Coverage in traditional insurance typically involves comprehensive protection with higher premiums and extensive policy terms, designed for individuals or businesses with significant risk exposures. Microinsurance offers affordable, targeted protection tailored to low-income populations, focusing on specific risks with simplified claim processes and lower coverage limits. Both types serve distinct market needs, with microinsurance expanding access to financial security for underserved communities.
Table of Comparison
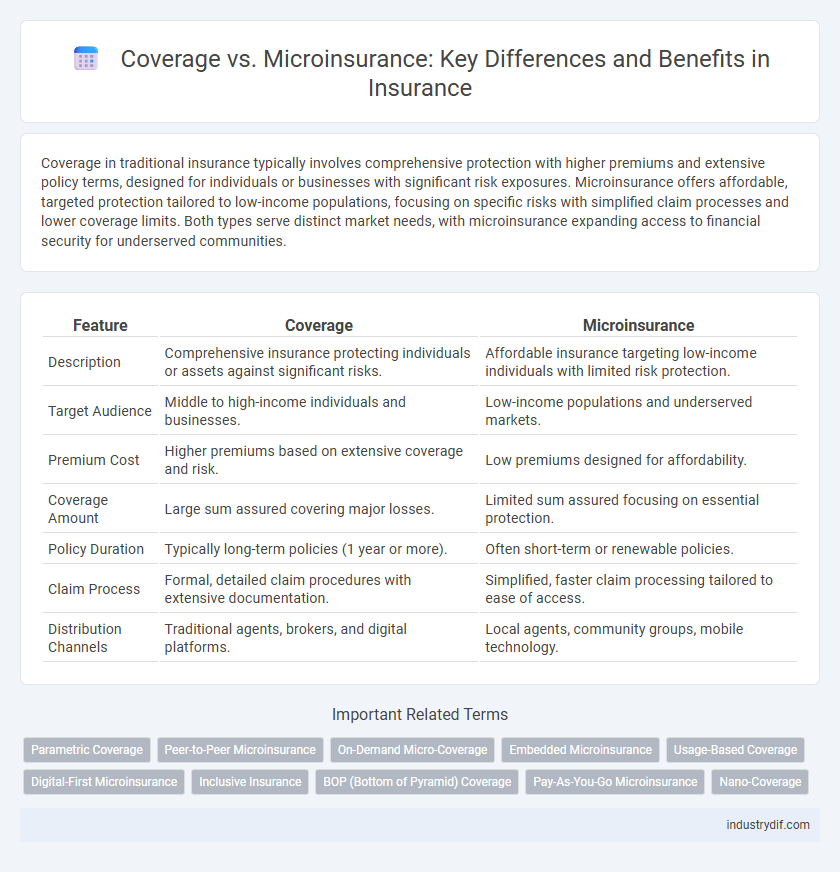
| Feature | Coverage | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Comprehensive insurance protecting individuals or assets against significant risks. | Affordable insurance targeting low-income individuals with limited risk protection. |
| Target Audience | Middle to high-income individuals and businesses. | Low-income populations and underserved markets. |
| Premium Cost | Higher premiums based on extensive coverage and risk. | Low premiums designed for affordability. |
| Coverage Amount | Large sum assured covering major losses. | Limited sum assured focusing on essential protection. |
| Policy Duration | Typically long-term policies (1 year or more). | Often short-term or renewable policies. |
| Claim Process | Formal, detailed claim procedures with extensive documentation. | Simplified, faster claim processing tailored to ease of access. |
| Distribution Channels | Traditional agents, brokers, and digital platforms. | Local agents, community groups, mobile technology. |
Understanding Coverage and Microinsurance
Coverage in insurance refers to the extent of protection provided by a policy against specified risks such as property damage, theft, or liability, typically involving higher premiums and comprehensive benefits. Microinsurance targets low-income individuals or underserved markets, offering affordable, limited coverage tailored to specific needs with simplified terms and lower cost. Understanding coverage differences helps consumers choose policies that balance protection scope with affordability, ensuring suitable financial risk management.
Key Differences Between Coverage and Microinsurance
Coverage generally refers to traditional insurance policies providing broader protection with higher premiums and substantial coverage limits, typically targeting individuals or businesses with more significant risk exposures. Microinsurance, designed for low-income populations, offers limited coverage with affordable premiums and simplified terms to increase accessibility and financial inclusion. Key differences include the scope of protection, cost structure, target market, and underwriting requirements, where coverage emphasizes comprehensive risk management while microinsurance focuses on basic, essential protection.
What is Traditional Insurance Coverage?
Traditional insurance coverage offers comprehensive protection against significant financial losses from events such as accidents, theft, natural disasters, or health emergencies, typically requiring higher premiums and longer policy durations. It provides broader scope and higher coverage limits tailored for individuals or businesses with greater asset values or risk exposure. This coverage often includes detailed underwriting processes and policy terms designed to mitigate substantial risks over extended periods.
What Defines Microinsurance?
Microinsurance is defined by its tailored coverage for low-income individuals, offering affordable premiums and simplified underwriting to address specific risks faced by vulnerable populations. Unlike traditional insurance, microinsurance emphasizes accessibility, providing protection against health, life, property, and agricultural risks on a small scale. This form of insurance aims to enhance financial resilience and reduce poverty by delivering essential coverage where conventional insurance is often unavailable or unaffordable.
Eligibility Criteria: Coverage vs Microinsurance
Coverage eligibility criteria often require formal documentation and proof of risk factors, targeting individuals or businesses with higher asset values or established credit history. Microinsurance eligibility focuses on low-income populations, minimizing documentation requirements to increase accessibility and affordability for vulnerable groups. Both types tailor their criteria to balance risk assessment with the need for broad market inclusion, ensuring coverage aligns with policy goals and customer capabilities.
