Health insurance typically offers comprehensive coverage for medical expenses, including hospitalization, surgeries, and prescription drugs, designed for individuals or families with higher protection needs. Micro-insurance provides affordable, limited coverage targeting low-income populations, focusing on basic health risks with lower premiums and simplified underwriting. Both serve to reduce financial barriers to healthcare, but micro-insurance aims to increase accessibility where traditional health insurance may be unaffordable.
Table of Comparison
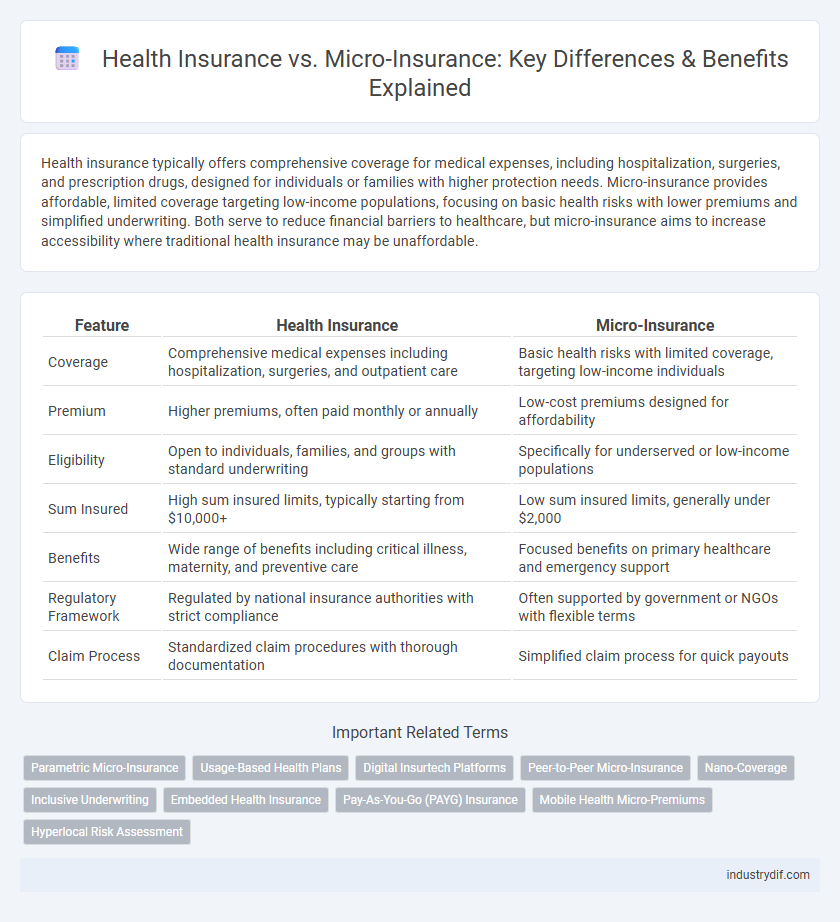
| Feature | Health Insurance | Micro-Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Comprehensive medical expenses including hospitalization, surgeries, and outpatient care | Basic health risks with limited coverage, targeting low-income individuals |
| Premium | Higher premiums, often paid monthly or annually | Low-cost premiums designed for affordability |
| Eligibility | Open to individuals, families, and groups with standard underwriting | Specifically for underserved or low-income populations |
| Sum Insured | High sum insured limits, typically starting from $10,000+ | Low sum insured limits, generally under $2,000 |
| Benefits | Wide range of benefits including critical illness, maternity, and preventive care | Focused benefits on primary healthcare and emergency support |
| Regulatory Framework | Regulated by national insurance authorities with strict compliance | Often supported by government or NGOs with flexible terms |
| Claim Process | Standardized claim procedures with thorough documentation | Simplified claim process for quick payouts |
Understanding Health Insurance: Key Features
Health insurance provides comprehensive coverage for medical expenses, including hospitalization, outpatient services, and preventive care, designed for broader protection with higher premium costs. Micro-insurance offers limited coverage tailored to low-income individuals, emphasizing affordable premiums and simplified claim processes. Key features of health insurance include extensive network access, policy flexibility, and coverage for chronic conditions, distinguishing it from the more basic and targeted scope of micro-insurance.
