in digital bancassurance ecosystems.
Micro-moment Underwriting
Agent-based distribution in insurance often involves personalized risk assessment during micro-moment underwriting, leveraging direct client interactions to tailor policies accurately. Embedded insurance integrates underwriting seamlessly into customer journeys through digital platforms, enabling real-time risk evaluation and instant policy issuance at critical decision points.
Platform-native Distribution
Platform-native distribution leverages embedded insurance solutions within digital ecosystems, enabling seamless policy integration and real-time risk assessment. This approach contrasts with traditional agent-based distribution by offering automated underwriting, personalized pricing, and enhanced customer engagement through API-driven platform connectivity.
Omni-channel Embedded Sales
Omni-channel embedded insurance sales integrate seamlessly across digital platforms, enabling real-time policy offers during customer journeys, which significantly enhances conversion rates compared to traditional agent-based distribution that relies on direct human interaction. The embedded approach leverages APIs to deliver personalized insurance products within e-commerce, travel, and automotive ecosystems, creating a streamlined and data-driven sales process that reduces friction and operational costs.
Invisible Insurance Touchpoints
Agent-based distribution relies on human agents to facilitate insurance purchases, often creating visible touchpoints that require direct customer interaction and negotiation. Embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly into everyday products or services, enabling invisible insurance touchpoints that enhance customer experience by providing proactive protection without explicit user effort.
Agent-based Distribution vs Embedded Insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com