Premiums and Payout Structures Compared
Coverage plans typically involve higher premiums with larger, structured payouts tailored to extensive risks, offering comprehensive financial protection. Microinsurance features significantly lower premiums designed for low-income individuals, with smaller, more immediate payouts that address specific, everyday risks. This contrast in premium costs and payout scales highlights microinsurance's role in expanding access to essential coverage for underserved populations.
Benefits and Limitations of Microinsurance
Microinsurance offers affordable, accessible coverage tailored to low-income populations, providing essential protection against risks like illness, accidents, and crop failure with lower premiums and simplified claims processes. Its benefits include inclusivity, quicker enrollment, and adaptability to specific community needs, but limitations involve lower coverage limits, reduced benefits compared to traditional insurance, and potential challenges in claim verification. Microinsurance helps bridge the protection gap for underserved groups, though it may not fully replace comprehensive insurance policies for larger or more complex risks.
Target Markets: Coverage vs Microinsurance
Coverage primarily targets individuals and businesses with moderate to high income levels seeking comprehensive protection against diverse risks, including health, property, and liability. Microinsurance focuses on low-income populations and underserved communities, offering affordable, simplified policies tailored to specific risks such as crop failure, health emergencies, or natural disasters. Both approaches address risk management, but microinsurance aims to enhance financial inclusion by providing accessible coverage where traditional insurance is unattainable.
Regulatory Frameworks for Coverage and Microinsurance
Regulatory frameworks for coverage and microinsurance differ significantly, with microinsurance often subject to simplified regulations to increase accessibility for low-income populations, such as tiered capital requirements and streamlined product approval processes. Traditional insurance coverage is regulated under comprehensive frameworks emphasizing solvency, consumer protection, and market stability, including rigorous licensing, disclosure norms, and risk-based capital standards. These regulatory distinctions aim to balance financial inclusion with market integrity, promoting tailored microinsurance products while maintaining systemic insurance sector stability.
Future Trends in Coverage and Microinsurance
Future trends in insurance coverage emphasize the integration of advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence to tailor policies to individual risk profiles, enhancing personalization and affordability. Microinsurance is expected to expand rapidly in emerging markets due to mobile technology penetration, offering cost-effective protection to underserved populations. The convergence of digital platforms and regulatory support will drive innovation, increasing accessibility and sustainability in both traditional coverage and microinsurance sectors.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Coverage
Parametric coverage in insurance offers predefined payouts based on triggering events measured by objective parameters, unlike traditional coverage that assesses actual loss, making it especially suitable for microinsurance clients facing rapid disaster relief needs. This model enhances efficiency and reduces claim processing time, providing transparent and swift financial support to underserved populations vulnerable to natural catastrophes.
Peer-to-Peer Microinsurance
Peer-to-peer microinsurance leverages community-based risk sharing to provide affordable, tailored coverage options for underserved populations, contrasting traditional insurance models that typically involve higher premiums and broader coverage scope. This innovative approach enhances trust and transparency by enabling members to pool resources directly, minimizing administrative costs and aligning incentives for timely claims management.
On-Demand Micro-Coverage
On-demand microinsurance offers highly flexible, short-term protection tailored to specific risks, contrasting traditional insurance coverage's broad and long-term policies. This innovative model leverages digital platforms to provide instant, affordable micro-coverage options that meet the dynamic needs of underserved or low-income populations.
Embedded Microinsurance
Embedded microinsurance integrates coverage directly into everyday financial products, offering affordable, tailored protection to underserved populations with limited access to traditional insurance. This model enhances risk management by utilizing digital platforms and partnerships, ensuring seamless, automated claims processing and broadening insurance penetration in emerging markets.
Usage-Based Coverage
Usage-based insurance coverage utilizes telematics and real-time data to customize premiums according to individual driving behavior, offering more precise risk assessment compared to traditional microinsurance models that provide basic, low-cost protection for low-income groups. By leveraging usage data, insurers can enhance policy affordability and flexibility, improving customer engagement and claims accuracy within diverse demographic segments.
Digital-First Microinsurance
Digital-first microinsurance leverages mobile and online platforms to offer affordable, customizable coverage tailored for low-income populations, bridging protection gaps often left by traditional insurance. This innovative approach ensures instant policy issuance, real-time claims processing, and seamless integration with digital payment systems, maximizing accessibility and convenience.
Inclusive Insurance
Inclusive insurance expands traditional coverage by offering microinsurance products designed to provide affordable, accessible protection for low-income and underserved populations. Microinsurance schemes focus on tailored policies with lower premiums and simplified claims processes, promoting financial inclusion and reducing vulnerability among marginalized communities.
BOP (Bottom of Pyramid) Coverage
Microinsurance provides affordable, tailored protection specifically designed for the Bottom of the Pyramid (BOP) population, addressing their unique risks and limited financial resources. Unlike traditional insurance coverage, microinsurance offers simplified policies with lower premiums and coverage limits to increase accessibility and financial inclusion for underserved communities.
Pay-As-You-Go Microinsurance
Pay-As-You-Go microinsurance offers flexible, affordable coverage tailored for low-income individuals, enabling incremental premium payments aligned with their cash flow. Unlike traditional insurance, this model enhances accessibility by removing high upfront costs and providing customizable protection for day-to-day risks.
Nano-Coverage
Nano-coverage offers ultra-small, affordable insurance policies designed to cover highly specific risks with minimal premiums, filling the gap between traditional insurance coverage and microinsurance. This innovative approach enhances financial inclusion by providing tailored protection to underserved populations through digital platforms and flexible payment options.
Coverage vs Microinsurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com