What is Micro-Insurance? An Overview
Micro-insurance is a specialized type of health insurance designed to provide affordable coverage for low-income individuals and families, typically in developing regions. It offers protection against specific health risks such as hospitalization, critical illness, and outpatient care, with lower premiums and simplified claim processes. This insurance model enhances financial inclusion by making essential health services accessible to populations often excluded from traditional insurance plans.
Target Demographics: Who Benefits Most?
Health insurance primarily targets middle to high-income individuals and families seeking comprehensive medical coverage with access to a wide network of healthcare providers. Micro-insurance focuses on low-income populations and informal sector workers who require affordable, basic coverage for essential health services to mitigate financial risks from unexpected medical expenses. Both insurance types address distinct demographic needs, with health insurance offering broader protection and micro-insurance enhancing healthcare accessibility for underserved communities.
Coverage Scope: Comprehensive vs. Limited Protection
Health insurance typically offers comprehensive coverage, including inpatient and outpatient care, prescription medications, preventive services, and specialist consultations, making it suitable for broader healthcare needs. Micro-insurance usually provides limited protection, focusing on specific health risks or conditions with lower premiums and reduced benefits, targeting low-income populations. The coverage scope difference significantly impacts out-of-pocket expenses and accessibility to extensive medical treatments.
Premiums and Affordability Comparison
Health insurance premiums are generally higher due to comprehensive coverage, encompassing hospitalization, outpatient care, and specialist visits, making them less affordable for low-income individuals. Micro-insurance offers targeted health coverage with significantly lower premiums, designed to be affordable for vulnerable populations while covering essential risks such as basic medical treatment and critical illness. The affordability of micro-insurance facilitates broader access to healthcare by minimizing financial barriers faced by underserved communities.
Claims Process: Simplicity and Accessibility
Health insurance typically involves a more complex claims process with detailed documentation and longer approval times due to extensive coverage and higher claim amounts. Micro-insurance offers a simpler, more accessible claims procedure designed for low-income individuals, featuring minimal paperwork and faster settlements to ensure timely financial support. This streamlined approach enhances claim accessibility, making micro-insurance an effective solution for underserved populations with limited resources.
Regulatory Framework in Health and Micro-Insurance
Health insurance is governed by comprehensive regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S., ensuring consumer protections, privacy, and standardized coverage requirements. Micro-insurance operates under tailored regulatory frameworks aimed at promoting accessibility for low-income populations, often featuring simplified product requirements and flexible premium structures to encourage market penetration. Regulatory bodies work to balance consumer protection with affordability and scalability to foster sustainable growth in both health insurance and micro-insurance sectors.
Distribution Channels: Traditional vs. Community-Based Models
Health insurance distribution primarily relies on traditional channels such as insurance agents, brokers, and digital platforms, providing wide accessibility and streamlined underwriting processes. Micro-insurance leverages community-based models, including local cooperatives, self-help groups, and nonprofit organizations, facilitating tailored product offerings and enhanced trust in underserved populations. This community-focused approach improves penetration in rural and low-income areas where conventional channels have limited reach.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Insurance Types
Health insurance often faces challenges such as high premiums, limited coverage for pre-existing conditions, and complex claim processes that can deter low-income individuals. Micro-insurance, designed for low-income populations, struggles with issues like insufficient coverage limits, lack of awareness, and difficulties in scaling due to administrative costs. Both insurance types encounter limitations in accessibility, affordability, and ensuring comprehensive protection against diverse health risks.
Choosing the Right Insurance: Factors to Consider
Choosing between health insurance and micro-insurance depends on coverage needs, premium affordability, and risk exposure. Health insurance offers comprehensive protection for major medical expenses, ideal for individuals seeking extensive coverage with higher premiums. Micro-insurance provides targeted, low-cost plans suited for low-income groups or those wanting minimal coverage for specific health risks.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Micro-Insurance
Health insurance provides comprehensive coverage for medical expenses and hospitalizations, whereas parametric micro-insurance offers fast, low-cost payouts triggered by predefined events, such as natural disasters or health outbreaks, without the need for claims adjustment. Parametric micro-insurance is designed to increase financial inclusion by delivering immediate liquidity to low-income populations vulnerable to health risks.
Usage-Based Health Plans
Usage-based health insurance plans utilize real-time data from wearable devices and health apps to tailor premiums and coverage, promoting healthier lifestyles through personalized risk assessment. Micro-insurance offers affordable, limited coverage for specific health risks, but lacks the customization and dynamic pricing advantages of usage-based health plans in managing individual health costs effectively.
Digital Insurtech Platforms
Digital insurtech platforms are revolutionizing health insurance by offering personalized coverage and faster claims processing, while micro-insurance targets low-income populations with affordable, small-scale policies tailored through mobile technology. These platforms leverage AI and big data analytics to optimize risk assessment and policy management, bridging accessibility gaps in both traditional health insurance and micro-insurance markets.
Peer-to-Peer Micro-Insurance
Health insurance typically offers comprehensive coverage with higher premiums, while peer-to-peer micro-insurance provides affordable, community-based risk-sharing models that focus on low-income populations. This innovative approach leverages social networks and technology to reduce administrative costs and enhance accessibility, making healthcare protection more inclusive.
Nano-Coverage
Health insurance typically offers comprehensive coverage with higher premiums and broader risk pools, whereas micro-insurance, especially nano-coverage, targets low-income populations with ultra-affordable premiums and limited, essential health benefits tailored for immediate medical needs. Nano-coverage enhances financial inclusion by enabling access to preventive care and basic treatment, reducing the economic burden of health emergencies in underserved communities.
Inclusive Underwriting
Health insurance typically involves comprehensive risk assessment, leading to selective underwriting practices that may exclude high-risk individuals, whereas micro-insurance employs inclusive underwriting focused on affordability and accessibility for low-income populations. Inclusive underwriting in micro-insurance utilizes simplified risk evaluation methods and community-based data, promoting broader coverage and financial protection in underserved markets.
Embedded Health Insurance
Embedded health insurance integrates micro-insurance benefits directly into products or services, offering seamless access to affordable healthcare coverage for underserved populations. This approach enhances traditional health insurance models by reducing barriers to enrollment and improving risk pooling through technology-driven platforms.
Pay-As-You-Go (PAYG) Insurance
Health insurance typically involves comprehensive coverage with fixed premiums and higher costs, whereas micro-insurance offers affordable, limited protection tailored for low-income individuals through Pay-As-You-Go (PAYG) models, enabling flexible payments aligned with actual usage or income flow. PAYG insurance leverages mobile technology to facilitate real-time premium payments and immediate claims processing, enhancing accessibility and financial inclusion for underserved populations.
Mobile Health Micro-Premiums
Mobile health micro-premiums offer affordable, flexible health insurance options tailored for low-income populations, enabling easy access to essential medical coverage through mobile platforms. Unlike traditional health insurance with higher premiums and comprehensive plans, micro-insurance focuses on specific health risks and short-term policies, maximizing coverage efficiency and promoting financial inclusion.
Hyperlocal Risk Assessment
Health insurance typically covers broader geographic regions and standardized risk profiles, while micro-insurance leverages hyperlocal risk assessment to tailor premiums and coverage based on localized factors such as community health trends, environmental conditions, and socioeconomic status. This precise risk evaluation enables micro-insurance to offer affordable, targeted protection for underserved populations facing unique, localized health risks.
Health Insurance vs Micro-Insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com